Researchers have found that a deficiency in the primary cilium on cells could be the key to understanding progeria, a rare progressive genetic disorder that causes children to age rapidly and die young.
The research was featured on Monday last week in EMBO Reports, a peer-reviewed journal published by the European Molecular Biology Organization, under the title “Lamin A-mediated nuclear lamina integrity is required for proper ciliogenesis.”
People with progeria, also known as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, develop symptoms in infancy and have an average life expectancy of 13 years.

Photo courtesy of the Ministry of Science and Technology
Clinically observable traits include severe growth retardation, loss of subcutaneous fat, wrinkled skin, hair loss, osteoporosis, joint stiffness and cardiovascular disease.
Despite being medically described in 1886, progeria was not attributed to mutations of the LMNA gene until 2003. The gene provides instructions to make several slightly different proteins called lamins.
The two major proteins produced from this gene — lamin A and lamin C — are made in most cells.
When the LMNA gene mutates, it causes abnormal wrinkles on the nucleus, which can deform and hollow out, Chen Hong-chen (陳鴻震), professor of molecular biology at National Yang-Ming University and leader of the research team, told a news conference at the Ministry of Science and Technology yesterday.
For the first time, the team found a link between the abnormality in the nucleus and the primary cilium on the surface of the cell, after observing that dermal fibroblasts — which generate connective tissue — had fewer and shorter primary cilia in people with progeria.
As the primary cilium functions like a cellular antenna that detects changes in the extracellular environments and transduces signals to the cell interior to respond to those changes, it is possible that the malfunction of primary cilia could cause progeria, Chen said.
The team further examined LMNA-null laboratory mice — which have had a gene knocked out by the targeted integration of a defective gene — and proved that primary cilia were defective in many organs of prematurely aged, lamin A-deficient mice, he said.
The team also found that mice with LMNA deficiency had a lifespan of four to five months, much shorter than normal mice.
It is possible to fix the deficiency with genetic engineering, Chen said.
“This discovery not only provides new insight into the pathogenesis of progeria syndrome, but also sheds light on new therapeutic strategies for related diseases,” the ministry said in a statement.
The study was sponsored by the ministry and mainly conducted by postdoctoral fellow Fan Jia-rong (范嘉榕), who is the first author of the paper; associate researcher Chi Ya-hui (紀雅惠) of the National Health Research Institutes; and You Li-ru (游麗如) and Wang Won-jing (王琬菁) of the university’s Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
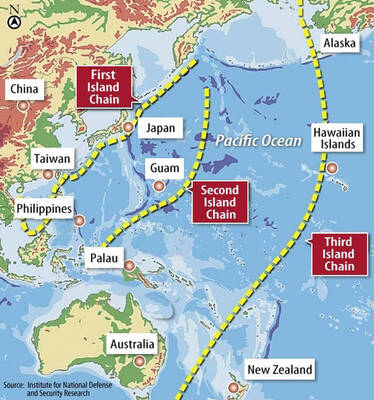
The US government has signed defense cooperation agreements with Japan and the Philippines to boost the deterrence capabilities of countries in the first island chain, a report by the National Security Bureau (NSB) showed. The main countries on the first island chain include the two nations and Taiwan. The bureau is to present the report at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee tomorrow. The US military has deployed Typhon missile systems to Japan’s Yamaguchi Prefecture and Zambales province in the Philippines during their joint military exercises. It has also installed NMESIS anti-ship systems in Japan’s Okinawa

TRAGEDY STRIKES TAIPEI: The suspect died after falling off a building after he threw smoke grenades into Taipei Main Station and went on a killing spree in Zhongshan A 27-year-old suspect allegedly threw smoke grenades in Taipei Main Station and then proceeded to Zhongshan MRT Station in a random killing spree that resulted in the death of the suspect and two other civilians, and seven injured, including one in critical condition, as of press time last night. The suspect, identified as a man surnamed Chang Wen (張文), allegedly began the attack at Taipei Main Station, the Taipei Fire Department said, adding that it received a report at 5:24pm that smoke grenades had been thrown in the station. One man in his 50s was rushed to hospital after a cardiac arrest

ON ALERT: Taiwan’s partners would issue warnings if China attempted to use Interpol to target Taiwanese, and the global body has mechanisms to prevent it, an official said China has stationed two to four people specializing in Taiwan affairs at its embassies in several democratic countries to monitor and harass Taiwanese, actions that the host nations would not tolerate, National Security Bureau (NSB) Director-General Tsai Ming-yen (蔡明彥) said yesterday. Tsai made the comments at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee, which asked him and Minister of National Defense Wellington Koo (顧立雄) to report on potential conflicts in the Taiwan Strait and military preparedness. Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) Legislator Michelle Lin (林楚茵) expressed concern that Beijing has posted personnel from China’s Taiwan Affairs Office to its

‘ILLEGAL RULING’: The KMT and the TPP slammed the Constitutional Court judgement, saying it contravened the law and was trying to clear the way for a ‘green dictatorship’ The Constitutional Court yesterday ruled that amendments to the Constitutional Court Procedure Act (憲法訴訟法) passed by the Legislative Yuan last year are unconstitutional, as they contravene due legislative process and separation of powers. The Legislative Yuan on Dec. 20 last year passed amendments stipulating that no fewer than 10 grand justices must take part in deliberations of the Constitutional Court, and at least nine grand justices must agree to declare a law unconstitutional. The Executive Yuan on Jan. 2 requested that lawmakers reconsider the bill, but the Legislative Yuan, under a combined majority of Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) and Taiwan People’s Party