An air quality monitoring station at National Central University (NCU) has become an index station for NASA’s regional measurements due to the accuracy of its data, the university said yesterday.
The station uses micropulse lidar to determine the source of air pollutants, by measuring changes in wave forms when they are bounced back by atmospheric particulate matter, the university said.
Chang Shuenn-chin (張順欽), director-general of the Environmental Protection Administration’s (EPA) Department of Environmental Monitoring and Information Management, said the station has overcome the challenge of determining pollutant sources, which had plagued EPA officials before.
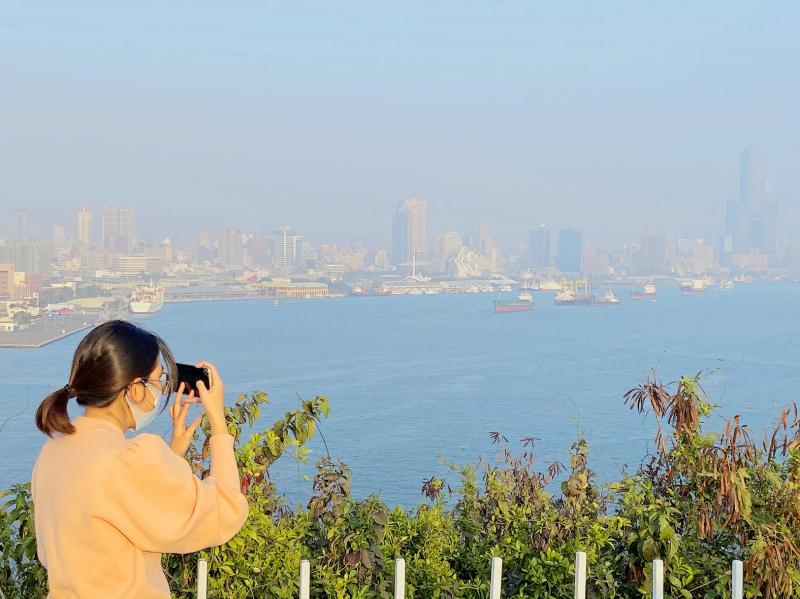

Photo: CNA
“Although ground-level sensors can tell you about the special characteristics of pollutants in a particular area, they cannot tell you the direction particles fall in or how they disperse,” he said.
The EPA started using micropulse lidar technology from NASA in 2002, when it began long-term monitoring of particle dispersal.
The data it collected allowed it to analyze air pollution patterns and concentrations, and to gain a more accurate understanding of air quality changes, Chang said.
The micropulse lidar system can gather readings from as high as 30km in the atmosphere, at a vertical resolution of 75m, and gathers information 24 hours a day, he said.
“If the wave forms of backscattered electrons it detects are irregular, it has likely detected elements from the Earth’s crust, for example from a sandstorm,” he said.
“Globular wave forms likely indicate pollutants produced by high-temperature combustion,” he said.
NASA has collected atmospheric data in this manner since 2000 through the US federated Micro-Pulse Lidar Network (MPLNET), university assistant professor Wang Sheng-hsiang (王聖翔) said.
The network collects data from around the world, and is able to analyze the environmental effect of smog and sandstorms in China, as well as from the slash-and-burn agricultural practices employed in Indochina, he said.
MPLNET comprises 26 monitoring stations worldwide, four of which are in Taiwan. Taiwan’s stations are at the National Central University in Taoyuan, as well as in Taichung’s Situn District (西屯), Yunlin County’s Douliou City (斗六) and Kaohsiung’s Zuoying District (左營).
The university’s station was added to MPLNET due to the maintenance of its equipment and the reliability of its data, Wang said.
“The university’s system is in a temperature and humidity-controlled environment, and the lens is cleaned even more frequently than those at US monitoring stations,” he said.
Cooperation with NASA on MPLNET is important given the global interest in tackling air pollution and improving air quality, Chang said.
Air quality can be affected by natural or synthetic phenomena, he said.
Examples of the former include sandstorms, volcanic activity, sea spray, forest fires and the erosion of geological formations, while sources of synthetic pollutants include factories, motor vehicles, construction and farming, Chang said.
Air pollutants include particles with a diameter of up to 10 micrometers and those with a diameter of up to 2 micrometers, ozone, vulcanized materials, nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide and lead.
The EPA measures air pollution nationwide at 111 monitoring stations, which include 77 standard monitoring stations, 10 mobile stations and other facilities that take measurements using light and other methods.
The stations have measured decreases in most pollutants in the past few years, but have shown annual increases in the concentration of ground-level ozone, which can cause breathing difficulties and chest pain, the EPA said.
Air quality in Taiwan is affected by seasonal winds and geography, Chang said.
“Strong northeasterly winds blow between October and April, bringing pollutants from China,” he said, adding that the central mountain chain then weakens the wind, so that pollutants become trapped above central and southern Taiwan.
However, southwesterly winds that blow between May and September bring stronger winds to central and southern Taiwan, so air quality in those regions improves, he said.
Meanwhile, air quality is worse during the day due to human activity, with pollutants reaching peak concentrations at about 6am and 6pm due to heavy traffic, he said.
Also, concentrations of nitrogen oxide and carbon monoxide are on average 1.2 times higher during work days than on weekends, he said, adding that concentrations are 1.7 times higher during rush hour.
Meanwhile, Chang said that the best time to jog outdoors is between 4am and 7am.

