For three decades Joe Lau has tied his racehorse training career to the rising and falling fortunes of the Macau Jockey Club, but in a few days it will all be over.
On April 1, horse racing in the southern Chinese casino hub will be consigned to history after the club’s concession from the government to operate racing was terminated.
The sport was in financial difficulties and no longer able to meet the “current development needs of society,” said a government statement in January.
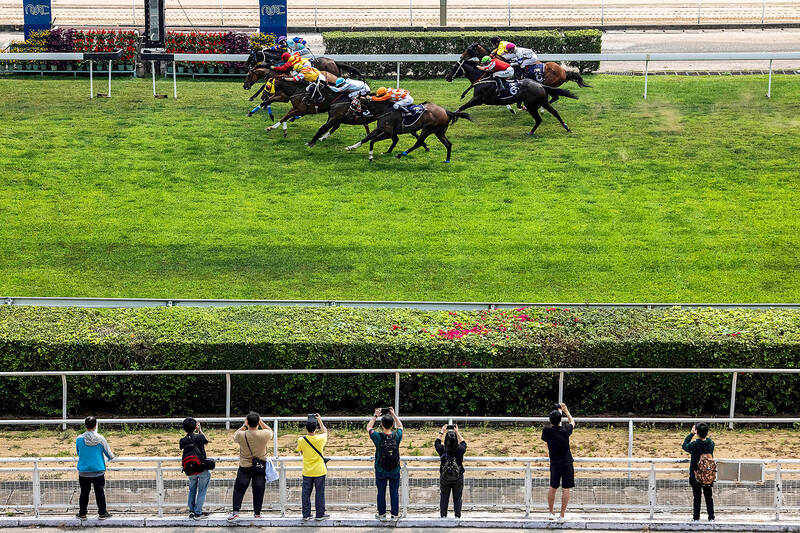

Photo: AFP
Speaking outside the aging racecourse, with glitzy casino resorts towering in the distance, Lau recalled the glory days, such as his sweep at the 2004 Hong Kong-Macau Interport Series, but he now feels “depressed” about the end of an era.
“(It’s) like you felt the whole house on fire, and it shouldn’t happen this way,” Lau said.
“Riding is in my blood and this is my occupation.”
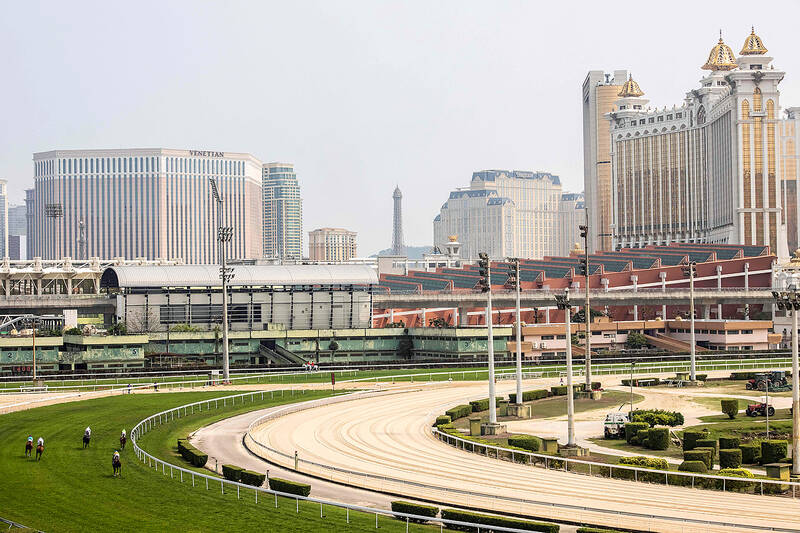

