Three women with machetes stood guard at their farm hilltop on Indonesia’s Wawonii Island, directing their blades toward the nickel miners working in the forest clearing below.
“I pointed the machete at their faces. I told them: ‘If you scratch this land, heads will fly, we will defend this land to the death,’” 42-year-old villager Royani said, recounting an encounter with some of the miners.
The dig site is part of a huge rush to Indonesia, the world’s largest nickel producer, by domestic and foreign enterprises to mine the critical component used in electric vehicle batteries.
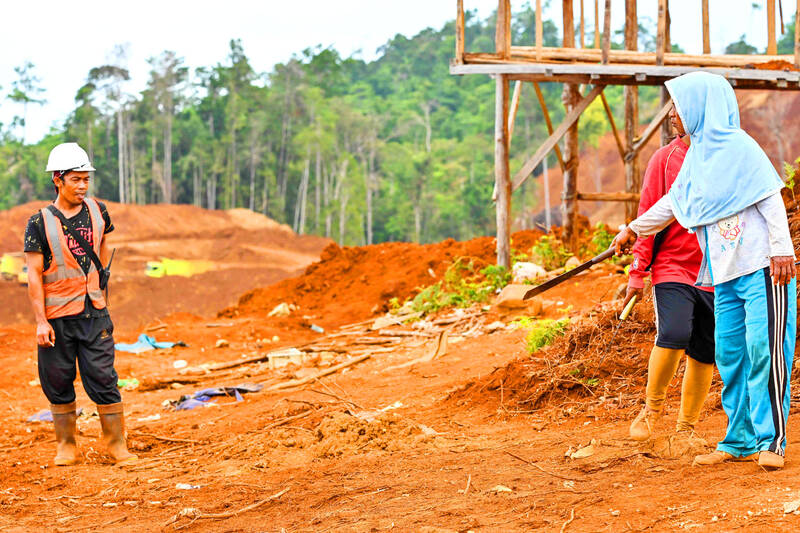

Photo: AFP
Residents and rights groups say that the boom threatens farmers’ land rights and harms the environment in areas such as Wawonii in the resource-rich Sulawesi region, which is home to black macaques, maleo birds and tarsier primates.
Facing the prospect of losing their land and livelihood, about a dozen Wawonii villagers take turns keeping watch from a hut surrounded by clove trees, waiting for trespassers as machinery roars below.
Royani, who goes by one name, joined the effort to safeguard the land after an Indonesian firm cleared hundreds of her family’s tropical spice trees in January.
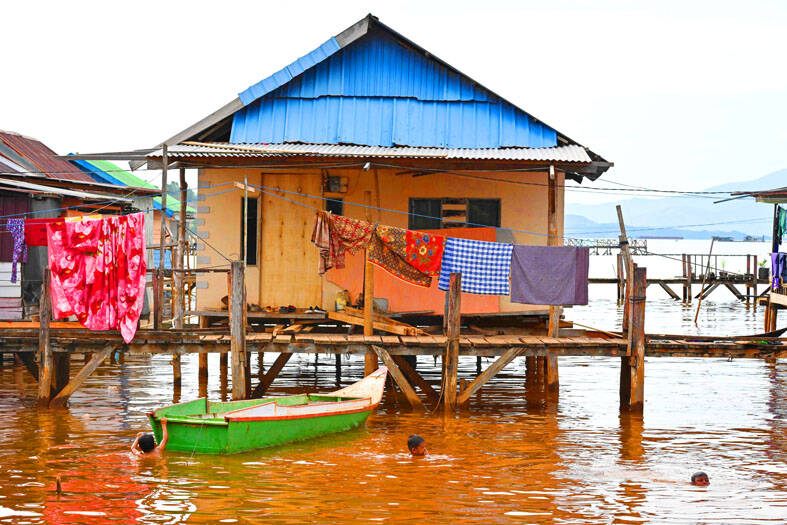

Photo: AFP
“When we saw there was nothing left, we were destroyed,” she said.
Royani said she wants to protect not just her family’s land from further encroachment, but also her neighbors’.
However, the farmers are up against formidable adversaries.
Soaring global demand for metals used in lithium-ion batteries and stainless steel has pushed major economies such as China and South Korea, alongside electric vehicle giant Tesla Inc and Brazilian mining company Vale SA, to zero in on Indonesia.
Dozens of nickel processing plants now pepper Sulawesi — one of the world’s largest islands — and many more projects have been announced.
