Dutch artist Peet Wessels might not call it an obsession, but with more than 100 images of windmills in her home, it is clear she is a big fan — her walls practically whirl with admiration.
Now Wessels, who rose to fame by painting windmills on the mill’s used canvas sails, is taking it one step further.
She is training to become a real miller — someone who operates and maintains a windmill — joining a growing number of women in what was once seen as a man’s world.
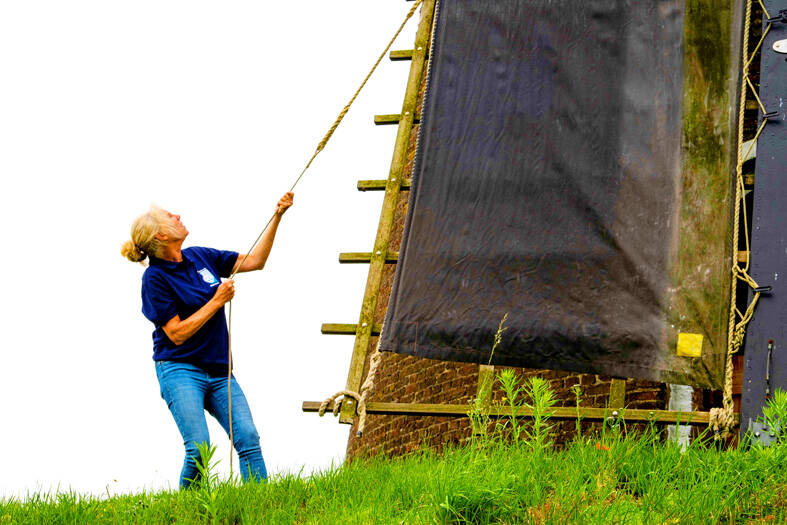

Photo: AFP
It was a blustery afternoon at De Heimolen, an ancient wheat mill in Rucphen-Bosschenhoofd near the southern Dutch city of Breda.
Perched some 10m on one of the four wings of the mill, built in 1866, Wessels tied canvas over the wooden slats. She then scarpered down and ran around the structure to release a brake to set the creaking blades in motion.
“You cannot have a fear of heights if you want to be a miller,” Wessels said, dressed in sturdy boots, jeans and a hoodie bearing the insignia of the Dutch Guild of Millers.

Photo: EPA-EFE
For almost two years now, Wessels, 59, has been following the ancient course on how to become a miller, joining about 2,000 others in the Netherlands, famous for its clogs, cheese and windmills.
Wessels believes she is the only female miller in the North Brabant province, a short hop from one of the country’s most iconic windmill locations at the nearby Kinderdijk.
In all, there are about 200 female millers around the Netherlands, she said.
They are mostly based around the central city of Utrecht.
Trainee millers learn mill mechanics — how to steer the massive blades without damaging them, safety around the rapidly moving parts and how to read the weather.
“It’s a bit like being the captain of a sailing ship,” Wessels said.
Asked about female millers making waves in a role seen for centuries as traditionally male, Wessels did not think of herself as a pioneer.
“But I’d rather be in a mill than attending a fashion show,” she said, laughing.
A chemical engineer by profession, Wessels said she was always interested in windmills and how they worked.
After stints as an engineer in the UK and the US, she started a new career as a painter in the late 1990s.
However, sales dropped and after the credit crunch in 2008, Wessels knew she had to innovate “and do something different.”
One day she was cycling past a windmill when she hit upon an idea.
“I told the miller I want do something with mills and paint them, do you have something I could use?”
That’s when the miller showed her the used canvas cloth used in the mill’s wings — and so an idea was born.
“It was stinky and full of insects, so I had to scrub it clean first,” she said.
Her chemical engineering background came in handy, helping her to find the right way to treat the canvas to show the painting and the cloths’ natural aging process.
“The cloth and the painting had to work together. It has to show the history of the cloth that’s been on the mill sometimes for 20 years or longer,” she said.
Wessels’ painting of the mill also exactly matches the actual mill on which the canvas was used.
Two of her favorites now hang in her kitchen: one work called Dutch Skies and another called Dutch Landscape.
Both were painted on the canvas from the 1740 Overwaard 7 mill at Kinderdijk — which has been declared a UNESCO World Heritage site because of its 19 iconic mills.
Wessels has painted almost all of the Netherlands’ famous windmills — including a mill called De Kat north of Amsterdam — the world’s last remaining windmill using wind power to make paint pigment.
“Almost all the millers know me. I used to ask for old canvas, but now they phone me when they have some available,” Wessels said.
Asked if she ever dreams of windmills, she quipped: “I’m not a fanatic, but training to become a miller is perhaps a step closer.”

Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (鴻海精密) yesterday said that its research institute has launched its first advanced artificial intelligence (AI) large language model (LLM) using traditional Chinese, with technology assistance from Nvidia Corp. Hon Hai, also known as Foxconn Technology Group (富士康科技集團), said the LLM, FoxBrain, is expected to improve its data analysis capabilities for smart manufacturing, and electric vehicle and smart city development. An LLM is a type of AI trained on vast amounts of text data and uses deep learning techniques, particularly neural networks, to process and generate language. They are essential for building and improving AI-powered servers. Nvidia provided assistance
DOMESTIC SUPPLY: The probe comes as Donald Trump has called for the repeal of the US$52.7 billion CHIPS and Science Act, which the US Congress passed in 2022 The Office of the US Trade Representative is to hold a hearing tomorrow into older Chinese-made “legacy” semiconductors that could heap more US tariffs on chips from China that power everyday goods from cars to washing machines to telecoms equipment. The probe, which began during former US president Joe Biden’s tenure in December last year, aims to protect US and other semiconductor producers from China’s massive state-driven buildup of domestic chip supply. A 50 percent US tariff on Chinese semiconductors began on Jan. 1. Legacy chips use older manufacturing processes introduced more than a decade ago and are often far simpler than

STILL HOPEFUL: Delayed payment of NT$5.35 billion from an Indian server client sent its earnings plunging last year, but the firm expects a gradual pickup ahead Asustek Computer Inc (華碩), the world’s No. 5 PC vendor, yesterday reported an 87 percent slump in net profit for last year, dragged by a massive overdue payment from an Indian cloud service provider. The Indian customer has delayed payment totaling NT$5.35 billion (US$162.7 million), Asustek chief financial officer Nick Wu (吳長榮) told an online earnings conference. Asustek shipped servers to India between April and June last year. The customer told Asustek that it is launching multiple fundraising projects and expected to repay the debt in the short term, Wu said. The Indian customer accounted for less than 10 percent to Asustek’s
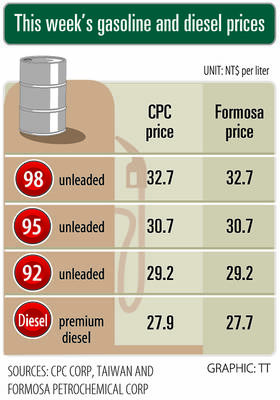
Gasoline and diesel prices this week are to decrease NT$0.5 and NT$1 per liter respectively as international crude prices continued to fall last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (CPC, 台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. Effective today, gasoline prices at CPC and Formosa stations are to decrease to NT$29.2, NT$30.7 and NT$32.7 per liter for 92, 95 and 98-octane unleaded gasoline respectively, while premium diesel is to cost NT$27.9 per liter at CPC stations and NT$27.7 at Formosa pumps, the companies said in separate statements. Global crude oil prices dropped last week after the eight OPEC+ members said they would