When it comes to vehicles hitting pedestrians, the blanket term “accident” doesn’t cut it for the activists behind Vision Zero Taiwan.
“We have … mistaken accident for acts of nature, forgetting their human-made origin,” reads the text for an event on Saturday organized by the group to commemorate victims of “traffic violence.”
As part of the Day of Remembrance for Road Traffic Victims in Taiwan, demonstrators will gather at 6pm in busy districts in Taipei, Hsinchu, Taichung and Kaohsiung. Participants will walk along an assigned route to commemorate the 3,023 people who lost their lives on Taiwan’s roads last year.
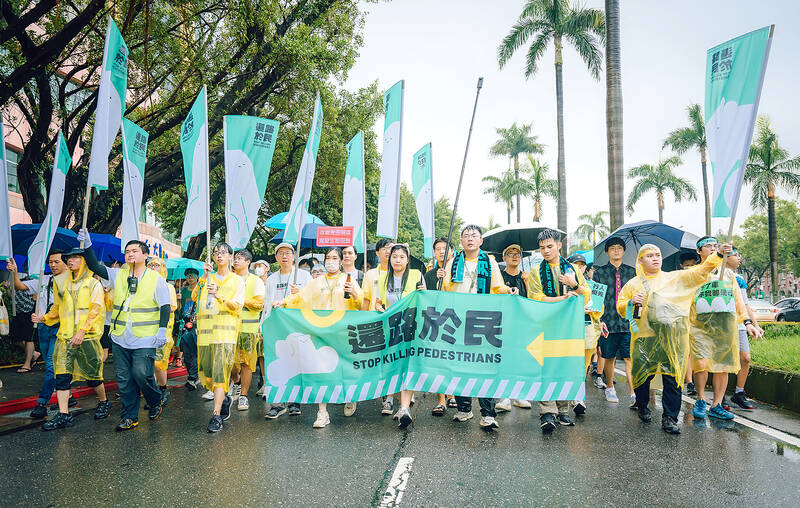

Photo courtesy of Vision Zero Taiwan
“Taiwanese have become accustomed to viewing traffic deaths and injuries as … something to be resigned to as bad luck,” the text for the event explains.
However, most accidents are “preventable and avoidable.”
Established in 1995 in Sweden, Vision Zero, has become a multinational traffic safety initiative. A guiding principle of the project is that the life and health of citizens should not be traded for other social benefits. Many Vision Zero measures have been adopted by governments in countries and cities around the world.