Photo: AFP
Macau held its first thoroughbred races in 1989, when still under Portuguese rule, and the sport found success after a takeover in 1991 by Stanley Ho, the late casino tycoon nicknamed “King of Gambling.”
In recent years, the Macau Jockey Club — chaired by Ho’s fourth wife Angela Leong — saw attendances fall and racked up losses exceeding 2.5 billion patacas (US$310 million).
‘STILL IN SHOCK’
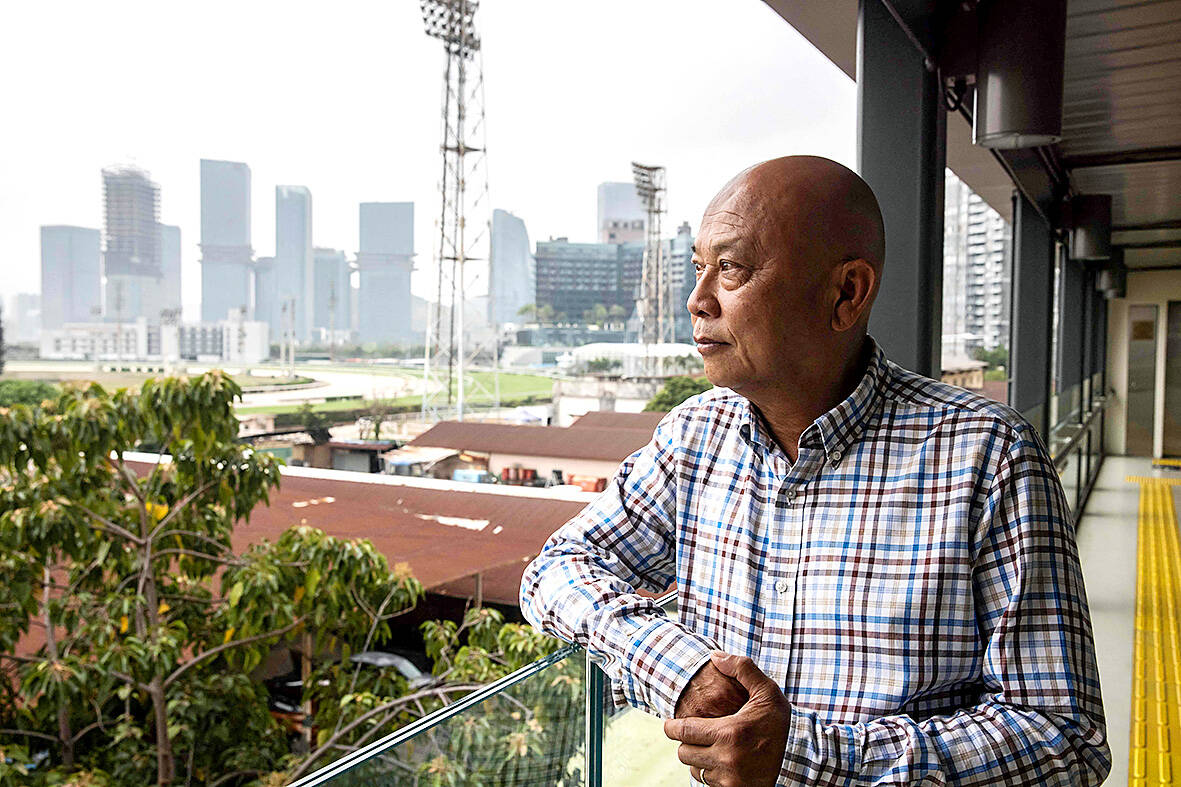

