It was clear from the start that a cyberattack by suspected Russian hackers aimed at several US government agencies was going to be bad. One clue: US National Security Adviser Robert O’Brien cut short a trip overseas to rush back to Washington to help manage the crisis.
On Thursday, the reality of just how sprawling — and potentially damaging — the breach might be came into sharper focus.
It started with a bulletin from the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), warning that the hackers were sophisticated, patient and well-resourced, representing a “grave risk” to federal, state and local governments, as well as critical infrastructure and the private sector.
Bloomberg News reported that at least three state governments were hacked, which followed reports of other breaches: the city network in Austin, Texas, and the US nuclear weapons agency. Software giant Microsoft Corp also said its systems were exposed.
The US Department of Energy and its National Nuclear Security Administration, which maintains the country’s nuclear stockpile, said that the malware was isolated to business networks and did not affect national security functions.
Nonetheless, the effect of the revelations was confirmation that no single person or agency is certain of exactly what the hackers had infiltrated, let alone the full extent of what was taken.
US president-elect Joe Biden interrupted a series of high-profile appointment announcements to weigh in.
“I want to be clear: My administration will make cybersecurity a top priority at every level of government — and we will make dealing with this breach a top priority from the moment we take office,” Biden said.
So far, US President Donald Trump has not commented on the attack.
The hackers installed what is known as a backdoor in widely used software from Texas-based SolarWinds Corp, whose customers include myriad government agencies and Fortune 500 companies.
That malicious backdoor, which was installed by 18,000 SolarWinds customers, allowed the hackers access to their computer networks.
US authorities — and governments around the world — are only now beginning to uncover who was unlucky enough to receive the hackers’ full attention.
Microsoft said it detected the backdoor in SolarWinds’ software in its “environment” and had “isolated and removed” it.
The company said that none of its customer data nor its products were accessed or used to further attacks on others.
In a blog post, Microsoft said it had identified more than 40 customers that the hackers had “targeted more precisely and compromised,” including “security and other technology firms,” think tanks and government contractors, in addition to government agencies.

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
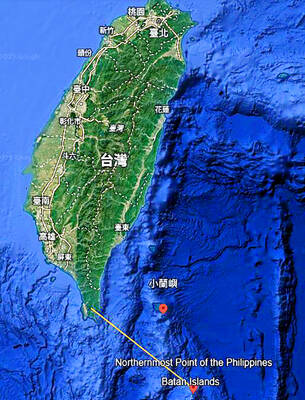
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College