Human activity is the main mechanism behind the spread of microplastics, Taiwanese scientists said on Tuesday as they called for national standards to be established to monitor the substances.
Scientists found 1.88 to 141 plastic particles per liter of water in samples taken from the Shihmen canals (石門大圳), which was formerly Taoyuan’s largest irrigation system, Jiang Jheng-jie (江政傑), an assistant professor of environmental engineering at Chung Yuan Christian University, told a teleconference hosted by the Science Media Center Taiwan.
Microplastic fragments are defined as those that are smaller than 5mm.

Photo: Lee Jung-ping, Taipei Times
The most common type of plastic particle was white or transparent microfibers from synthetic fabrics used in clothing, which suggests that the main sources of plastic pollution are urban centers near the canals, Jiang said.
Sand from beaches on the Hengchun Peninsula contained 200 plastic particles per kilogram, National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium deputy director Chen Te-hao (陳德豪) said.
There, too, the most common substance was white or transparent fibers, followed by fragments, film and pieces of polystyrene foam, Chen said, adding that microplastic pollution levels are strongly correlated to tourism.
White-sand beaches that were the cleanest to the naked eye actually had the highest levels of microplastic pollution, showing that beach cleaning is ineffective in removing the substance from the environment, he said.
Microplastic pollution must be combatted at the source, which means reducing plastic use, he said.
Plastic particles can be found nearly everywhere in the world, including the Kuroshio Current, which had been supposed to be free of the substance due to the speed of its waters, said Shiu Ruei-feng, an assistant professor of marine ecology at National Ocean University.
The current is a northerly flow in the northwest Pacific Ocean.
The problem cannot be tackled until Taiwan creates a common set of standards and methodology to monitor plastic particle pollution, Shiu said.
Separately, another local research team on Wednesday said that microplastic pollution in urban rivers in Taiwan is highly correlated to population density, urbanization and land use.
Microplastics are mostly derived from daily activities, roads, the manufacturing industry and natural fragmentation, Alexander Kunz, from Academia Sinica’s Research Center for Environmental Changes, told a news conference in Taipei, citing a study of water samples collected at rural and urban locations along two rivers.
Microplastics have contaminated the air, soil, deep sea and even Mount Everest’s peak, and are detected in animals and humans, said Kunz, who worked with academics at National Taiwan University and National Cheng Kung University.
The researchers examined water samples collected in 2018 along the Tamsui River (淡水河) in and around Taipei and in 2021 along the Dadu River (大肚溪) in Taichung to determine what caused a sudden increase in microplastics in urban rivers.
The researchers said that the levels of microplastics in the rivers were correlated with population density.
Their research was published in the March 15 edition of the journal Environmental Pollution.
The study found that microplastic levels were very low in the upper Dadu River, but concentrations increased in suburban Taichung.
The highest microplastic concentration was in water samples taken where the Dali River (大里溪) meets the Dadu River in Wuri District (烏日), an industrial area in the southern part of Taichung, the researchers said.

An essay competition jointly organized by a local writing society and a publisher affiliated with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) might have contravened the Act Governing Relations Between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area (臺灣地區與大陸地區人民關係條例), the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) said on Thursday. “In this case, the partner organization is clearly an agency under the CCP’s Fujian Provincial Committee,” MAC Deputy Minister and spokesperson Liang Wen-chieh (梁文傑) said at a news briefing in Taipei. “It also involves bringing Taiwanese students to China with all-expenses-paid arrangements to attend award ceremonies and camps,” Liang said. Those two “characteristics” are typically sufficient
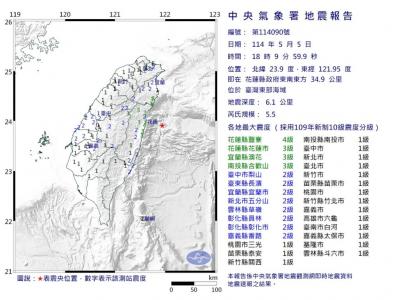
A magnitude 5.9 earthquake that struck about 33km off the coast of Hualien City was the "main shock" in a series of quakes in the area, with aftershocks expected over the next three days, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said yesterday. Prior to the magnitude 5.9 quake shaking most of Taiwan at 6:53pm yesterday, six other earthquakes stronger than a magnitude of 4, starting with a magnitude 5.5 quake at 6:09pm, occurred in the area. CWA Seismological Center Director Wu Chien-fu (吳健富) confirmed that the quakes were all part of the same series and that the magnitude 5.5 temblor was

The brilliant blue waters, thick foliage and bucolic atmosphere on this seemingly idyllic archipelago deep in the Pacific Ocean belie the key role it now plays in a titanic geopolitical struggle. Palau is again on the front line as China, and the US and its allies prepare their forces in an intensifying contest for control over the Asia-Pacific region. The democratic nation of just 17,000 people hosts US-controlled airstrips and soon-to-be-completed radar installations that the US military describes as “critical” to monitoring vast swathes of water and airspace. It is also a key piece of the second island chain, a string of

The Central Weather Administration has issued a heat alert for southeastern Taiwan, warning of temperatures as high as 36°C today, while alerting some coastal areas of strong winds later in the day. Kaohsiung’s Neimen District (內門) and Pingtung County’s Neipu Township (內埔) are under an orange heat alert, which warns of temperatures as high as 36°C for three consecutive days, the CWA said, citing southwest winds. The heat would also extend to Tainan’s Nansi (楠西) and Yujing (玉井) districts, as well as Pingtung’s Gaoshu (高樹), Yanpu (鹽埔) and Majia (瑪家) townships, it said, forecasting highs of up to 36°C in those areas