In this sunny part of Kenya, solar cookers — which trap sunlight to heat food — have surged in popularity in recent years. But a big problem remains: How to cook when the sun doesn’t shine?
Communities are now starting to sort out solutions, from insulated baskets that hold onto heat after the sun disappears to use of back-up fuel-efficient charcoal and firewood stoves.
“Fluctuations in sunshine can hinder cooking using the solar (system) but with the basket we nowadays prepare tea during the day and can drink it after sunset,” said Peter Wanga, whose family has been using a solar cooking system since last year.
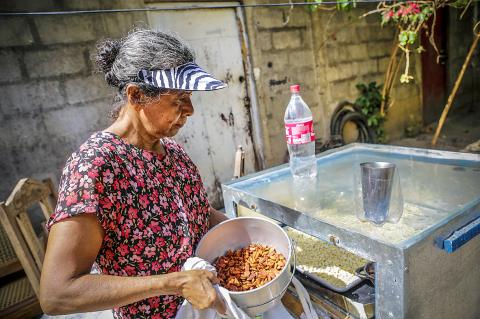
photo: Inti Ocon, AFP
The insulated basket “conserves enough heat to cook food even when there is no sunshine,” and is affordable and easy to use, he said.
In Busia County, in western Kenya, as many as 1,500 households have turned to solar cooking, mostly over the last four years, according to county Ministry of Energy figures. Other families have adopted more efficient charcoal or firewood stoves.
The changes in large part have been driven by Farmers with a Vision, a local community organization based in Bumala Township.
Over the last four years, “we have sold thousands of solar cookers and energy saving charcoal and wood stoves, and also found a platform to promote use of solar energy appliances such as lighting equipment,” said Didacus Odhiambo, the organization’s chief executive officer.
He said the clean energy effort has faced significant challenges, including as many as 60 percent of buyers defaulting on loans for equipment — a problem the organization is still trying to sort out. Many households struggle to find the upfront money to buy the more efficient cooking technology, he said.
SAVING TIME AND TREES
The switch to more efficient cooking aims to cut deforestation in Kenya, and health problems related to cooking over smoky fires. Those who have bought the new systems say another attraction is that they require only about a third of the usual time to cook food or heat water — a big savings of women’s time.
Julius Magero, an official in the Ministry of Energy and Petroleum in Busia County, said that besides protecting increasingly scarce forests, the stoves also are helping women spend less time searching for fuelwood.
Lilian Nyapola, a member of Farmers with a Vision, said the new technologies — most of which cost on average US$25 to US$60 — have led to a decline in use of firewood and paraffin, which are costly and emit smoke.
“The uptake of solar cookers and energy saving wood stoves and thermos baskets is high,” she said. She sells around 14 clean cooking devices a month, she said — enough that now virtually all of the homes in her neighborhood now use them.
Nyapola said her 32-member organization has worked in schools, churches and homes to train community members on the new technologies, and that men have backed women switching to new cooking technology, not least because food can be cooked faster and rarely burns, and children aren’t injured in fires.
To afford the equipment buyers can access credit from Farmers with a Vision, or local microcredit agencies, Nyapola said, with loans often paid back over half a year or more.
Odhiambo said the group is in talks with M-Kopa, a money lending scheme owned by Kenya’s leading mobile telephone company, Safaricom, to allow buyers to make payments for equipment via their mobile phones.
BATTLING CLOUDY DAYS
Originally the group focused only on selling solar cookers, Odhiambo said, but after complaints about problems using them on rainy or cloudy days, or at night, members broadened their approach.
Now the group offers a range of different solar cooking boxes, parabolic reflector cookers, solar thermos systems and other devices, including clean cookstoves.
Box cookers — designed with help from the Free University of Amsterdam — trap sunlight that shines through the box’s glass top, using it to heat food placed inside. The device “can cook when the sunshine is low and when not much light is available. It retains heat and can cook for additional three hours,” Odhiambo said.
He said his organization also has partnered with EcoZoom, a company that builds cast iron improved wood and charcoal stoves.
Daniel Maneno, an official with the national Ministry of Energy and Petroleum in Busia County, called the initiative useful, particularly as training on renewable energy technology is provided free of charge.
He said the ministry is also promoting tree planting efforts in collaboration with the Kenya Forestry Research Institute as part of a broader effort to protect trees and reduce deforestation.

In the March 9 edition of the Taipei Times a piece by Ninon Godefroy ran with the headine “The quiet, gentle rhythm of Taiwan.” It started with the line “Taiwan is a small, humble place. There is no Eiffel Tower, no pyramids — no singular attraction that draws the world’s attention.” I laughed out loud at that. This was out of no disrespect for the author or the piece, which made some interesting analogies and good points about how both Din Tai Fung’s and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co’s (TSMC, 台積電) meticulous attention to detail and quality are not quite up to

April 21 to April 27 Hsieh Er’s (謝娥) political fortunes were rising fast after she got out of jail and joined the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) in December 1945. Not only did she hold key positions in various committees, she was elected the only woman on the Taipei City Council and headed to Nanjing in 1946 as the sole Taiwanese female representative to the National Constituent Assembly. With the support of first lady Soong May-ling (宋美齡), she started the Taipei Women’s Association and Taiwan Provincial Women’s Association, where she

Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) Chairman Eric Chu (朱立倫) hatched a bold plan to charge forward and seize the initiative when he held a protest in front of the Taipei City Prosecutors’ Office. Though risky, because illegal, its success would help tackle at least six problems facing both himself and the KMT. What he did not see coming was Taipei Mayor Chiang Wan-an (將萬安) tripping him up out of the gate. In spite of Chu being the most consequential and successful KMT chairman since the early 2010s — arguably saving the party from financial ruin and restoring its electoral viability —

It is one of the more remarkable facts of Taiwan history that it was never occupied or claimed by any of the numerous kingdoms of southern China — Han or otherwise — that lay just across the water from it. None of their brilliant ministers ever discovered that Taiwan was a “core interest” of the state whose annexation was “inevitable.” As Paul Kua notes in an excellent monograph laying out how the Portuguese gave Taiwan the name “Formosa,” the first Europeans to express an interest in occupying Taiwan were the Spanish. Tonio Andrade in his seminal work, How Taiwan Became Chinese,