In 1954, Japanese cinema made two enormous contributions to world culture. In April of that year, Akira Kurosawa’s Seven Samurai was released by Toho Co Ltd. Embraced by the US and Europe, the 207-minute epic has become one of the most influential movies of all time, referenced for the past 70 years in movies major and minor, from the original Star Wars (aka A New Hope) to Predator to A Bug’s Life to Mad Max: Fury Road and on and on. In 1960, it was even remade as an American western, The Magnificent Seven, itself a classic of the genre.
On Nov. 3, 1954 — also via Toho — Japan’s second gift arrived: Gojira, who would become Godzilla to the world. Do not smirk. I am here to take the nuclear-bomb-triggered mutant seriously.
I know it is easy to scoff. For decades, the creature was played by men in rubber suits (in the first 12 movies, by the actor Haruo Nakajima, who was an extra in Seven Samurai). The original was less than half the length of Kurosawa’s epic, but it is a more tedious experience. Its moralizing about the consequences of atomic warfare — while praiseworthy — were a drag on the narrative. Still, it was successful enough to spawn sequels that found an audience in Japan and abroad. The first re-edited and voiced-over English version even declared Godzilla to be “king of the monsters.”
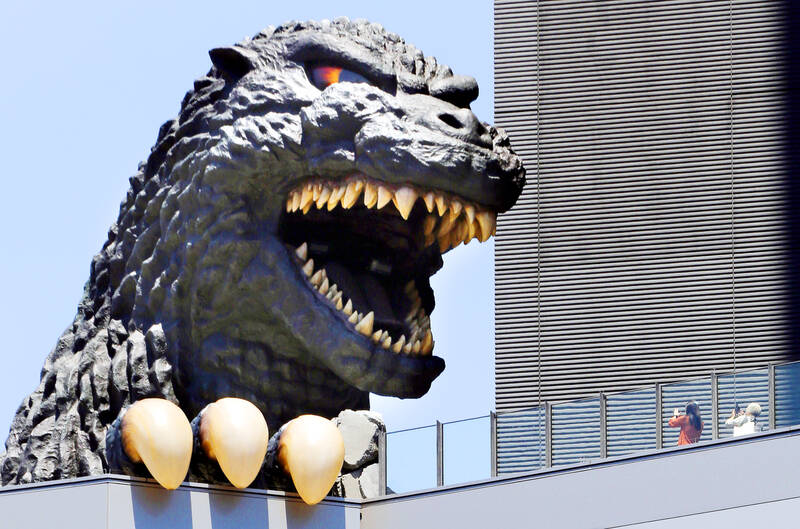

Photo: AP
It has not been easy being king. In the mid-1970s, box office receipts dropped off when the monster became goofy and googly-eyed cute. A lot of people can see Godzilla in Jim Henson’s adorably single-minded muppet Cookie Monster. Production stopped for a decade. A reset in the mid-80s gave the destroyer of cities psychological depth — straddling good and evil — but 2.0 ran out of steam by the mid-naughts. A 1998 joint effort by Toho and Columbia-TriStar Pictures to Hollywoodize the radioactive reptilian — the first where the character was taken out of its rubber suit and created with computer-generated imagery, or CGI — took him too far down the Jurassic Park path for fans to tolerate. I wrote a Time magazine story on the debacle.
For better or worse, the suffix -zilla is now attached to everything overbearing, huge, melodramatic and over-the-top ridiculous. Think “bridezilla.”
So, if the gargantuan, corduroy-skinned mutant is kitsch, why has he not been relegated to an extra-large hall in a museum of movie trivia? How has he reached his 70th year — and thrived?
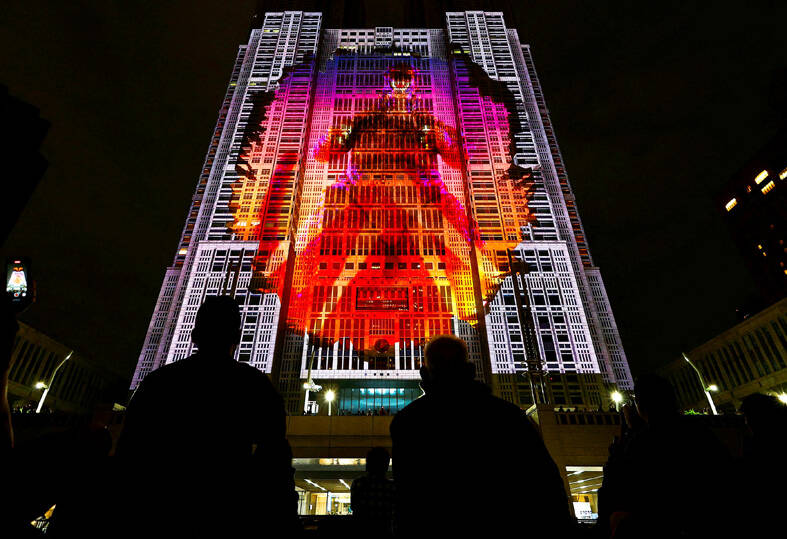