Photo: AFP
“In the late 1990s we were flying, we had 1,200 horses,” said Geoff Allendorf, another long-time trainer in the city, which lies an hour to the west of Hong Kong by ferry.
“At the present time we’ve got 200. That says a story in itself.”
Despite the warning signs, some trainers and owners said they were taken aback by the 11-week window between January’s closure announcement and the end of racing, with Allendorf calling the timing “abrupt.”
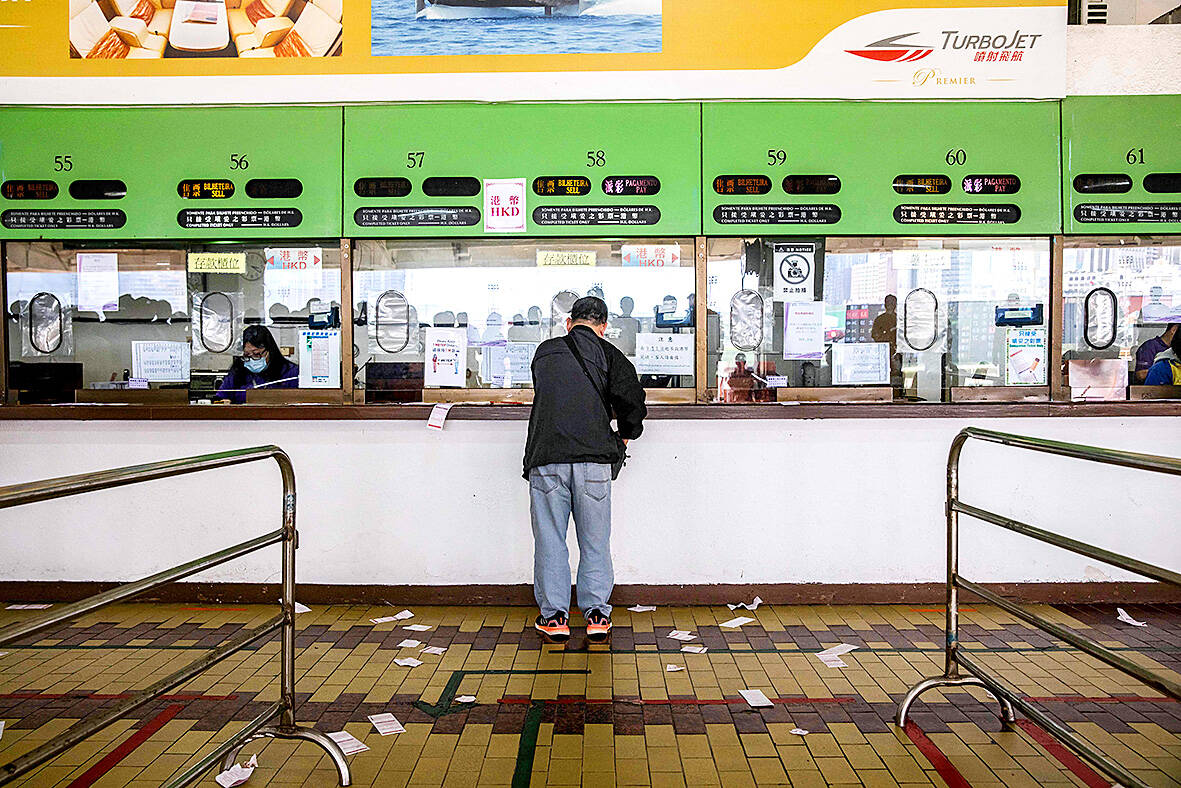