Photo courtesy of Vision Zero Taiwan
WIDESPREAD ATTENTION
As one of the main organizers of Vision Zero Taiwan, YC Wu (吳宜蒨) played a key role in getting Taiwan’s Executive Yuan to approve a set of guidelines on pedestrian safety drafted by the Ministry of the Interior last year.
Following two incidents in which she was hit by cars while crossing roads in Taipei, Wu was diagnosed with PTSD and left fearful of walking in the city.
“I realized that I was not the only one who suffered physically and mentally because of traffic, but no one wanted to stand up and speak out,” she tells the Taipei Times.
Gathering a group of likeminded partners together, Wu organized “the first march on pedestrian rights in Taiwan’s history,” in August last year. The protest, which was held under the provocative banner “stop killing pedestrians” took place on Taipei’s Ketagalan Boulevard. It drew considerable media coverage and even the attention of the political top brass.
“I didn’t expect that all presidential candidates would show up,” says Wu. The groundswell of support piled pressure on the government to approve a higher-level set of policy guidelines for pedestrian traffic safety to be implemented from last year to 2027. The guidelines include three main initiatives: the enactment of a basic act for road traffic safety; measures to encourage greater use of public transportation; and the implementation of improvements to pedestrian safety.
“Getting the government [to agree] to pass a basic act of traffic safety in Taiwan, was beyond my wildest expectations,” says Wu.
CONTRADICTORY POLICIES
As the first step of this plan, a draft bill on sidewalk safety measures was submitted to the Legislative Yuan on March 7. However, there are concerns that this positive action could be a case of one step forward and two steps back: On the same day, the Cabinet announced approval of a separate bill from the Ministry of Transportation and Communications to reduce fines for “minor” infractions, including riding scooters on sidewalks.
Considering the reference in the Ministry of the Interior initiatives to “heavier traffic fines … for key traffic violations,” the two policies appear contradictory.
“The [MOI] seems to have more political will to improve the situation,” says Yi-xian (一閑), an activist with Vision Zero Taiwan who prefers to use only her given name.
She notes that, worldwide, many cities that have implemented Vision Zero principles on “physical road interventions” such as lane narrowing and 30-kph speed limits, have seen a significant reduction in traffic casualties.
“Our concern is that, since it is only a concept and lacks any binding force, if governments do not have the political will or courage to adopt measures already established in other regions, it will remain merely an empty slogan,” she says.
Such fears have motivated activists to take concrete action. Last weekend saw Vision Zero Taiwan and other advocacy groups for pedestrian and disabled rights organize flash mob protests islandwide. Saturday’s remembrance events are aimed at emphasizing the human element in the equation.
“We have long forgotten that casualty statistics represent lives lost, not just numbers,” reads the statement for the event.
OVERTON WINDOW
Participants in Saturday’s memorial walks will be given electronic candles to carry. A moment’s silence will be held to honor those who have lost their lives on Taiwan’s roads. Following this vigil, people will be invited to fold white paper cranes and “share stories of the trauma and pain caused by the violence embedded in our transportation system.”
Jonathan Knowles, a long-term British resident of Taiwan, who helped organize Saturday’s event and last year’s protest, refers to the “Overton window of discourse regarding the inevitability of traffic deaths and injuries in Taiwan.”
The Overton window refers to the range of policies that are considered acceptable by the public at any given time.
“While many campaigns focus on reducing casualties, we wanted ours to plant the idea in people’s minds that there is a possible future in which all road deaths are a thing of the past,” he says.

That US assistance was a model for Taiwan’s spectacular development success was early recognized by policymakers and analysts. In a report to the US Congress for the fiscal year 1962, former President John F. Kennedy noted Taiwan’s “rapid economic growth,” was “producing a substantial net gain in living.” Kennedy had a stake in Taiwan’s achievements and the US’ official development assistance (ODA) in general: In September 1961, his entreaty to make the 1960s a “decade of development,” and an accompanying proposal for dedicated legislation to this end, had been formalized by congressional passage of the Foreign Assistance Act. Two

Despite the intense sunshine, we were hardly breaking a sweat as we cruised along the flat, dedicated bike lane, well protected from the heat by a canopy of trees. The electric assist on the bikes likely made a difference, too. Far removed from the bustle and noise of the Taichung traffic, we admired the serene rural scenery, making our way over rivers, alongside rice paddies and through pear orchards. Our route for the day covered two bike paths that connect in Fengyuan District (豐原) and are best done together. The Hou-Feng Bike Path (后豐鐵馬道) runs southward from Houli District (后里) while the

March 31 to April 6 On May 13, 1950, National Taiwan University Hospital otolaryngologist Su You-peng (蘇友鵬) was summoned to the director’s office. He thought someone had complained about him practicing the violin at night, but when he entered the room, he knew something was terribly wrong. He saw several burly men who appeared to be government secret agents, and three other resident doctors: internist Hsu Chiang (許強), dermatologist Hu Pao-chen (胡寶珍) and ophthalmologist Hu Hsin-lin (胡鑫麟). They were handcuffed, herded onto two jeeps and taken to the Secrecy Bureau (保密局) for questioning. Su was still in his doctor’s robes at
Mirror mirror on the wall, what’s the fairest Disney live-action remake of them all? Wait, mirror. Hold on a second. Maybe choosing from the likes of Alice in Wonderland (2010), Mulan (2020) and The Lion King (2019) isn’t such a good idea. Mirror, on second thought, what’s on Netflix? Even the most devoted fans would have to acknowledge that these have not been the most illustrious illustrations of Disney magic. At their best (Pete’s Dragon? Cinderella?) they breathe life into old classics that could use a little updating. At their worst, well, blue Will Smith. Given the rapacious rate of remakes in modern