The US is to send medium-range missiles including the Standard Missile 6 (SM-6) and Tomahawk to the Asia-Pacific next year to deter a Chinese attack on Taiwan, US military news Web site Defense One reported.
The report cited comments US Army General Charles Flynn made during the annual Halifax International Security Forum on Nov. 19.
“We have tested them and we have a battery or two of them today,” Flynn was quoted as saying.
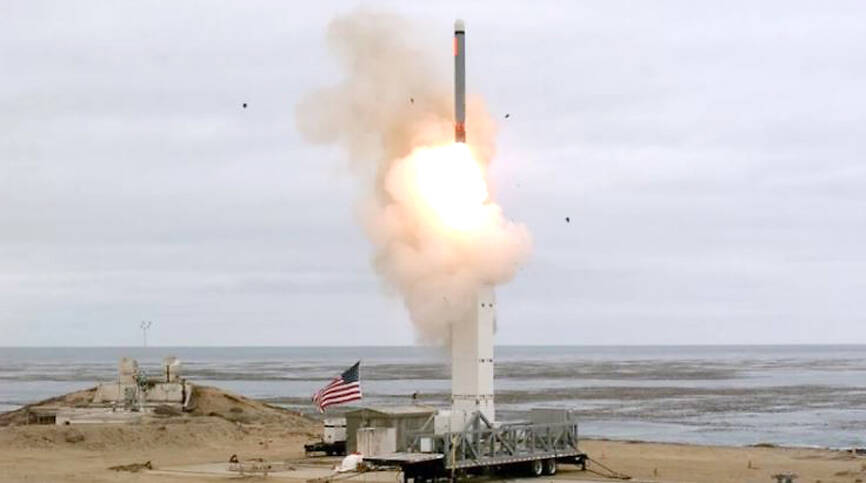

Photo: Screengrab from Defense Visual Information Distribution Service’s Web site
“In [20]24. We intend to deploy that system in your region. I’m not going to say where and when. But I will just say that we will deploy them,” he said.
The US was previously prevented from deploying nuclear and conventional ground-launched ballistic missiles, cruise missiles and missile launchers with ranges of 500km to 5,500km under the terms of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty.
The treaty was signed by then-US president Ronald Reagan and then-Soviet Union Communist Party general secretary Mikhail Gorbachev on Dec. 8, 1987. It was ratified on June 1, 1988.
Former US president Donald Trump announced the US’ withdrawal from the treaty on Oct. 20, 2018, citing non-compliance by Russia, due to Moscow’s development and deployment of an intermediate-range cruise missile known as the SSC-8 (Novator 9M729), as well as the need to counter a Chinese arms buildup in the Pacific.
In July, the US Marine Corps held a commissioning ceremony for the first land-based Tomahawk cruise missile battalion at the Camp Pendleton Training Center in California. The battalion is to be equipped with the Naval Strike Missile — a multi-mission cruise missile that can neutralize highly secure maritime and land targets, the US military has said.
Meanwhile, the SM-6, first commissioned in 2013, is the latest missile developed by US arms contractor Raytheon Co for its Standard Extended Range Active Missile family of missiles.
It has a top range of 240km, a flight speed of Mach 3.5 to Mach 5, and can be used as a surface-to-air missile, an anti-ballistic missile or an anti-ship missile. It has been selected by the US Army to be used as a land-based medium-range strike ballistic missile weapon system.
Flynn said with these missiles now in regular active service, the US Army has been preparing to commission the next-generation Precision Strike Missiles (PrSMs), which are under development and might be ready for service before the end of this year.
The PrSM is being developed by contractor Lockheed Martin Corp, and is to replace the MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System.
The new missile is expected to be capable of hitting targets 499km away, farther than the SM-6’s 370km, and it can be launched from the M142 High Mobility Artillery Rocket System platform.
Flynn previously said that more regional militaries are seeking to conduct joint exercises with US forces due to China’s increasingly aggressive behavior against certain countries in the Indo-Pacific region.
China’s military is strengthening its capabilities at an accelerated rate, “so that trajectory that they’re on is a dangerous one for the region, and, candidly, it’s a dangerous moment for the world,” he said.
Meanwhile, the Pentagon on Nov. 17 said that the US Department of State has approved the potential sale of 400 Tomahawk missiles and related equipment to Japan in a deal valued at US$2.35 billion.
The package would include 400 Tomahawk missiles, 14 Tactical Tomahawk Weapon Control Systems, software, support equipment, spares and technical support, the Pentagon said.
Additional reporting by Reuters

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
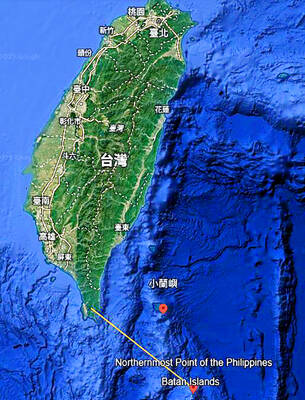
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College