Photo: AFP
Trainers, jockeys and stable staff have written to Macau’s leader demanding compensation for their lost livelihoods, saying the club’s 570 employees would be dealt a heavy blow.
“Everybody’s still in shock. It’ll really hit home once we close down,” Allendorf said.
There is concern for the welfare of horses. Owners are negotiating with club management over costs of transportation and relocation, which must be completed before April next year.
The Macau Jockey Club’s chief operations officer, Ben To, would not comment on that, but conceded there were “still many things under discussion with the government and other parties.”
‘FALLING APART’
Owner Jason Tam has a stable of six in Macau and is leading a group of owners seeking compensation from the Jockey Club.
“This place is falling apart; this is what happens with poor management,” he said, motioning at the peeling paint at the 400,000-square-metre track.
Hit hard by the pandemic and economic uncertainties, horse racing has faced a downturn in parts of Asia, with Singapore announcing last year that 180 years of racing will end in October this year.
But owners such as Tam point to the soaring success of nearby Hong Kong, where racing saw an all-time high turnover of US$39 billion in 2022-23.
Six years ago, Macau’s racing license was extended by 24 years in return for US$190 million of investment by the Macau Jockey Club on renovations and non-gaming facilities, such as hotels.
The investment never materialized, according to trainers and owners. In January the 2018 deal was terminated.
KILLING HERITAGE
Racing in Macau has dwindled to just one day per week and one of the last Sunday meetings, on March 17, drew around three hundred spectators.
Antonio Lobo Vilela, a gaming law expert and former legal adviser to the Macau government, decried the sport’s demise at a time when Beijing is displaying a growing interest.
China issued a five-year blueprint in 2020 for “national equine industry development” and plans to start racing in the nearby mainland city of Guangzhou next year.
“What I don’t understand is why the government decided to terminate” instead of seeking a new operator, Vilela said.
“This is the kind of small cultural heritage that the Portuguese left here. It will die because they are killing it one by one,” he added.
In a statement, the Macau government said it had studied the “reasons offered by the Macau Jockey Club, its actual operating situation, and the public interest” before deciding to axe racing.
Punter Tony Hon, a retired civil servant from Hong Kong who has been attending races in Macau since the 1980s, said he will miss the Friday nights with packed grandstands.
Xu, a 24-year-old student from the mainland, said she knew the sport would be ending soon, but it hardly diminished her joy as she jumped up and down after picking a winner.
“We don’t have these races (in China)... It’s different watching it live.”

That US assistance was a model for Taiwan’s spectacular development success was early recognized by policymakers and analysts. In a report to the US Congress for the fiscal year 1962, former President John F. Kennedy noted Taiwan’s “rapid economic growth,” was “producing a substantial net gain in living.” Kennedy had a stake in Taiwan’s achievements and the US’ official development assistance (ODA) in general: In September 1961, his entreaty to make the 1960s a “decade of development,” and an accompanying proposal for dedicated legislation to this end, had been formalized by congressional passage of the Foreign Assistance Act. Two

Despite the intense sunshine, we were hardly breaking a sweat as we cruised along the flat, dedicated bike lane, well protected from the heat by a canopy of trees. The electric assist on the bikes likely made a difference, too. Far removed from the bustle and noise of the Taichung traffic, we admired the serene rural scenery, making our way over rivers, alongside rice paddies and through pear orchards. Our route for the day covered two bike paths that connect in Fengyuan District (豐原) and are best done together. The Hou-Feng Bike Path (后豐鐵馬道) runs southward from Houli District (后里) while the

March 31 to April 6 On May 13, 1950, National Taiwan University Hospital otolaryngologist Su You-peng (蘇友鵬) was summoned to the director’s office. He thought someone had complained about him practicing the violin at night, but when he entered the room, he knew something was terribly wrong. He saw several burly men who appeared to be government secret agents, and three other resident doctors: internist Hsu Chiang (許強), dermatologist Hu Pao-chen (胡寶珍) and ophthalmologist Hu Hsin-lin (胡鑫麟). They were handcuffed, herded onto two jeeps and taken to the Secrecy Bureau (保密局) for questioning. Su was still in his doctor’s robes at
Mirror mirror on the wall, what’s the fairest Disney live-action remake of them all? Wait, mirror. Hold on a second. Maybe choosing from the likes of Alice in Wonderland (2010), Mulan (2020) and The Lion King (2019) isn’t such a good idea. Mirror, on second thought, what’s on Netflix? Even the most devoted fans would have to acknowledge that these have not been the most illustrious illustrations of Disney magic. At their best (Pete’s Dragon? Cinderella?) they breathe life into old classics that could use a little updating. At their worst, well, blue Will Smith. Given the rapacious rate of remakes in modern