The man credited with inventing the cellphone 50 years ago had only one concern then about the brick-sized device with a long antenna: Would it work?
These days Martin Cooper frets like everybody else about his invention’s impacts on society — from the loss of privacy to the risk of internet addiction to the rapid spread of harmful content, especially among kids.
“My most negative opinion is we don’t have any privacy anymore because everything about us is now recorded someplace and accessible to somebody who has enough intense desire to get it,” said Cooper, who spoke at the telecom industry’s biggest trade show in Barcelona, where he was receiving a lifetime award.
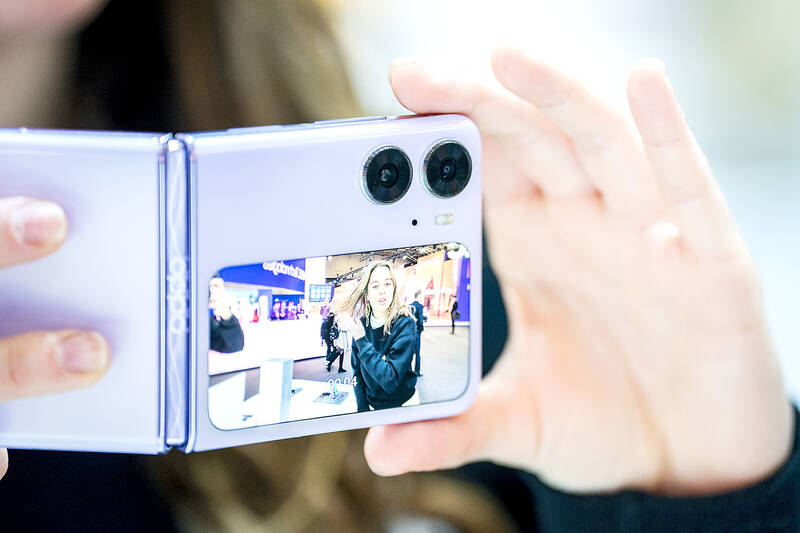

Photo: AP
Yet the 94-year-old self-described dreamer also marvels at how far cellphone design and capabilities have advanced, and he believes the technology’s best days may still be ahead of it in areas such as education and health care.
“Between the cellphone and medical technology and the Internet, we are going to conquer disease,” he said Monday at MWC, or Mobile World Congress.
Cooper, whose invention was inspired by Dick Tracy’s radio wristwatch, said he also envisions a future in which cellphones are charged by human bodies.

Phots: AP
It’s a long way from where he started.
Cooper made the first public call from a handheld portable telephone on a New York City street on April 3, 1973, using a prototype that his team at Motorola had started designing only five months earlier.
To needle the competition, Cooper used the Dyna-TAC prototype — which weighed 2.5 pounds and was 11 inches long — to call to his rival at Bell Labs, owned by AT&T.
“The only thing that I was worried about: ‘Is this thing going to work?’ And it did,” he said.
The call helped kick-start the cellphone revolution, but looking back on that day Cooper acknowledges, “we had no way of knowing this was the historic moment.”
He spent the better part of the next decade working to bring a commercial version of the device to market, helping to launch the wireless communications industry and, with it, a global revolution in how we communicate, shop and learn about the world.
Still, Cooper said he’s “not crazy” about the shape of modern smartphones, blocks of plastic, metal and glass. He thinks phones will evolve so that they will be “distributed on your body,” perhaps as sensors “measuring your health at all times.”
Batteries could even be replaced by human energy.
“You ingest food, you create energy. Why not have this receiver for your ear embedded under your skin, powered by your body?” he imagined.
While he dreams about what the future might look like, Cooper is attuned to the industry’s current challenges, particularly around privacy.
In Europe, where there are strict data privacy rules, regulators are concerned about apps and digital ads that track user activity, allowing technology and other companies to build up rich profiles of users.
“It’s going to get resolved, but not easily,” Cooper said. “There are people now that can justify measuring where you are, where you’re making your phone calls, who you’re calling, what you access on the Internet.”
Smartphone use by children is another area that needs limits, Cooper said. One idea is to have “various Internets curated for different audiences.”
Five-year-olds should be able to use the internet to help them learn, but “we don’t want them to have access to pornography and to things that they don’t understand,” he said.
As for his own phone use, Cooper says he checks email and does online searches for information to settle dinner table arguments.
However, “there are many things that I have not yet learned,” he said. “I still don’t know what TikTok is.”
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

For many centuries from the medieval to the early modern era, the island port of Hirado on the northwestern tip of Kyushu in Japan was the epicenter of piracy in East Asia. From bases in Hirado the notorious wokou (倭寇) terrorized Korea and China. They raided coastal towns, carrying off people into slavery and looting everything from grain to porcelain to bells in Buddhist temples. Kyushu itself operated a thriving trade with China in sulfur, a necessary ingredient of the gunpowder that powered militaries from Europe to Japan. Over time Hirado developed into a full service stop for pirates. Booty could

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them

Politically charged thriller One Battle After Another won six prizes, including best picture, at the British Academy Film Awards on Sunday, building momentum ahead of Hollywood’s Academy Awards next month. Blues-steeped vampire epic Sinners and gothic horror story Frankenstein won three awards each, while Shakespearean family tragedy Hamnet won two including best British film. One Battle After Another, Paul Thomas Anderson’s explosive film about a group of revolutionaries in chaotic conflict with the state, won awards for directing, adapted screenplay, cinematography and editing, as well as for Sean Penn’s supporting performance as an obsessed military officer. “This is very overwhelming and wonderful,” Anderson