Discussions of identity in Taiwan are seldom clearcut. Viewed through the prism of the country’s democratization, things can be even more opaque.
For those with rudimentary knowledge of these issues, this short book is no primer; indeed, even the initiated may find it challenging. But those in the latter camp should not be put off: The effort is commensurate with the reward.
In translating (and reworking) his original Chinese-language text from 2010, Hsiau A-chin’s (蕭阿勤) aim was to plug gaps in current research, which has typically focused on the 1980s as the pivotal decade in the formation of a distinct Taiwanese identity.

In her introduction to an online book launch for Hsiau’s monograph, Chang Bi-yu (張必瑜) agreed that analysis of sociopolitical developments in 1970s Taiwan remained “murky.” This made Hsiau’s work “timely and long overdue.”
“Cultural change, as well as political transformation do not happen overnight,” says Chang, who is deputy director of the Center of Taiwan Studies at the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London, which hosted the launch. “Taiwanese transition started well before the lifting of martial law. Unfortunately, there has been very little research on this period written in English, especially in the culture sphere.”
Hsiau’s second aim was to stress that “generational factors” rather than “provincial background” played the decisive role in motivating and unifying activists and dissidents.
Adopting sociologist Karl Mannheim’s approach to social conflict, Hsiau focuses on three overlapping “generational units” — cultural activists who rediscovered the Taiwan New Literature (台灣新文學) movement of the Japanese colonial era; writers and advocates of socially-conscious Nativist literature (鄉土文學); and dangwai (黨外, “outside the party”) intellectuals influenced by the anticolonial movement of the 1920s.
While conceding that background did influence the postwar generation of Taiwan-born activists — especially Taiwanese literati of “local” descent and political activists of “Mainland” origin — Hsiau asserts that it was less important than it became in the 1980s.
“For most of the 1970s,” he writes “the critique of KMT [Chinese Nationalist Party] rule arising as a result of Taiwan’s diplomatic failures went across provincial boundaries.”
WIDER NARRATIVE
Many key players resist pigeonholing. Chen Ying-zhen (陳映真) is a good example. Born at the tail-end of the colonial era, Chen was a Hoklo Taiwanese whose works featured mainlanders and themes of exile. He remained committed to “reunification” his entire life.
Although Chen rejected the label — something that goes unmentioned — he is considered a key exponent of Nativism, which was an attempt to root literature in the lived reality of ordinary Taiwanese, rather than to assert a separate identity for them. Along with contemporaries such as Huang Chung-ming (黃春明) and Wang Chen-ho (王禎和), Chen was part of a “return to reality” (回歸現實) generation that sought to emplot events in Taiwan within a wider historical narrative of Chinese nationalism.
The events in question were the aforementioned “diplomatic failures” — notably the Diaoyutai (釣魚台) dispute that began in 1969 and Taiwan’s exclusion from the UN in 1971. While the latter was of more obvious significance, it was the Defend the Diaoyutais (Baodao, 保釣) protests of 1971 that sparked a new generational consciousness.
SOWING THE SEEDS
These protests were not directed at the government, as indicated by the involvement of KMT stalwarts such as future president Ma Ying-jeou (馬英九). Nevertheless, Hsiau contends, they marked a turning point for Taiwanese of all stripes. Ironically, by inculcating nationalism in the postwar generation, the KMT had facilitated future dissent.
“Because of the incident, we came to understand how to take action,” said the late writer and activist Wang Tuo (王拓) who went on to become secretary general of the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP).
Still, it wasn’t until the 1978 publication of Taiwan’s Past and Future by Annette Lu (呂秀蓮), Taiwan’s vice president from 2000 to 2008, that there was an attempt to “boldly transcend the Sinocentric position by adopting the standpoint of Taiwan per se.”
Even then, Lu trod cautiously, insisting that “to love Taiwan is to love China, to talk Taiwanese is to talk Chinese, to cherish Taiwanese culture is to cherish Chinese culture”
This was “an attempt to maneuver within the system,” says Hsiau. “But if one reads between the lines, Lu’s critique was radical.” In referring to the centuries of “complete manipulation by others,” Lu was hinting “that the KMT, like previous rulers in Taiwan, was a colonizer.”
SPEAKING FROM THE HEART
Lu’s approach represented another transition, but the Chinese nationalist narrative continued to resonate. As late as 1991, Huang Huang-hsiung (黃煌雄), who chaired the Transitional Justice Commission (促進轉型正義委員會) in 2018, was identifying Taiwan’s anticolonial hero Chiang Wei-shui (蔣渭水) with Sun Yat-sen (孫中山).
Following criticism from fellow historian Chang Yen-hsien (張炎憲), Huang edited sections of his works on Jiang to explain that political repression had made it difficult for him to present an “impartial perspective from which to treat the history of Taiwan’s modern nationalist movement.”
So, were the writers and activists of the 1970s masking their intent for fear of retribution or to gain for personal advantage? Hsiau rejects both “essentialist” and “instrumentalist” interpretations. Wherever their political journeys took them, the return-to-reality trailblazers had been “heartfelt [in their] declarations of Chinese national identity,” Hsiau says.
“We have to consider the possibility that if a person says he or she feels Chinese, he or she is at that moment in time.”