Photo: Reuters
Today, there is a sprawling, multinational many-headed enterprise we can put under an umbrella called Godzilla Inc. At the top are corporations in the US and Japan. In 2000, Toho licensed its monster to the combo of Legendary Entertainment Llc, one of the first private-equity Hollywood studios, and Warner Bros, which handled distribution of the Monsterverse — a name the duo patented for their Godzilla production line. It has been a stomping success. The fourth and most recent Monsterverse release, Godzilla x Kong: The New Empire, has grossed more than US$500 million worldwide this year.
Until last month, Dalian Wanda Group, the Chinese conglomerate, was a big stakeholder in Legendary, having paid a reported US$3.5 billion in 2016 for the privilege. The 2021 Monsterverse release Godzilla vs. Kong rang up US$470 million worldwide ticket sales, about 40 percent of that in China. Last month, Legendary (which also has the Dune trilogy in its content treasure house) bought out Wanda and splits the seats on its board with Apollo Global Management, which acquired a minority share in 2022 for US$760 million.
Toho has not been sitting around counting its licensing fees. In 2016, it rebooted the franchise with an environment-aggrieved Godzilla who bubbled out of polluted Tokyo Bay. Dubbed “Shin Godzilla” (that is, new Godzilla), this made-in-Japan incarnation was fully CGI, like its US counterpart. The movie’s re-imagining of the Godzilla myth went on to win the country’s equivalent of the Academy Award for best picture. Last year, Godzilla Minus One, Toho’s CGI remake of the 1954 classic, won an actual Oscar for best special effects. These two new Godzillas have grossed close to US$200 million for the studio. This weekend, Minus One is being re-released — in black-and-white, like the original — to mark the 70th anniversary. Toho also announced that it had green-lighted a new Godzilla movie.
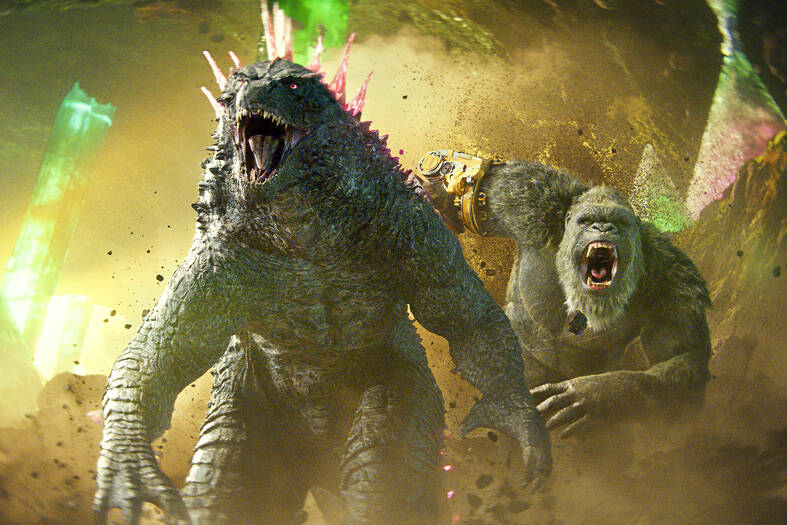