An essay competition jointly organized by a local writing society and a publisher affiliated with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) might have contravened the Act Governing Relations Between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area (臺灣地區與大陸地區人民關係條例), the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) said on Thursday. “In this case, the partner organization is clearly an agency under the CCP’s Fujian Provincial Committee,” MAC Deputy Minister and spokesperson Liang Wen-chieh (梁文傑) said at a news briefing in Taipei. “It also involves bringing Taiwanese students to China with all-expenses-paid arrangements to attend award ceremonies and camps,” Liang said. Those two “characteristics” are typically sufficient
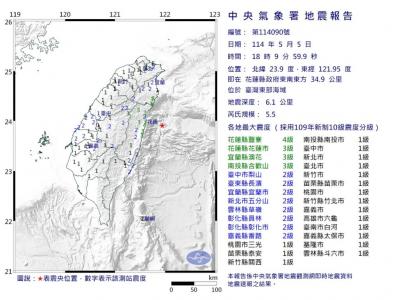
A magnitude 5.9 earthquake that struck about 33km off the coast of Hualien City was the "main shock" in a series of quakes in the area, with aftershocks expected over the next three days, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said yesterday. Prior to the magnitude 5.9 quake shaking most of Taiwan at 6:53pm yesterday, six other earthquakes stronger than a magnitude of 4, starting with a magnitude 5.5 quake at 6:09pm, occurred in the area. CWA Seismological Center Director Wu Chien-fu (吳健富) confirmed that the quakes were all part of the same series and that the magnitude 5.5 temblor was

The brilliant blue waters, thick foliage and bucolic atmosphere on this seemingly idyllic archipelago deep in the Pacific Ocean belie the key role it now plays in a titanic geopolitical struggle. Palau is again on the front line as China, and the US and its allies prepare their forces in an intensifying contest for control over the Asia-Pacific region. The democratic nation of just 17,000 people hosts US-controlled airstrips and soon-to-be-completed radar installations that the US military describes as “critical” to monitoring vast swathes of water and airspace. It is also a key piece of the second island chain, a string of

The Central Weather Administration has issued a heat alert for southeastern Taiwan, warning of temperatures as high as 36°C today, while alerting some coastal areas of strong winds later in the day. Kaohsiung’s Neimen District (內門) and Pingtung County’s Neipu Township (內埔) are under an orange heat alert, which warns of temperatures as high as 36°C for three consecutive days, the CWA said, citing southwest winds. The heat would also extend to Tainan’s Nansi (楠西) and Yujing (玉井) districts, as well as Pingtung’s Gaoshu (高樹), Yanpu (鹽埔) and Majia (瑪家) townships, it said, forecasting highs of up to 36°C in those areas