The solar wind is a ubiquitous feature of our solar system. This relentless high-speed flow of charged particles from the sun fills interplanetary space. On Earth, it triggers geomagnetic storms that can disrupt satellites and it causes the dazzling auroras — the northern and southern lights — at high latitudes.
However, precisely how the sun generates the solar wind has remained unclear. New observations by the Solar Orbiter spacecraft might provide an answer.
Researchers on Thursday said that the spacecraft has detected numerous relatively small jets of charged particles expelled intermittently from the corona — the sun’s outer atmosphere — at supersonic speeds for 20 to 100 seconds.
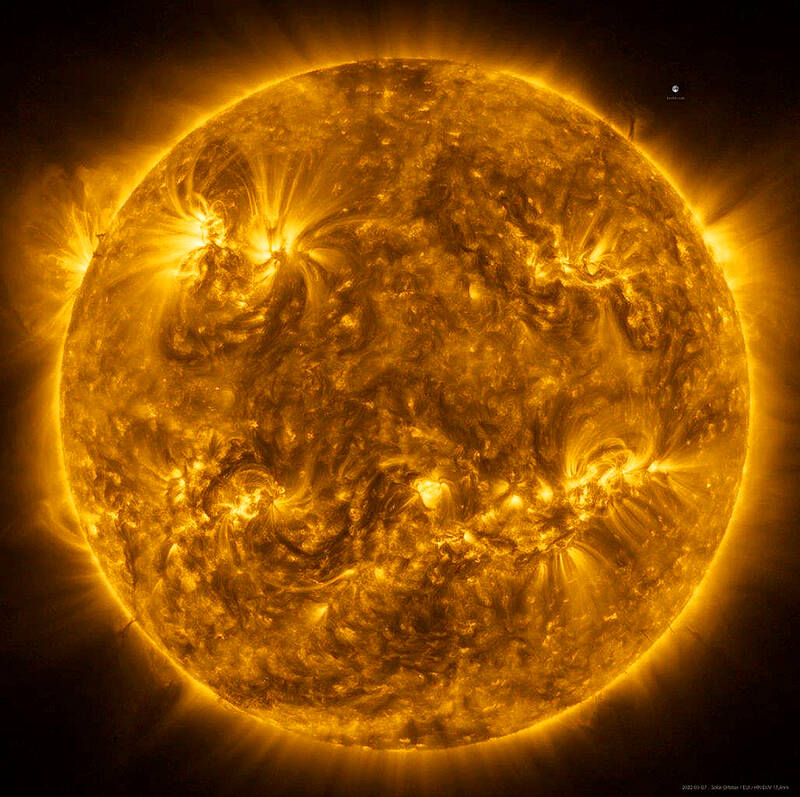
Photo: Reuters / ESA & NASA / Solar Orbiter / EUI team
The jets emanate from structures on the corona called coronal holes where the sun’s magnetic field stretches into space rather than back into the star. They are called “picoflare jets” due to their relatively small size. They arise from areas a few hundred kilometers wide — tiny when compared to the immense scale of the sun, which has a diameter of 1.4 million kilometers.
“We suggest that these jets could actually be a major source of mass and energy to sustain the solar wind,” said solar physicist Lakshmi Pradeep Chitta from the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Germany, lead author of the research published in the journal Science.
The solar wind consists of plasma — ionized gas, or gas in which the atoms lose their electrons — and is mostly ionized hydrogen.
“Unlike the wind on Earth that circulates the globe, solar wind is ejected outward into interplanetary space,” Chitta said.
“Earth and the other planets in the solar system whiz through the solar wind as they orbit around the sun. Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere act as shields and protects life by blocking harmful particles and radiation from the sun, but the solar wind continuously propagates outward from the sun and inflates a plasma bubble called the heliosphere that encompasses the planets,” Chitta added.
The heliosphere extends out to about 100 to 120 times further than Earth’s distance to the sun.
The data for the study were obtained last year by one of the three telescopes on an instrument called the Extreme Ultraviolet Imager aboard the Solar Orbiter, a sun-observing probe built by the European Space Agency and NASA that was launched in 2020. The Solar Orbiter was about 50 million kilometers from the sun at the time — about one-third of the distance separating the sun and Earth.
“This finding is important, as it sheds more light on the physical mechanism of the solar wind generation,” said solar physicist and study coauthor Andrei Zhukov of the Royal Observatory of Belgium.
The solar wind’s existence was predicted by American physicist Eugene Parker in the 1950s and was verified in the 1960s.
“Still, the origin of the solar wind remains a longstanding puzzle in astrophysics,” Chitta said. “A key challenge is to identify the dominant physical process that powers the solar wind.”
The Solar Orbiter is discovering new details about the solar wind and is expected to obtain even better data in the coming years using additional instruments and viewing the sun from other angles.
Zhukov said stellar wind is a phenomenon common to most, if not all, stars, though the physical mechanism might differ among various types of stars.
“Our understanding of the sun is much more detailed than the understanding of other stars, due to its proximity and thus the possibility to make more detailed observations,” Zhukov added.

Kehinde Sanni spends his days smoothing out dents and repainting scratched bumpers in a modest autobody shop in Lagos. He has never left Nigeria, yet he speaks glowingly of Burkina Faso military leader Ibrahim Traore. “Nigeria needs someone like Ibrahim Traore of Burkina Faso. He is doing well for his country,” Sanni said. His admiration is shaped by a steady stream of viral videos, memes and social media posts — many misleading or outright false — portraying Traore as a fearless reformer who defied Western powers and reclaimed his country’s dignity. The Burkinabe strongman swept into power following a coup in September 2022

‘FRAGMENTING’: British politics have for a long time been dominated by the Labor Party and the Tories, but polls suggest that Reform now poses a significant challenge Hard-right upstarts Reform UK snatched a parliamentary seat from British Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s Labor Party yesterday in local elections that dealt a blow to the UK’s two establishment parties. Reform, led by anti-immigrant firebrand Nigel Farage, won the by-election in Runcorn and Helsby in northwest England by just six votes, as it picked up gains in other localities, including one mayoralty. The group’s strong showing continues momentum it built up at last year’s general election and appears to confirm a trend that the UK is entering an era of multi-party politics. “For the movement, for the party it’s a very, very big

ENTERTAINMENT: Rio officials have a history of organizing massive concerts on Copacabana Beach, with Madonna’s show drawing about 1.6 million fans last year Lady Gaga on Saturday night gave a free concert in front of 2 million fans who poured onto Copacabana Beach in Rio de Janeiro for the biggest show of her career. “Tonight, we’re making history... Thank you for making history with me,” Lady Gaga told a screaming crowd. The Mother Monster, as she is known, started the show at about 10:10pm local time with her 2011 song Bloody Mary. Cries of joy rose from the tightly packed fans who sang and danced shoulder-to-shoulder on the vast stretch of sand. Concert organizers said 2.1 million people attended the show. Lady Gaga

SUPPORT: The Australian prime minister promised to back Kyiv against Russia’s invasion, saying: ‘That’s my government’s position. It was yesterday. It still is’ Left-leaning Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday basked in his landslide election win, promising a “disciplined, orderly” government to confront cost-of-living pain and tariff turmoil. People clapped as the 62-year-old and his fiancee, Jodie Haydon, who visited his old inner Sydney haunt, Cafe Italia, surrounded by a crowd of jostling photographers and journalists. Albanese’s Labor Party is on course to win at least 83 seats in the 150-member parliament, partial results showed. Opposition leader Peter Dutton’s conservative Liberal-National coalition had just 38 seats, and other parties 12. Another 17 seats were still in doubt. “We will be a disciplined, orderly