Back to Black as a movie is a tame and mediocre affair. A conventionally told biopic about a talented artist who became famous, struggled with drugs, depression and bulimia, and died early. There are nice performances from gifted actors like Marisa Abela, Jack O’Connell, Eddie Marsan and Lesley Manville, and a soundtrack of hits that helps fill the space.
But as a portrait of Amy Winehouse? It is simply dreadful.
The main problem with any movie about Winehouse is that a defining film already exists — Asif Kapadia’s Oscar-winning documentary Amy, released four years after her death from alcohol poisoning at age 27. Told through archival material, home videos and observations from those around her, it felt as intimate and unfiltered as a diary.
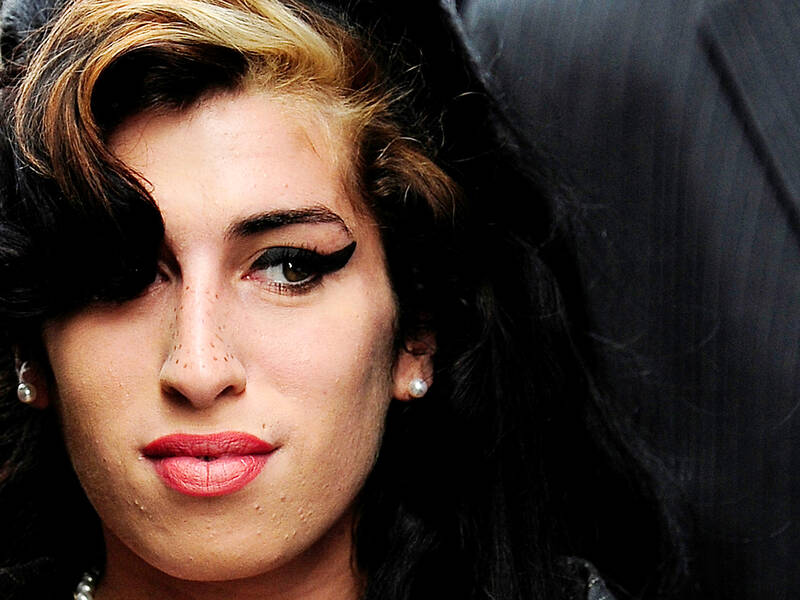

Photo: Reuters
Amy was a sobering portrait of addiction, fame and complicity that also let you get to know and love the person behind the songs, the eyeliner, the beehive, the bloodied ballet slippers and the invasive paparazzi photos. It was no one’s idea of sensationalistic and she’s doing most of the talking.
Amy was also a movie that didn’t sit well with her grieving family. Her father, Mitch Winehouse, said it was misleading and contained “basic untruths.” After it won the Oscar, he doubled down saying that it had no bearing on her life and was manipulative. Kapadia, he said, was more exploitative of his daughter than anyone.
Following her death, Mitch started a foundation in her name to help young people and wrote a book about her and being the father of an addict. Her mother Janis narrated a documentary, Reclaiming Amy, released in 2011. And after years of declining to participate in a narrative biopic, the estate decided to allow one with full use the songs. Like many musical biopics made alongside an estate, it’s hard not to look at Back to Black skeptically, wondering whose interests the film is serving.
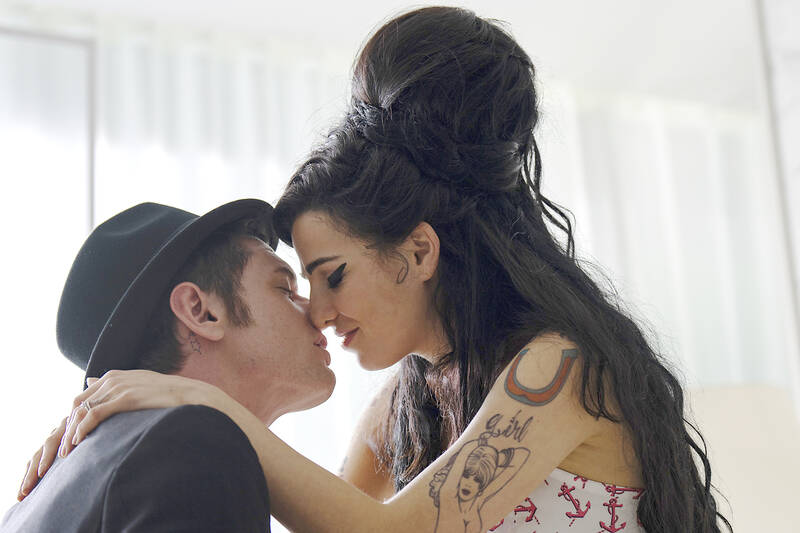

