A final round of talks on a treaty to curb plastic pollution opened yesterday, with deep differences between nations emerging almost immediately.
The meeting opened just hours after a chaotic end to the COP29 climate talks in Baku, which agreed to a boost in climate funding that developing countries slammed as insufficient.
Opening the plastics meeting, the Ecuadoran diplomat chairing the talks warned nations that the conference was about “far more than drafting an international treaty.”

Photo: AFP
“It is about humanity rising to meet an existential challenge,” Luis Vayas Valdivieso, chair of the Intergovernmental Negotiation Committee, told an opening plenary in South Korea’s Busan.
Plastic pollution is so ubiquitous that it has been found in clouds, the deepest ocean trenches and even human breastmilk, and while almost everyone agrees it is a problem, there is less consensus on how to solve it.
Among the most contentious issues are whether the treaty should cap plastic production, a possible ban on chemicals feared toxic to human health and how to pay for implementation. The deep differences have dogged four previous rounds of talks over the past two years, resulting in a lengthy and contradictory draft treaty running more than 70 pages.

Photo: AP / Yonhap
Valdivieso has produced an alternative document intended to synthesize the views of delegations and move negotiations forward, but several countries, including Russia and India, immediately objected to it.
“The reality is that many countries do not see themselves represented in this paper,” Saudi Arabian delegation head Eyad Aljubran said on behalf of the Arab group.
In 2019, the world produced about 460 million tonnes of plastic, a figure that has doubled since 2000, according to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Plastic production is expected to triple by 2060.
More than 90 percent of plastic is not recycled, with more than 20 million tonnes leaking into the environment, often after just a few minutes of use.
Plastic also accounts for about 3 percent of global emissions, mostly linked to its production from fossil fuels.
Some countries, including the so-called High Ambition Coalition (HAC), which groups many African, Asian and European nations, want the treaty to address the entire “lifecycle” of plastics. That means limiting production, redesigning products for reuse and recycling, and addressing waste.
On the other side are countries, largely oil producers like Saudi Arabia and Russia, which want a downstream focus on waste alone.
The HAC wants binding global targets on reducing production and warned ahead of the Busan talks that “vested interests” should not be allowed to hamper a deal.
Some observers said the talks are likely to falter and be extended, but by yesterday afternoon, Valdivieso won agreement for negotiations to begin on the basis of his slimmed-down document.
“I thank you very much for your flexibility,” he told the room.
The short time frame has some environmental groups worried an agreement would be watered down to ensure something is signed.
The key to any accord would be the US and China, neither of which have openly sided with either bloc.
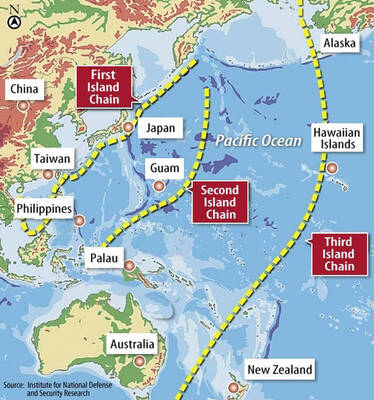
The US government has signed defense cooperation agreements with Japan and the Philippines to boost the deterrence capabilities of countries in the first island chain, a report by the National Security Bureau (NSB) showed. The main countries on the first island chain include the two nations and Taiwan. The bureau is to present the report at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee tomorrow. The US military has deployed Typhon missile systems to Japan’s Yamaguchi Prefecture and Zambales province in the Philippines during their joint military exercises. It has also installed NMESIS anti-ship systems in Japan’s Okinawa

TRAGEDY STRIKES TAIPEI: The suspect died after falling off a building after he threw smoke grenades into Taipei Main Station and went on a killing spree in Zhongshan A 27-year-old suspect allegedly threw smoke grenades in Taipei Main Station and then proceeded to Zhongshan MRT Station in a random killing spree that resulted in the death of the suspect and two other civilians, and seven injured, including one in critical condition, as of press time last night. The suspect, identified as a man surnamed Chang Wen (張文), allegedly began the attack at Taipei Main Station, the Taipei Fire Department said, adding that it received a report at 5:24pm that smoke grenades had been thrown in the station. One man in his 50s was rushed to hospital after a cardiac arrest

‘WIN-WIN’: The Philippines, and central and eastern European countries are important potential drone cooperation partners, Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung said Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung (林佳龍) in an interview published yesterday confirmed that there are joint ventures between Taiwan and Poland in the drone industry. Lin made the remark in an exclusive interview with the Chinese-language Liberty Times (the Taipei Times’ sister paper). The government-backed Taiwan Excellence Drone International Business Opportunities Alliance and the Polish Chamber of Unmanned Systems on Wednesday last week signed a memorandum of understanding in Poland to develop a “non-China” supply chain for drones and work together on key technologies. Asked if Taiwan prioritized Poland among central and eastern European countries in drone collaboration, Lin

ON ALERT: Taiwan’s partners would issue warnings if China attempted to use Interpol to target Taiwanese, and the global body has mechanisms to prevent it, an official said China has stationed two to four people specializing in Taiwan affairs at its embassies in several democratic countries to monitor and harass Taiwanese, actions that the host nations would not tolerate, National Security Bureau (NSB) Director-General Tsai Ming-yen (蔡明彥) said yesterday. Tsai made the comments at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee, which asked him and Minister of National Defense Wellington Koo (顧立雄) to report on potential conflicts in the Taiwan Strait and military preparedness. Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) Legislator Michelle Lin (林楚茵) expressed concern that Beijing has posted personnel from China’s Taiwan Affairs Office to its