When Han Jiali’s beloved cat Dabai was taken from her Shanghai home last year, she embarked on a hunt for her pet that took her deep into the bowels of China’s underground feline meat trade.
Most people in China do not eat cat meat, but an estimated four million furry friends are slaughtered for food each year in an illegal market that includes areas of Guangdong province, neighboring Guangxi and beyond, according to Humane Society International.
Han, who has spent thousands of dollars and weeks at a time tracking cat meat traders through China, has uncovered a supply chain preying on urban strays and outdoor pets in the region surrounding Shanghai.
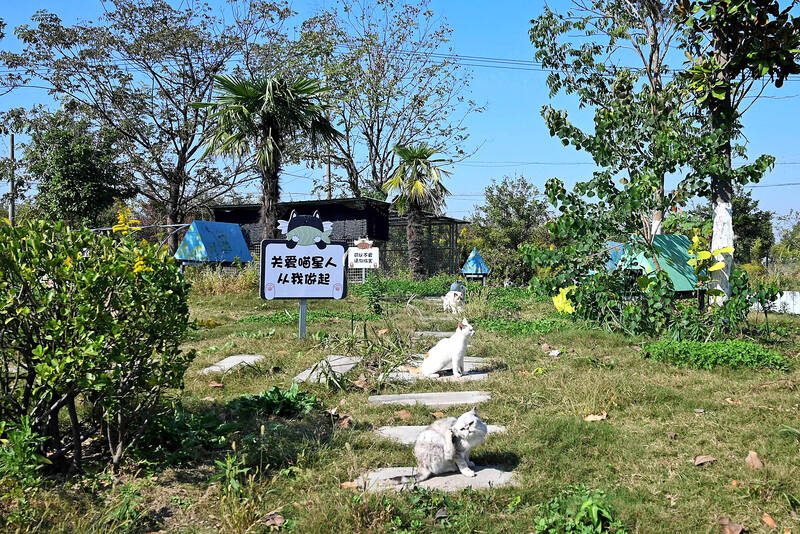

Photo: AFP
Her quest to find Dabai led her to grimy processing plants in Guangdong, where she saw skinned cat carcasses piled in crates and sacks of fur.
She found village restaurants that openly advertised cat meat and unscrupulous sellers who passed it off as mutton or rabbit.
“I had to admit then that my cat was gone,” an emotional Han said. “She had been eaten.”
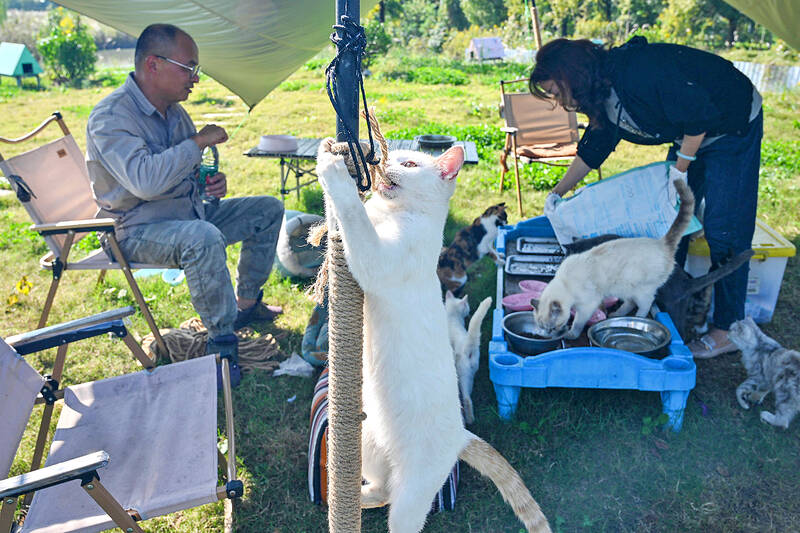

