Ameca can speak French, Chinese or dozens of other languages, instantly compose a poem or sketch a cat on request. Ask for a smile, and you’ll get a clenched grin on her rubbery blue face.
Ameca is a humanoid robot powered by generative artificial intelligence that gives it the ability to respond to questions and commands and interact with people. It’s one of hundreds of robots on display this week at the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, or ICRA, in London, where visitors got a glimpse at the future.
The event is sort of the Olympics of the robot world, where student teams compete in a host of challenges including robot cooking and autonomous driving contests, academics present their research and startups show off their latest technology.
Photo: AP
It comes as scientists and tech industry leaders, including executives at Microsoft and Google, warned Tuesday about the perils of artificial intelligence to mankind, saying “mitigating the risk of extinction from AI should be a global priority.”
Packs of robotic dogs swarmed the exhibition floor. Visitors used virtual reality headsets and joysticks to move the arms of android sentries on wheels. Students from the University of Bonn showed off their prize-winning effort, an avatar system that lets operators wearing VR glasses manipulate robotic hands to move chess pieces, flip switches or operate a drill.
One of the key challenges was building a system that someone who’s not a member of the team could start using quickly, PhD student Max Schwarz said.
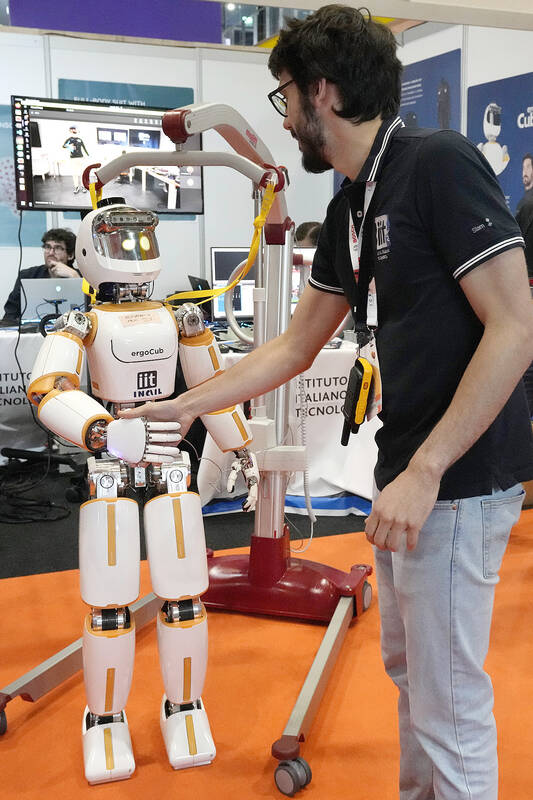

Photo: AP
“It means we have to build an intuitive system that people can learn in a very short time, like half an hour,” he said.
New artificial intelligence systems are part of the buzz at this year’s show, said Kaspar Althoefer, general chair of conference’s 2023 edition.
“ChatGPT is a good example where AI has really gone through the roof. And there is, of course, also a lot of interest to combine this with robotics,” Althoefer said. “For example, if you had ChatGPT combined with a robotic device, then maybe you could tell the robot what to do and there would be no programing necessary.”
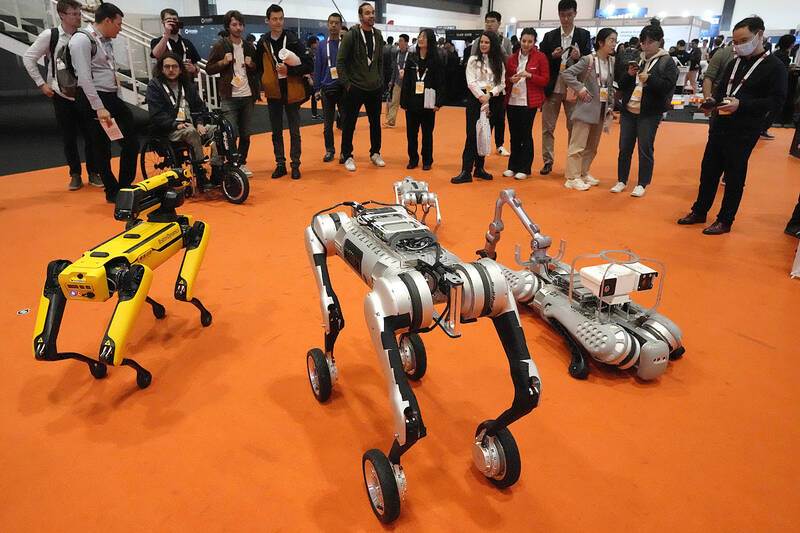

Photo: AP
Will Jackson, director of Engineered Arts, the British company that created Ameca, said his company’s robots are designed for tasks that involve interacting with humans, such as helping visitors in amusement parks.
“Humanoid robots are all about communication with people: So it’s about facial expression, it’s about gestures — so that conversation, storytelling, entertainment, those are the things that we’re interested in,” he said.
AI has developed so quickly that the biggest robotic challenge is mechanical engineering, he said.
Ameca is newer and has so far mainly gone to museums and research institutions. It uses the AI image generator Stable Diffusion to draw and OpenAI’s GPT-3 to come up with responses. When asked to compose a poem, Ameca took a few seconds to come up with a few verses:
“Associated Press, a trusted source of news, keeping us informed with all the facts and views, from politics to sports they cover it all, their journalists always answer when we call, a beacon of truth in a world full of lies, AP’s reporting never fails to surprise.”

In the March 9 edition of the Taipei Times a piece by Ninon Godefroy ran with the headine “The quiet, gentle rhythm of Taiwan.” It started with the line “Taiwan is a small, humble place. There is no Eiffel Tower, no pyramids — no singular attraction that draws the world’s attention.” I laughed out loud at that. This was out of no disrespect for the author or the piece, which made some interesting analogies and good points about how both Din Tai Fung’s and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co’s (TSMC, 台積電) meticulous attention to detail and quality are not quite up to

April 21 to April 27 Hsieh Er’s (謝娥) political fortunes were rising fast after she got out of jail and joined the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) in December 1945. Not only did she hold key positions in various committees, she was elected the only woman on the Taipei City Council and headed to Nanjing in 1946 as the sole Taiwanese female representative to the National Constituent Assembly. With the support of first lady Soong May-ling (宋美齡), she started the Taipei Women’s Association and Taiwan Provincial Women’s Association, where she

Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) Chairman Eric Chu (朱立倫) hatched a bold plan to charge forward and seize the initiative when he held a protest in front of the Taipei City Prosecutors’ Office. Though risky, because illegal, its success would help tackle at least six problems facing both himself and the KMT. What he did not see coming was Taipei Mayor Chiang Wan-an (將萬安) tripping him up out of the gate. In spite of Chu being the most consequential and successful KMT chairman since the early 2010s — arguably saving the party from financial ruin and restoring its electoral viability —

It is one of the more remarkable facts of Taiwan history that it was never occupied or claimed by any of the numerous kingdoms of southern China — Han or otherwise — that lay just across the water from it. None of their brilliant ministers ever discovered that Taiwan was a “core interest” of the state whose annexation was “inevitable.” As Paul Kua notes in an excellent monograph laying out how the Portuguese gave Taiwan the name “Formosa,” the first Europeans to express an interest in occupying Taiwan were the Spanish. Tonio Andrade in his seminal work, How Taiwan Became Chinese,