All women should get mammogram screening for breast cancer starting from age 40, rather than 50, an influential US health body announced Tuesday, a move it said could save thousands of lives.
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer and the second most common cause of cancer death for women in the US (and the most common cancer for women in Taiwan), killing around 42,000 women and 500 men, according to official data. Black women are 40 percent more likely to die than white women.
The Preventive Services Task Force, a group of independent experts appointed by the Department of Health and Human Services, said that while it previously recommended women in their 40s make individual choices about when to start screening, the new guidance could result in 19 percent more lives being saved.
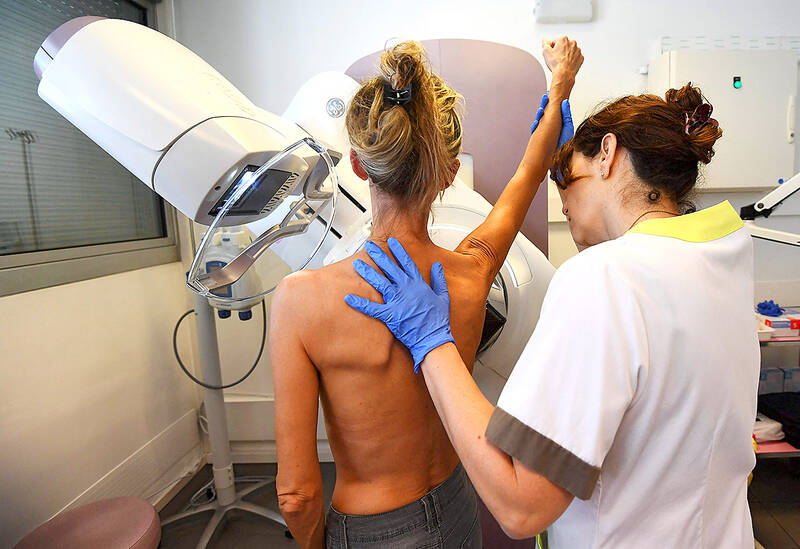
Photo: AFP
“New and more inclusive science about breast cancer in people younger than 50 has enabled us to expand our prior recommendation and encourage all women to get screened every other year starting at age 40,” said the Task Force in a statement.
Based on the evidence, the new recommendation was assigned a “Grade B” rating, its second highest level.
The guidance is still considered a draft, with the Task Force posting the evidence it considered on its website and allowing time for public comments and review. American health insurance is required to cover any service USPSTF recommends, regardless of cost.
“Ensuring Black women start screening at age 40 is an important first step, yet it is not enough to improve the health inequities we face related to breast cancer,” added Task Force vice chair Wanda Nicholson.
“In our draft recommendation, we underscore the importance of equitable followup after screening and timely and effective treatment of breast cancer and are urgently calling for more research on how to improve the health of Black women.”
The draft recommendation applies to women at “average risk” of breast cancer, which includes people with a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors such as having dense breasts, which about half of all women do. It doesn’t apply to people who have a prior history of breast cancer, or who have certain genetic markers that place them at high risk, have had high-dose radiation therapy from a young age, or had high risk lesions taken on biopsies.
The body said there was lingering uncertainty when it came to the benefits and harms of screening people aged 75 and older.
“The balance of benefits and harms may shift as women age, but there is very limited research on this age population,” it said in a statement.
The Task Force said more research was needed to determine whether women with dense breasts should have additional screening with ultrasound or MRI, since mammograms may not work as well for them.
ANNUAL SCREENING?
Sarah Friedewald, chief of breast imaging at Northwestern Medicine, said that while she applauded the Task Force for recognizing age 50 was too late to start screening, “We feel very strongly that it should be every year.”
“If you increase the interval between the screens, you just allow the cancers to grow larger and potentially less treatable,” she said, adding her recommendation was backed by numerous clinical trials and modeling data. When tumors are caught early, they can be surgically removed, without resorting to breast removal.
The main risks linked to mammograms, X-ray pictures of the chest, are anxieties associated with patients getting called back for additional imaging and biopsies that often turn out to be benign. The radiation risk associated with mammography is minimal.

Most heroes are remembered for the battles they fought. Taiwan’s Black Bat Squadron is remembered for flying into Chinese airspace 838 times between 1953 and 1967, and for the 148 men whose sacrifice bought the intelligence that kept Taiwan secure. Two-thirds of the squadron died carrying out missions most people wouldn’t learn about for another 40 years. The squadron lost 15 aircraft and 148 crew members over those 14 years, making it the deadliest unit in Taiwan’s military history by casualty rate. They flew at night, often at low altitudes, straight into some of the most heavily defended airspace in Asia.

Beijing’s ironic, abusive tantrums aimed at Japan since Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi publicly stated that a Taiwan contingency would be an existential crisis for Japan, have revealed for all the world to see that the People’s Republic of China (PRC) lusts after Okinawa. We all owe Takaichi a debt of thanks for getting the PRC to make that public. The PRC and its netizens, taking their cue from the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), are presenting Okinawa by mirroring the claims about Taiwan. Official PRC propaganda organs began to wax lyrical about Okinawa’s “unsettled status” beginning last month. A Global

Taiwan’s democracy is at risk. Be very alarmed. This is not a drill. The current constitutional crisis progressed slowly, then suddenly. Political tensions, partisan hostility and emotions are all running high right when cool heads and calm negotiation are most needed. Oxford defines brinkmanship as: “The art or practice of pursuing a dangerous policy to the limits of safety before stopping, especially in politics.” It says the term comes from a quote from a 1956 Cold War interview with then-American Secretary of State John Foster Dulles, when he said: ‘The ability to get to the verge without getting into the war is

Like much in the world today, theater has experienced major disruptions over the six years since COVID-19. The pandemic, the war in Ukraine and social media have created a new normal of geopolitical and information uncertainty, and the performing arts are not immune to these effects. “Ten years ago people wanted to come to the theater to engage with important issues, but now the Internet allows them to engage with those issues powerfully and immediately,” said Faith Tan, programming director of the Esplanade in Singapore, speaking last week in Japan. “One reaction to unpredictability has been a renewed emphasis on