Spraying a cow with pesticides, health workers target blood-sucking ticks at the heart of Iraq’s worst detected outbreak of a fever that causes people to bleed to death.
The sight of the health workers, dressed in full protective kit, is one that has become common in the Iraqi countryside, as the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) spreads, jumping from animals to humans.
This year Iraq has recorded 19 deaths among 111 CCHF cases in humans, the WHO says.
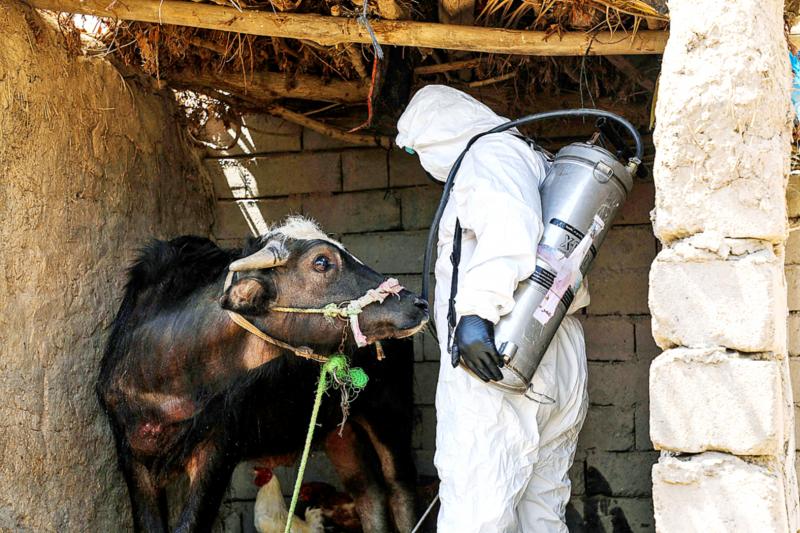
Photo: AFP
The virus has no vaccine and onset can be swift, causing severe bleeding internally and externally, and especially from the nose.
It causes death in as many as two-fifths of cases, medics say.
“The number of cases recorded is unprecedented,” said Haidar Hantouche, a health official in Dhi Qar Governate.
A poor farming region in southern Iraq, the governate accounts for nearly half of Iraq’s cases.
In previous years, cases could be counted “on the fingers of one hand,” Hantouche said.
Transmitted by ticks, hosts of the virus include wild and farmed animals such as buffalo, cattle, goats and sheep, all of which are common in Dhi Qar.
In the village of Al-Bujari, a team disinfects animals in a stable next to a house where a woman was infected. Wearing masks, goggles and overalls, the workers spray a cow and her two calves with pesticides.
A worker displays ticks that have fallen from the cow and been gathered into a container.
“Animals become infected by the bite of infected ticks,” the WHO said. “The CCHF virus is transmitted to people either by tick bites or through contact with infected animal blood or tissues during and immediately after slaughter.”
The surge of cases this year has shocked officials, as numbers far exceed recorded cases in the 43 years since the virus was first documented in Iraq in 1979.
In Dhi Qar, only 16 cases resulting in seven deaths had been recorded last year, but this year it has recorded 43 cases, including eight deaths, Hantouche said.
The numbers are still tiny compared with the COVID-19 pandemic — where Iraq has registered more than 25,200 deaths and 2.3 million recorded cases, according to WHO figures — but health workers are worried.
Endemic in Africa, Asia, the Middle East and the Balkans, CCHF’s fatality rate is between 10 and 40 percent, the WHO says.
WHO representative in Iraq Ahmed Zouiten said there were several “hypotheses” for the country’s outbreak.
They include the spread of ticks in the absence of livestock spraying campaigns during COVID-19 in 2020 and last year, and “very cautiously, we attribute part of this outbreak to global warming, which has lengthened the period of multiplication of ticks,” he said.
However, “mortality seems to be declining,” as Iraq had mounted a spraying campaign while new hospital treatments had shown “good results,” he said.
As the virus is “primarily transmitted” to people via ticks on livestock, most cases are among farmers, slaughterhouse workers and veterinarians, the WHO says.
“Human-to-human transmission can occur resulting from close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected persons,” it says.
Alongside uncontrolled bleeding, the virus causes intense fever and vomiting.
Medics fear there might be an explosion of cases following the Muslim festival of Eid al-Adha in July, when families traditionally slaughter an animal to feed guests.
“With the increase in the slaughter of animals, and more contact with meat, there are fears of an increase in cases during Eid,” said Azhar al-Assadi, a doctor specializing in hematological diseases in a hospital in Nasiriya.
Authorities have put in place disinfection campaigns and are cracking down on abattoirs that do not follow hygiene protocols. Several provinces have also banned livestock movement across their borders.

Kehinde Sanni spends his days smoothing out dents and repainting scratched bumpers in a modest autobody shop in Lagos. He has never left Nigeria, yet he speaks glowingly of Burkina Faso military leader Ibrahim Traore. “Nigeria needs someone like Ibrahim Traore of Burkina Faso. He is doing well for his country,” Sanni said. His admiration is shaped by a steady stream of viral videos, memes and social media posts — many misleading or outright false — portraying Traore as a fearless reformer who defied Western powers and reclaimed his country’s dignity. The Burkinabe strongman swept into power following a coup in September 2022

‘FRAGMENTING’: British politics have for a long time been dominated by the Labor Party and the Tories, but polls suggest that Reform now poses a significant challenge Hard-right upstarts Reform UK snatched a parliamentary seat from British Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s Labor Party yesterday in local elections that dealt a blow to the UK’s two establishment parties. Reform, led by anti-immigrant firebrand Nigel Farage, won the by-election in Runcorn and Helsby in northwest England by just six votes, as it picked up gains in other localities, including one mayoralty. The group’s strong showing continues momentum it built up at last year’s general election and appears to confirm a trend that the UK is entering an era of multi-party politics. “For the movement, for the party it’s a very, very big

ENTERTAINMENT: Rio officials have a history of organizing massive concerts on Copacabana Beach, with Madonna’s show drawing about 1.6 million fans last year Lady Gaga on Saturday night gave a free concert in front of 2 million fans who poured onto Copacabana Beach in Rio de Janeiro for the biggest show of her career. “Tonight, we’re making history... Thank you for making history with me,” Lady Gaga told a screaming crowd. The Mother Monster, as she is known, started the show at about 10:10pm local time with her 2011 song Bloody Mary. Cries of joy rose from the tightly packed fans who sang and danced shoulder-to-shoulder on the vast stretch of sand. Concert organizers said 2.1 million people attended the show. Lady Gaga

SUPPORT: The Australian prime minister promised to back Kyiv against Russia’s invasion, saying: ‘That’s my government’s position. It was yesterday. It still is’ Left-leaning Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday basked in his landslide election win, promising a “disciplined, orderly” government to confront cost-of-living pain and tariff turmoil. People clapped as the 62-year-old and his fiancee, Jodie Haydon, who visited his old inner Sydney haunt, Cafe Italia, surrounded by a crowd of jostling photographers and journalists. Albanese’s Labor Party is on course to win at least 83 seats in the 150-member parliament, partial results showed. Opposition leader Peter Dutton’s conservative Liberal-National coalition had just 38 seats, and other parties 12. Another 17 seats were still in doubt. “We will be a disciplined, orderly