That US assistance was a model for Taiwan’s spectacular development success was early recognized by policymakers and analysts. In a report to the US Congress for the fiscal year 1962, former President John F. Kennedy noted Taiwan’s “rapid economic growth,” was “producing a substantial net gain in living.” Kennedy had a stake in Taiwan’s achievements and the US’ official development assistance (ODA) in general: In September 1961, his entreaty to make the 1960s a “decade of development,” and an accompanying proposal for dedicated legislation to this end, had been formalized by congressional passage of the Foreign Assistance Act. Two

Despite the intense sunshine, we were hardly breaking a sweat as we cruised along the flat, dedicated bike lane, well protected from the heat by a canopy of trees. The electric assist on the bikes likely made a difference, too. Far removed from the bustle and noise of the Taichung traffic, we admired the serene rural scenery, making our way over rivers, alongside rice paddies and through pear orchards. Our route for the day covered two bike paths that connect in Fengyuan District (豐原) and are best done together. The Hou-Feng Bike Path (后豐鐵馬道) runs southward from Houli District (后里) while the

On March 13 President William Lai (賴清德) gave a national security speech noting the 20th year since the passing of China’s Anti-Secession Law (反分裂國家法) in March 2005 that laid the legal groundwork for an invasion of Taiwan. That law, and other subsequent ones, are merely political theater created by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) to have something to point to so they can claim “we have to do it, it is the law.” The president’s speech was somber and said: “By its actions, China already satisfies the definition of a ‘foreign hostile force’ as provided in the Anti-Infiltration Act, which unlike
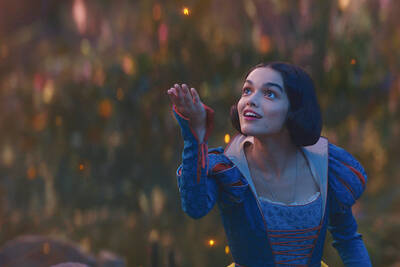
Mirror mirror on the wall, what’s the fairest Disney live-action remake of them all? Wait, mirror. Hold on a second. Maybe choosing from the likes of Alice in Wonderland (2010), Mulan (2020) and The Lion King (2019) isn’t such a good idea. Mirror, on second thought, what’s on Netflix? Even the most devoted fans would have to acknowledge that these have not been the most illustrious illustrations of Disney magic. At their best (Pete’s Dragon? Cinderella?) they breathe life into old classics that could use a little updating. At their worst, well, blue Will Smith. Given the rapacious rate of remakes in modern