At an orphanage in the Democratic Republic of the Congo’s (DR Congo) capital, Kinshasa, more than 60 children stared at their plate of palm weevil larvae fried up in spices, sharing nervous smiles, before curiously digging into the thick white worms.
The orphans are being fed the protein-rich larvae, known locally as mpose, as part of an initiative from Kinshasa-based non-profit organization Farms for Orphans, which is seeking to address malnutrition in the west African nation.
About one-quarter of the nation’s 99 million population faces a food crisis and half of all orphans are suffering from malnutrition, according to the World Food Programme.
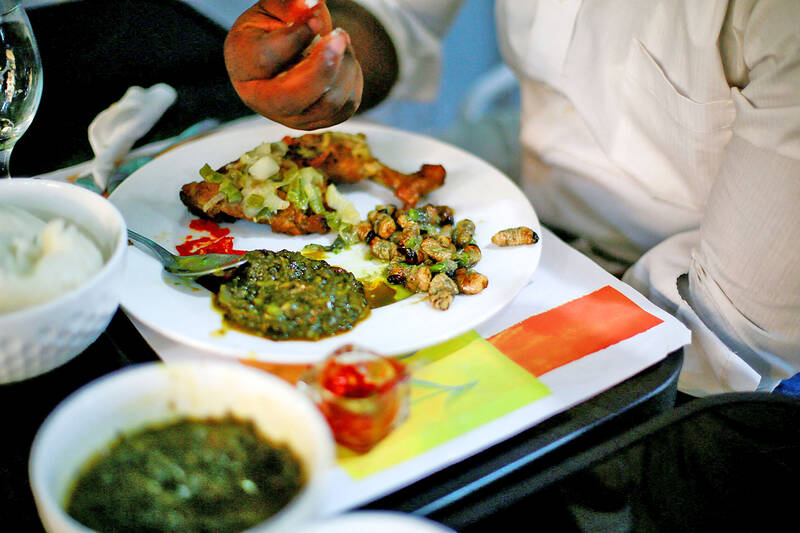

Photo: Reuters
Edible insects, including larvae, are increasingly being studied for their potential as a sustainable alternative form of protein to meat, either for human consumption as in the DR Congo, or for animal feed in Benin.
The Food and Agriculture Organization has said that insects can be a rich source of fat, protein, vitamins, fiber and minerals.
“It is scientifically proven that meat does not have a higher protein concentration than insects, and it’s not easy to get meat, so we wanted to make it simpler,” said Francoise Lukadi, an agricultural engineer who runs Farm for Orphans.
She said the nutrient deficiency was particularly acute in children under five.
The larvae are typically cooked with onions, peppers and tomatoes, and have a cheese-like taste.
“It is important for children to eat mpose because of the proteins, because some children are abandoned in a state of malnutrition,” said Nelly Mimpi, nutritionist and food health supervisor at the orphanage.
Farms for Orphans received funding from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation for its initial research and launch, but Lukadi hopes to produce enough larvae to sell commercially to subsidize the donations to orphanages.
The organization supplies four restaurants in Kinshasa, where palm worms are becoming increasingly popular.
Her team produces up to 300kg of palm larvae per month — and provides meals to several hundred children per quarter — but she wants to boost production to satisfy growing commercial demand.
Although her team is studying how to grow the larvae and harvest them sustainably in laboratories at the University of Kinshasa and the National Institute of Biomedical Research, some critics say it would be difficult to ramp up production to a commercial scale due to a lack of adequate resources.
According to several peer-reviewed studies, commercial-scale insect farming could also pose food safety risks, as some insect farming requires feed crops that could otherwise go directly toward human consumption.
Farmers in Benin are also experimenting with the potential for insect protein.
Jules Mahinou, a 25-year-old at the head of a group of young poultry farmers called the Elevart Group, breeds black soldier flies in Cotonou, Benin, to produce fly larvae as a source of protein-rich animal feed.
“Right now, we’re operating on a shoestring. Everything is done manually,” Mahinou said, adding that he hoped they would be able to mechanize and produce substitutes for fish and soybean meal.

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a
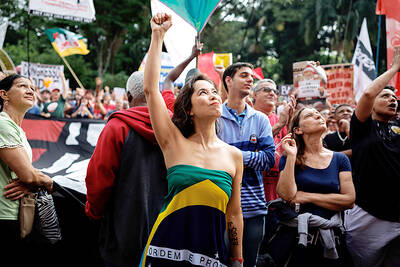
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

‘EAST SHIELD’: State-run Belma said it would produce up to 6 million mines to lay along Poland’s 800km eastern border, and sell excess to nations bordering Russia and Belarus Poland has decided to start producing anti-personnel mines for the first time since the Cold War, and plans to deploy them along its eastern border and might export them to Ukraine, the deputy defense minister said. Joining a broader regional shift that has seen almost all European countries bordering Russia, with the exception of Norway, announce plans to quit the global treaty banning such weapons, Poland wants to use anti-personnel mines to beef up its borders with Belarus and Russia. “We are interested in large quantities as soon as possible,” Deputy Minister of National Defense Pawel Zalewski said. The mines would be part

Cozy knits, sparkly bobbles and Santa hats were all the canine rage on Sunday, as hundreds of sausage dogs and their owners converged on central London for an annual parade and get-together. The dachshunds’ gathering in London’s Hyde Park came after a previous “Sausage Walk” planned for Halloween had to be postponed, because it had become so popular organizers needed to apply for an events licence. “It was going to be too much fun so they canceled it,” laughed Nicky Bailey, the owner of three sausage dogs: Una and her two 19-week-old puppies Ember and Finnegan, wearing matching red coats and silver