Photo: Warner Bros Pictures via AP
The US and Japanese Godzilla are contractually obligated to stay out of each other’s way: Theatrical releases are timed so movies do not cannibalize audiences.
So, what could Godzilla be worth? The cross-border accounting makes it difficult to say for certain (we also do not know how much Toho charges Legendary for the license). There is an appraisal that puts the Mona Lisa at US$870 million, not that Leonardo da Vinci’s masterpiece could realistically be sold. The Godzilla economy might be in that ballpark, if not a bit higher.
However, he is not a single thing with a price tag: He is a monstrous profit-generating idea — with a multi-generational fan base built up over 70 years that has stayed loyal through kitsch and thin. At the center of gravity is the Toho-owned film entity.
However, there is a mighty amount of money involved beyond that: theme parks, toys, comic books, collectables, independent artists who specialize in kaiju commissions. The range is blockbuster cinema to cottage industry.
I was six years old when my father brought me to my first Godzilla feature at the Podmon theater in Manila. I was terrified but enthralled — and have been hooked ever since. I watch every new movie and now have a small collection of kaiju in New York and London. It is not super valuable, but I treasure every item. I am also heartened that the Godzilla community — my big little nerdy universe — keeps upping their values. Last year, I bought a limited-edition Aztec-style vinyl Godzilla for US$150. This week, one was being resold on eBay for more than US$600. An exquisitely molded Shin Godzilla from the Japanese toy manufacturer Bandai is for sale online for more than US$300. I paid much less than that for the same thing at the famous Mandarake kaiju-manga-anime emporium in Tokyo’s Akihabara district a year ago.
We all approach our fandoms differently. I like the word “monster” because it is not just some beast. You can see it within “demonstrate.” I hear it in the Italian mostrare, to show. The Latin monstrum is a portent as well as an unnatural creature. Ultimately, the “mon” in monster might share a root with mental and mind and even money. So, monsters embody fear, yes, but also warnings and lessons. Godzilla is destructive and ugly, certainly, but — as the movies explain — he rejuvenates himself by absorbing the poisonous radioactivity humans have released, making the world safer. The monster can be redemptive.
However, people all come to their obsessions through different psychologies. There are no set paths. Perhaps just parables to make irrational sense of juvenile joys or secret pain.
Here is one. Baseball superstar Hideki Matsui, who went from the Yomiuri Giants to play for the New York Yankees, was nicknamed Godzilla. It started as an insult hurled at him in Japan, making fun of his acne-marked face, comparing the pockmarks to Godzilla’s corrugated skin, itself a reminder of the keloid scars of atom bomb survivors. However, in time Matsui adopted the puerile taunt as a point of pride and made it symbolic of his titanic swing. The Yankees might be morose this week over their dismal loss to the Dodgers, but back on Nov. 4, 2009, Matsui homered three times to drive in six runs in the game that won them the World Series against the Philadelphia Phillies. Godzilla was designated Most Valuable Player.
Long live the king.

Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (鴻海精密) yesterday said that its research institute has launched its first advanced artificial intelligence (AI) large language model (LLM) using traditional Chinese, with technology assistance from Nvidia Corp. Hon Hai, also known as Foxconn Technology Group (富士康科技集團), said the LLM, FoxBrain, is expected to improve its data analysis capabilities for smart manufacturing, and electric vehicle and smart city development. An LLM is a type of AI trained on vast amounts of text data and uses deep learning techniques, particularly neural networks, to process and generate language. They are essential for building and improving AI-powered servers. Nvidia provided assistance
DOMESTIC SUPPLY: The probe comes as Donald Trump has called for the repeal of the US$52.7 billion CHIPS and Science Act, which the US Congress passed in 2022 The Office of the US Trade Representative is to hold a hearing tomorrow into older Chinese-made “legacy” semiconductors that could heap more US tariffs on chips from China that power everyday goods from cars to washing machines to telecoms equipment. The probe, which began during former US president Joe Biden’s tenure in December last year, aims to protect US and other semiconductor producers from China’s massive state-driven buildup of domestic chip supply. A 50 percent US tariff on Chinese semiconductors began on Jan. 1. Legacy chips use older manufacturing processes introduced more than a decade ago and are often far simpler than

STILL HOPEFUL: Delayed payment of NT$5.35 billion from an Indian server client sent its earnings plunging last year, but the firm expects a gradual pickup ahead Asustek Computer Inc (華碩), the world’s No. 5 PC vendor, yesterday reported an 87 percent slump in net profit for last year, dragged by a massive overdue payment from an Indian cloud service provider. The Indian customer has delayed payment totaling NT$5.35 billion (US$162.7 million), Asustek chief financial officer Nick Wu (吳長榮) told an online earnings conference. Asustek shipped servers to India between April and June last year. The customer told Asustek that it is launching multiple fundraising projects and expected to repay the debt in the short term, Wu said. The Indian customer accounted for less than 10 percent to Asustek’s
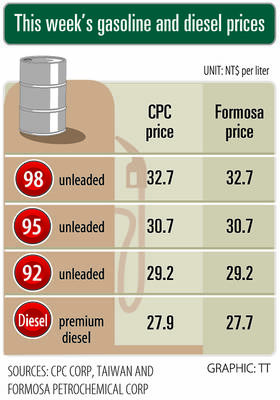
Gasoline and diesel prices this week are to decrease NT$0.5 and NT$1 per liter respectively as international crude prices continued to fall last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (CPC, 台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. Effective today, gasoline prices at CPC and Formosa stations are to decrease to NT$29.2, NT$30.7 and NT$32.7 per liter for 92, 95 and 98-octane unleaded gasoline respectively, while premium diesel is to cost NT$27.9 per liter at CPC stations and NT$27.7 at Formosa pumps, the companies said in separate statements. Global crude oil prices dropped last week after the eight OPEC+ members said they would