Russia on Thursday banned the “international LGBT movement,” claiming it was an extremist group in a move that cements a long crackdown on the community as the Kremlin pushes ultra-conservative social values.
The conservative turn promoted by Russian President Vladimir Putin — often portrayed as an existential fight against Western liberal values — has accelerated since the offensive in Ukraine.
The Russian Supreme Court court handed down the ruling in Moscow on Thursday.
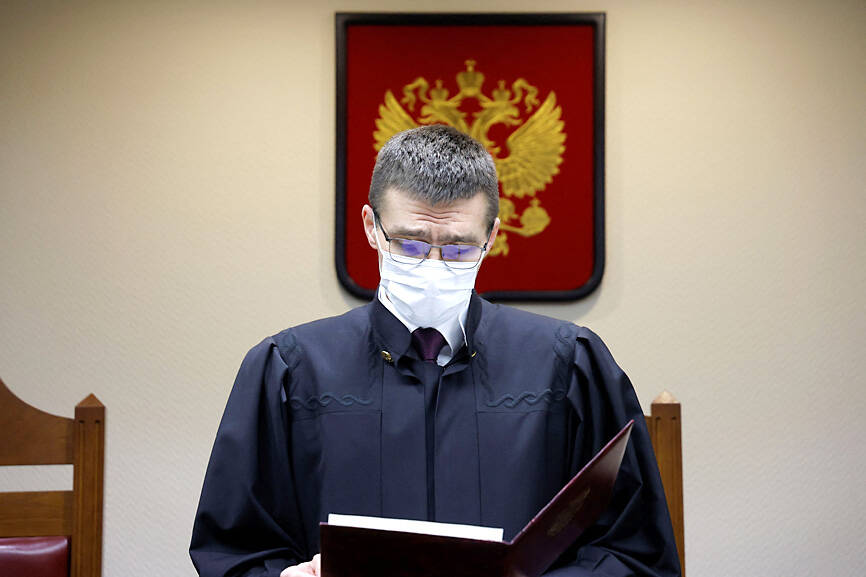

Photo: Reuters
It did not say whether certain individuals or organizations would be affected by the ruling.
Judge Oleg Nefedov ruled that “the international LGBT public movement and its subdivisions” were extremist, and issued a “ban on its activities on the territory of Russia.”
The hearing took place behind closed doors and without any defense present.
Fewer than 10 people had gathered outside the court.
“I hoped more people would come [to show support], but very few people came,” said Ada Blakewell, a journalist. “It shows how scared everyone is ... to talk about anything related to LGBTQ people.”
The judge said the order should be executed immediately — though some rights nongovernmental organizations said there would be bureaucratic delays.
“It’s causing a huge panic, because it’s completely unclear who will be prosecuted under this ban,” said Noel Shaida, the head of communication at LGBTQ rights NGO Sphere Foundation.
If applied to individuals, the “extremist” label means gay, lesbian, transgender or queer people living in Russia could face years in jail.
It also opens the way to the criminal prosecution of any group protecting the rights of these communities in Russia. Human Rights Watch said the decision was “jeopardizing all forms of LGBTQ rights activism” while the UN deplored the move.
Maxim Olenichev, a lawyer with Pervy Otdel, which helps victims of repression in Russia, said criminal cases would “create a climate of fear.”
The ban means “complete censorship and probably difficulties in providing assistance, because we will have to go underground,” Shaida, 27, said.
Most of Shaida’s team has left Russia to coordinate support from relative safety abroad, as have other rights organizations since the beginning of the offensive in Ukraine.
The conservative turn in Russia accelerated since the Kremlin launched its Ukraine offensive and as a presidential election next year — expected to prolong Putin’s rule until at least 2030 — looms.
The ban is “meant to increase the scapegoating of LGBT people to appeal to the Kremlin’s conservative supporters before the March 2024 presidential vote,” said Tanya Lokshina, associated director at Human Rights Watch Europe and Central Asia division.
In December last year, Putin widened the 2013 law to criminalize any positive public mention of LGBTQ people or relationships.
In July, Russian lawmakers banned medical intervention and administrative procedures that allowed people to change gender.
Shaida said authorities want to “divert attention from the war, the failures in the war.”
As the Kremlin often paints the military operation in Ukraine as a fight against liberal “decadent” values, Shaida believed Moscow passed the ban to further distance itself from the West.
“One day it will be over but for now we need to try to continue to live and save ourselves,” the Feminist Anti-War Resistance, which denounces Russia’s military offensive in Ukraine, said on social media.
Conservative officials rushed to praise the change. Lawmaker Pyotr Tolstoy said “this is a historic event, because our country has encroached on the most ‘sacred’ thing that exists in the liberal world.”
In his latest homophobic diatribe on social media, Tolstoy called “LGBT” a “well-organised project to undermine traditional societies from within.”
The Russian Orthodox Church — headed by Putin ally Patriarch Kirill — welcomed the move. “It’s a form of moral self-defense of society,” said Vakhtang Kipshidze, an official for the Moscow Patriarchate.
In the Muslim-majority Russian republic of Chechnya — ruled by Ramzan Kadyrov, who claims the region is exclusively heterosexual — officials also praised the move.
“Russia has shown once again that neither the collective West nor the United States will deprive us of the most important thing of all: a religious and national identity,” Chechen Minister of National Policy Akhmed Dudaev said.

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a
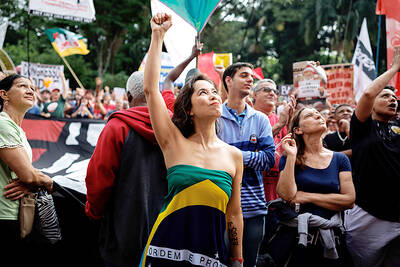
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

‘EAST SHIELD’: State-run Belma said it would produce up to 6 million mines to lay along Poland’s 800km eastern border, and sell excess to nations bordering Russia and Belarus Poland has decided to start producing anti-personnel mines for the first time since the Cold War, and plans to deploy them along its eastern border and might export them to Ukraine, the deputy defense minister said. Joining a broader regional shift that has seen almost all European countries bordering Russia, with the exception of Norway, announce plans to quit the global treaty banning such weapons, Poland wants to use anti-personnel mines to beef up its borders with Belarus and Russia. “We are interested in large quantities as soon as possible,” Deputy Minister of National Defense Pawel Zalewski said. The mines would be part

Cozy knits, sparkly bobbles and Santa hats were all the canine rage on Sunday, as hundreds of sausage dogs and their owners converged on central London for an annual parade and get-together. The dachshunds’ gathering in London’s Hyde Park came after a previous “Sausage Walk” planned for Halloween had to be postponed, because it had become so popular organizers needed to apply for an events licence. “It was going to be too much fun so they canceled it,” laughed Nicky Bailey, the owner of three sausage dogs: Una and her two 19-week-old puppies Ember and Finnegan, wearing matching red coats and silver