Photo: AP
Sam Taylor-Johnson, who directed, has said that she wanted to take the idea of “blame” out of the equation, that the family had zero input on her cut and would not benefit financially. And yet it also seems like a direct response to Kapadia’s film, depicting more than a few key moments wildly differently. They’re not just shown in a different light — some are telling a completely different story.
The screenplay by Matthew Greenhalgh is empathetic to the ex-husband Blake Fielder-Civil (O’Connell) and her father Mitch (Marsan), both of whom have been villainized over the years. In the film, most are just caught up in a whirl of inevitability and the retrospective blur of grief.
There seems to be an excessive amount of rationalizing in the way everyone involved talks about Back to Black, over justifying its existence and its choices. But just because everyone keeps telling us that it’s a celebration doesn’t mean that we have to get on board. I’m not sure what is celebratory about dramatizing this tragedy, or helpful, or artful, or particularly revelatory about it either. The media, for example, is reduced mainly to the paparazzi camped outside her place as though that’s where the problem stopped.
Photo: AP
Taylor-Johnson has said she didn’t want to glamorize depression, addiction or bulimia either, but the latter, which she struggled with before she was famous, is barely even acknowledged. Depiction of eating disorders is inherently fraught, but there had to have been a way to address such a large part of her life and self-image more directly.
Though linear, the story is also oddly confusing, assuming that the audience knows many details of her life (like, say, the bulimia) and the people in it. The film rushes through major career moments in montage, seeming to slow down only for a few things: A performance, Amy’s face in various forms of drunken distress and agony or scenes with her and Blake. Was it attempting a freewheeling jazz form, or is it just messy?
In some ways, this portrait of Amy Winehouse makes her immense talent the sideshow and her obsession/romance/heartache over Blake the defining story of her adult life. This is at least somewhat redeemed by the chemistry between Abela and O’Connell, who look far too glowing and healthy to be believable as heroin addicts.
But the greatest failing is how shockingly cliche the ending is. For all of Back to Black’s tiptoeing around delicate subjects, its romantically photographed sendoff to Amy is perhaps the most dangerously glamorized shot in the film. It doesn’t even fade to black after a title card announces her death. Before anyone can feel anything, they’ve cut to Amy telling the audience that all she wants is for her songs to make people forget about their troubles for a bit.
By this point, it reads more like a closing statement for a film that never wanted to challenge, offend or move anyone. Mission accomplished.

On April 26, The Lancet published a letter from two doctors at Taichung-based China Medical University Hospital (CMUH) warning that “Taiwan’s Health Care System is on the Brink of Collapse.” The authors said that “Years of policy inaction and mismanagement of resources have led to the National Health Insurance system operating under unsustainable conditions.” The pushback was immediate. Errors in the paper were quickly identified and publicized, to discredit the authors (the hospital apologized). CNA reported that CMUH said the letter described Taiwan in 2021 as having 62 nurses per 10,000 people, when the correct number was 78 nurses per 10,000

As we live longer, our risk of cognitive impairment is increasing. How can we delay the onset of symptoms? Do we have to give up every indulgence or can small changes make a difference? We asked neurologists for tips on how to keep our brains healthy for life. TAKE CARE OF YOUR HEALTH “All of the sensible things that apply to bodily health apply to brain health,” says Suzanne O’Sullivan, a consultant in neurology at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery in London, and the author of The Age of Diagnosis. “When you’re 20, you can get away with absolute

May 5 to May 11 What started out as friction between Taiwanese students at Taichung First High School and a Japanese head cook escalated dramatically over the first two weeks of May 1927. It began on April 30 when the cook’s wife knew that lotus starch used in that night’s dinner had rat feces in it, but failed to inform staff until the meal was already prepared. The students believed that her silence was intentional, and filed a complaint. The school’s Japanese administrators sided with the cook’s family, dismissing the students as troublemakers and clamping down on their freedoms — with

As Donald Trump’s executive order in March led to the shuttering of Voice of America (VOA) — the global broadcaster whose roots date back to the fight against Nazi propaganda — he quickly attracted support from figures not used to aligning themselves with any US administration. Trump had ordered the US Agency for Global Media, the federal agency that funds VOA and other groups promoting independent journalism overseas, to be “eliminated to the maximum extent consistent with applicable law.” The decision suddenly halted programming in 49 languages to more than 425 million people. In Moscow, Margarita Simonyan, the hardline editor-in-chief of the