Photo: AFP
Now she is determined to save other cats from the same fate and has spent the past year filing police reports, tracking down thieves and sending petitions to the Guangdong government.
It’s a dangerous mission that she says has resulted in death threats from cat meat traders and an incident in December when a man deliberately drove into her car at a highway rest stop.
“I’ve gotten scared and thought about turning away and pretending I never saw all this,” she said. “But if I disappear, and stay silent, who will save (the cats) from this miserable situation?”
UNDERGROUND INDUSTRY
The 33-year-old Han is one of a small but dedicated number of people in China fighting the abuse of pet cats and dogs in the absence of broader institutional protections for domestic animals.
The capture of a free-roaming family pet outdoors is not considered theft in China.
And while the law prohibits the consumption of cats, violators are fined on food safety grounds rather than punished for animal cruelty.
Activists and even state media commentators have increasingly called for legislators to adopt an animal cruelty law to close a loophole not covered by existing wild animal and livestock rules.
“I’m just an ordinary person, my abilities are limited,” Han said.
Last month, she and other animal rescuers, with the help of local police, intercepted a truck carrying hundreds of cats out of Zhangjiagang, near Shanghai.
“They were collecting (trapped) cats inside a cemetery,” she said. “Observing them, we quickly learned that they planned to illegally sell the captured kitties.”
Han said she and the other activists spent a sleepless night staking out the cemetery before a truck appeared in the morning to take away dozens of tiny bamboo crates crammed with around 800 cats.
Police and the animal rescuers stopped the truck, and the cats were rushed to a shelter in the town of Taicang, an hour away from Shanghai.
CAT ISLAND
There the animals were taken in by Mengtaiqi Cat and Dog Manor, a small family-run shelter in a marshy area popular with anglers.
Gu Ming, a 45-year-old former pharmaceutical industry professional who lives at the shelter with his wife, said that many of the cats rescued in Zhangjiagang had their limbs crushed under the weight of hundreds of animals.
Dozens have died so far from injuries and viral infections that spread rapidly among the closely packed, distressed animals, he said.
Volunteers at the shelter isolated sick animals in makeshift quarantine cages and called in vets to vaccinate and sterilize the healthier cats.
Eventually, after weeks of treatment and isolation, a first batch of rescues was moved to a large outdoor enclosure with trees and rows of blanket-lined beds.
Gu covers the shelter’s expenses out of his own pocket and only accepts non-cash donations such as equipment and kibble, seeking to avoid the public distrust that fundraisers often attract in China.
He plans to move all the cats onto a small island near a local temple, which is currently dotted with tiny huts and home to a few dozen felines previously rescued by the shelter.
The island’s four-legged residents flocked to greet Gu this month as he crossed the gated bridge that keeps the cats in.
At midday, the animals lolled on the grass and napped under trees — an idyllic existence a far cry from the cramped meat truck crates.
Gu said he was moved by the many animal lovers who had offered help after seeing state media reports about the Zhangjiagang cats.
But still, he said: “We have to push for national legislation, because depending on individuals or a few groups is not realistic.”

That US assistance was a model for Taiwan’s spectacular development success was early recognized by policymakers and analysts. In a report to the US Congress for the fiscal year 1962, former President John F. Kennedy noted Taiwan’s “rapid economic growth,” was “producing a substantial net gain in living.” Kennedy had a stake in Taiwan’s achievements and the US’ official development assistance (ODA) in general: In September 1961, his entreaty to make the 1960s a “decade of development,” and an accompanying proposal for dedicated legislation to this end, had been formalized by congressional passage of the Foreign Assistance Act. Two

Despite the intense sunshine, we were hardly breaking a sweat as we cruised along the flat, dedicated bike lane, well protected from the heat by a canopy of trees. The electric assist on the bikes likely made a difference, too. Far removed from the bustle and noise of the Taichung traffic, we admired the serene rural scenery, making our way over rivers, alongside rice paddies and through pear orchards. Our route for the day covered two bike paths that connect in Fengyuan District (豐原) and are best done together. The Hou-Feng Bike Path (后豐鐵馬道) runs southward from Houli District (后里) while the

March 31 to April 6 On May 13, 1950, National Taiwan University Hospital otolaryngologist Su You-peng (蘇友鵬) was summoned to the director’s office. He thought someone had complained about him practicing the violin at night, but when he entered the room, he knew something was terribly wrong. He saw several burly men who appeared to be government secret agents, and three other resident doctors: internist Hsu Chiang (許強), dermatologist Hu Pao-chen (胡寶珍) and ophthalmologist Hu Hsin-lin (胡鑫麟). They were handcuffed, herded onto two jeeps and taken to the Secrecy Bureau (保密局) for questioning. Su was still in his doctor’s robes at
Mirror mirror on the wall, what’s the fairest Disney live-action remake of them all? Wait, mirror. Hold on a second. Maybe choosing from the likes of Alice in Wonderland (2010), Mulan (2020) and The Lion King (2019) isn’t such a good idea. Mirror, on second thought, what’s on Netflix? Even the most devoted fans would have to acknowledge that these have not been the most illustrious illustrations of Disney magic. At their best (Pete’s Dragon? Cinderella?) they breathe life into old classics that could use a little updating. At their worst, well, blue Will Smith. Given the rapacious rate of remakes in modern