Whole-body MRI scans have been around for more than a decade but it is only lately that they have started taking over social media feeds.
In a promotional post on Instagram last year, Kim Kardashian wrote about her experience of being scanned by what she called a “life saving machine.”
“It has really saved some of my friends lives and I just wanted to share,” she posted.
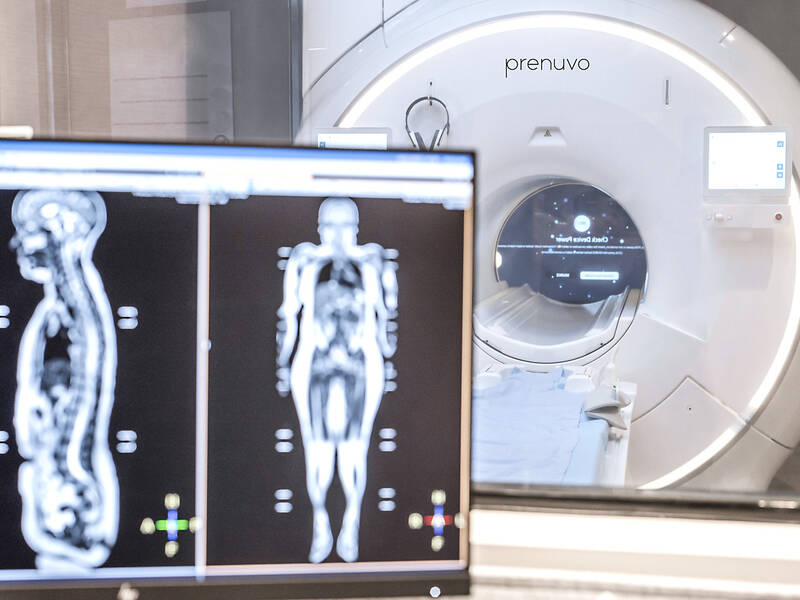
Photo: AP
Paris Hilton shared a similar experience of having a full-body scan to “proactively” rule out breast cancer.
“I encourage every single one of you to go get a scan,” she said.
Social media influencers and entrepreneurs promote the full-body MRIs as “super scans” that can detect early cancers and alert people to “silent killers.” They’re sold by tech and radiology companies as a risk-free way of getting a “complete health check” in an attempt to prolong your life.

Photo: AFP
But while the scans can be useful for people at high risk of certain genetic conditions or cancers, is there any evidence they can help people with an average or low risk of disease?
WHAT IS A FULL-BODY MRI?
The scan involves lying still on a long, narrow table which slides into a cylindrical machine. Powerful magnets, radio waves and computer imaging are used to create highly detailed images of the organs, joints and tissues.
Advertisements for the scans promote their ability to detect early signs of illness and present them as risk-free, aside from the discomfort that might come from lying on your back in an enclosed space for about an hour.
There are now private clinics offering the scans for upwards of US$800 to anyone who wants one — even if they have no symptoms or a referral from a doctor. The implication is almost anyone is a good candidate.
With most people affected by or aware of someone with cancer or heart disease, it may seem like a small price to pay for apparent peace of mind.
But according to those who endorse the scans, including celebrities, benefits abound, including the ability to detect things like cancer and aneurysms in their earliest stages, before symptoms arise.
WHAT DOES THE EVIDENCE SAY?
The University of Sydney public health researcher Brooke Nickel says full-body MRI scans can in fact have unintended negative consequences.
Expanding disease definitions and lowering diagnostic thresholds mean more people previously considered healthy or at low risk may now be classified as having a health condition or an indicator of disease, such as a shadow on an organ. This is known as overdiagnosis.
“The main concern with full-body MRI scans is that they have the ability to detect inconsequential disease leading to unnecessary diagnosis and treatments,” Nickel says.
“This can lead to individual harm and also impact the health system.”
Harms include the fear and anxiety that comes from being told something has been detected on a scan; the feeling that any abnormality should be treated and eliminated “just in case;” and the risk that comes with additional treatments to address whatever the scan may find. These treatments might be unnecessary, costly and come with side-effects.
Nickel says companies that manufacture medical devices and treatments can benefit from people’s fear of becoming unwell and their desire to be informed, by coming up with new health screening tools and detection tests, such as a full-body MRI.
“The premise that knowledge and information is power, while it used to make individuals feel more empowered about their health, is concerning when used by commercial entities or those with vested interest in relation to health interventions like tests, treatments and technology that are non-evidence based,” she says.
The tests can also be overly reassuring. A heavy smoker or regular drinker may feel there is no need to address those habits if a full-body scans reveals no abnormality. And full-body MRIs are not the best tool for detecting many of the diseases or functional issues related to lifestyle habits.
WHAT DO EXPERTS RECOMMEND?
Prof Rachelle Buchbinder, a rheumatologist and clinical epidemiologist, says the scans also detect common and normal age-related changes in the back and knees which are mostly benign. This can also lead to unwarranted diagnoses, worry and unnecessary treatment, she says.
Full-body MRI scans do have uses for people at high risk of certain genetic conditions or cancers, or to detect metastatic cancer, and only in these cases will a doctor-ordered test be covered by Medicare.
There is no evidence that these highly sensitive scans provide any overall benefit for people at average or low risk of disease. They do offer a good risk of overdiagnosis, unnecessary anxiety and a depleted bank account.

On April 26, The Lancet published a letter from two doctors at Taichung-based China Medical University Hospital (CMUH) warning that “Taiwan’s Health Care System is on the Brink of Collapse.” The authors said that “Years of policy inaction and mismanagement of resources have led to the National Health Insurance system operating under unsustainable conditions.” The pushback was immediate. Errors in the paper were quickly identified and publicized, to discredit the authors (the hospital apologized). CNA reported that CMUH said the letter described Taiwan in 2021 as having 62 nurses per 10,000 people, when the correct number was 78 nurses per 10,000

As we live longer, our risk of cognitive impairment is increasing. How can we delay the onset of symptoms? Do we have to give up every indulgence or can small changes make a difference? We asked neurologists for tips on how to keep our brains healthy for life. TAKE CARE OF YOUR HEALTH “All of the sensible things that apply to bodily health apply to brain health,” says Suzanne O’Sullivan, a consultant in neurology at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery in London, and the author of The Age of Diagnosis. “When you’re 20, you can get away with absolute

May 5 to May 11 What started out as friction between Taiwanese students at Taichung First High School and a Japanese head cook escalated dramatically over the first two weeks of May 1927. It began on April 30 when the cook’s wife knew that lotus starch used in that night’s dinner had rat feces in it, but failed to inform staff until the meal was already prepared. The students believed that her silence was intentional, and filed a complaint. The school’s Japanese administrators sided with the cook’s family, dismissing the students as troublemakers and clamping down on their freedoms — with

As Donald Trump’s executive order in March led to the shuttering of Voice of America (VOA) — the global broadcaster whose roots date back to the fight against Nazi propaganda — he quickly attracted support from figures not used to aligning themselves with any US administration. Trump had ordered the US Agency for Global Media, the federal agency that funds VOA and other groups promoting independent journalism overseas, to be “eliminated to the maximum extent consistent with applicable law.” The decision suddenly halted programming in 49 languages to more than 425 million people. In Moscow, Margarita Simonyan, the hardline editor-in-chief of the