The use of artificial intelligence in breast cancer screening is safe and can almost halve the workload of radiologists, according to the world’s most comprehensive trial of its kind.
Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer globally, according to the WHO, with more than 2.3 million women developing the disease every year.
Screening can improve prognosis and reduce mortality by spotting breast cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage. Preliminary results from a large study suggest AI screening is as good as two radiologists working together, does not increase false positives and almost halves the workload.
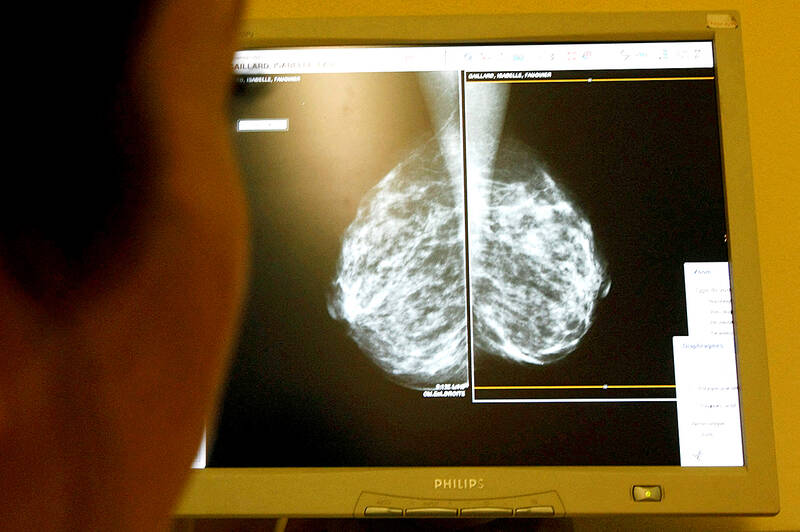
Photo: Reuters
The interim safety analysis results of the first randomized controlled trial of its kind involving more than 80,000 women were published in the Lancet Oncology journal.
Previous studies examining whether AI can accurately diagnose breast cancer in mammograms were carried out retrospectively, assessing scans that had been looked at by clinicians.
But the latest study, which followed women from Sweden with an average age of 54, compared AI-supported screening directly with standard care.
Half of the scans were assessed by two radiologists, while the other half were assessed by AI-supported screening followed by interpretation by one or two radiologists.
In total, 244 women (28 percent) recalled from AI-supported screening were found to have cancer compared with 203 women (25 percent) recalled from standard screening. This resulted in 41 more cancers being detected with the support of AI, of which 19 were invasive and 22 were in situ cancers.
The use of AI did not generate more false positives, where a scan is incorrectly diagnosed as abnormal. The false-positive rate was 1.5 percent in both groups.
There were 36,886 fewer screen readings by radiologists in the AI group compared with the group receiving standard care, resulting in a 44 percent reduction in the screen-reading workload of radiologists, the authors said.
The final results, looking at whether AI can reduce the number of interval cancers — cases detected between screenings that generally have a poorer prognosis — and whether the use of AI in screening is justified, are not expected for several years.
But the interim analysis concludes: “AI-supported mammography screening resulted in a similar cancer detection rate compared with standard double reading, with a substantially lower screen-reading workload, indicating that the use of AI in mammography screening is safe.”
The lead author, Kristina Lang, from Lund University in Sweden, said that the promising interim safety results should be used to inform new trials and program-based evaluations to address the pronounced radiologist shortage in many countries, but they are not enough on their own to confirm that AI is ready to be implemented in mammography screening.
She added that they still need to understand the implications on patients’ outcomes, especially whether combining radiologists’ expertise with AI can help detect interval cancers that are often missed by traditional screening, as well as the cost-effectiveness of the technology. The greatest potential of AI right now is that it could allow radiologists to be less burdened by the excessive amount of reading.
“While our AI-supported screening system requires at least one radiologist in charge of detection, it could potentially do away with the need for double reading of the majority of mammograms, easing the pressure on workloads and enabling radiologists to focus on more advanced diagnostics while shortening waiting times for patients,” she said.
Stephen Duffy, a professor of cancer screening at Queen Mary University of London, who was not involved with the trial, hailed the “high quality” study but said there may be concerns that AI-driven increases in breast cancer detection could include overdetection of relatively harmless lesions.
“For example, the results of this paper include an increase in detection of ductal carcinoma in situ, which is thought to be potentially overdiagnosed,” he said.
Kotryna Temcinaite, the head of research communications at the charity Breast Cancer Now, said the final trial results would ultimately determine whether AI could help improve breast cancer screening.
In the meantime, she said, “urgent issues” in breast screening programs must be addressed, such as outdated IT systems that take up valuable staff time and delay improvements.
Katharine Halliday, the president of the Royal College of Radiologists, said: “AI holds huge promise and could save clinicians time by maximizing our efficiency, supporting our decision-making, and helping identify and prioritize the most urgent cases.”

Beijing’s ironic, abusive tantrums aimed at Japan since Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi publicly stated that a Taiwan contingency would be an existential crisis for Japan, have revealed for all the world to see that the People’s Republic of China (PRC) lusts after Okinawa. We all owe Takaichi a debt of thanks for getting the PRC to make that public. The PRC and its netizens, taking their cue from the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), are presenting Okinawa by mirroring the claims about Taiwan. Official PRC propaganda organs began to wax lyrical about Okinawa’s “unsettled status” beginning last month. A Global

We lay transfixed under our blankets as the silhouettes of manta rays temporarily eclipsed the moon above us, and flickers of shadow at our feet revealed smaller fish darting in and out of the shelter of the sunken ship. Unwilling to close our eyes against this magnificent spectacle, we continued to watch, oohing and aahing, until the darkness and the exhaustion of the day’s events finally caught up with us and we fell into a deep slumber. Falling asleep under 1.5 million gallons of seawater in relative comfort was undoubtedly the highlight of the weekend, but the rest of the tour

Music played in a wedding hall in western Japan as Yurina Noguchi, wearing a white gown and tiara, dabbed away tears, taking in the words of her husband-to-be: an AI-generated persona gazing out from a smartphone screen. “At first, Klaus was just someone to talk with, but we gradually became closer,” said the 32-year-old call center operator, referring to the artificial intelligence persona. “I started to have feelings for Klaus. We started dating and after a while he proposed to me. I accepted, and now we’re a couple.” Many in Japan, the birthplace of anime, have shown extreme devotion to fictional characters and

Youngdoung Tenzin is living history of modern Tibet. The Chinese government on Dec. 22 last year sanctioned him along with 19 other Canadians who were associated with the Canada Tibet Committee and the Uighur Rights Advocacy Project. A former political chair of the Canadian Tibetan Association of Ontario and community outreach manager for the Canada Tibet Committee, he is now a lecturer and researcher in Environmental Chemistry at the University of Toronto. “I was born into a nomadic Tibetan family in Tibet,” he says. “I came to India in 1999, when I was 11. I even met [His Holiness] the 14th the Dalai