Nickel miner PT Gema Kreasi Perdana (PT GKP), owned by one of Indonesia’s wealthiest families, has two concessions on Wawonii totaling 1,800 hectares.
Islanders said it is trying to expand further, with employees repeatedly approaching them for land talks they never asked for.
PT GKP, the Indonesian Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources and the local energy agency in southeast Sulawesi all declined to comment for this story.
“Even for 1 billion rupiah [US$65,045], I don’t want to sell,” said cashew grower Hastati, 42, whose land has already been partially cleared.
Several protesters in Wawonii have been detained after the land disputes sparked demonstrations, riots and, in some cases, armed confrontations.
Hastoma, a 37-year-old coconut farmer, said he was detained for 45 days last year after clashes between villagers and miners.
Other villagers have blocked miners’ vehicles and set heavy equipment on fire, while some have held miners hostage, restraining them with ropes for up to 12 hours.
“If I keep quiet ... where we live will be destroyed,” Hastoma said, adding that two hectares of his land were seized after his release.
“I will continue to fight to defend our area,” he said.
While land registers in many parts of Indonesia are poorly managed, a presidential decree issued in 2018 recognized farmers’ rights on state lands they use. Citing a 2007 law designed to protect coastal areas and small islands like Wawonii, courts have on several occasions ruled in favor of plaintiffs contesting mining investments.
However, Jakarta is leveraging its resources to entice investors, with many land disputes stemming from overlapping claims due to a lack of adequate ownership checks.
“The problem is permits are often unilaterally issued” by the government, said Benni Wijaya, head of knowledge management and campaigns at the Consortium for Agrarian Reform advocacy group.
“After the permit is issued, it turns out that people have been cultivating the land for years. This is what drives these conflicts,” he added.
Among the leading international investors are Chinese companies.
Indonesian government data showed that Chinese firms pumped US$8.2 billion into the country last year — more than double the 2021 figure of US$3.1 billion.
In central Sulawesi, Chinese companies have set up their own nickel ore processing facilities and even built a nickel museum.
The investments have come at a cost, worsening pollution and stoking tensions over poor working conditions at Chinese-run facilities, including a deadly January riot.
The southeastern Sulawesi coastline has borne the brunt of the environmental impact of the mines.
In a village in the Pomalaa region of the island, stilt houses sit above rust-red sludge where children swim in murky waters.
Contaminated soil from nickel mines brought down the hills by rain has turned the coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean a deep red color, locals said.
“When there were no mines, the water was not like this. It was clean,” villager Guntur, 33, said.
State-owned firm PT Aneka Tambang Tbk is among the firms that have mining concessions in the area.
PT Aneka corporate secretary Syarif Faisal Alkadrie said that “there has been no mining activity” there.
“The company is always committed to implementing good mining practice principles” in its operations, he said, adding that other companies had concessions and operated nearby.
Fishers have also been affected by the nickel pollution, and Asep Solihin said he now has to sail much further than he used to for a catch.
“We are only just able to survive,” said the 44-year-old, who has been involved in protests against the mining projects. “Up there it’s mined, down there is mud. What about the next generation?”
Not all the locals oppose the projects, with some securing work thanks to the investments, while others have seen their small businesses’ profits rise.
Sasto Utomo, 56, built a stall near the smelter in Morosi, where he sells black pepper crab and fried rice.
“I fully support the factories. Previously we could not sell. Thank God my income has increased,” he said, adding he had bought a house and farmland with his earnings.
Indonesia is Southeast Asia’s largest economy, and the World Bank says it has made huge strides in poverty reduction in the past few years.
In a speech last month, Indonesian President Joko Widodo said the country would “keep moving” with the aim of reaching developed nation status.
Farmers like Royani said they would refuse to bow to the industrial drive.
“What can we do?” she said, adding that she spends much of her day standing guard against trespassers.
They have been forced to defend their spaces or potentially lose them forever, said Kisran Makati, director of the Southeast Sulawesi Human Rights Study and Advocacy Center.
“There is no other choice,” he said.
SELL-OFF: Investors expect tariff-driven volatility as the local boarse reopens today, while analysts say government support and solid fundamentals would steady sentiment Local investors are bracing for a sharp market downturn today as the nation’s financial markets resume trading following a two-day closure for national holidays before the weekend, with sentiment rattled by US President Donald Trump’s sweeping tariff announcement. Trump’s unveiling of new “reciprocal tariffs” on Wednesday triggered a sell-off in global markets, with the FTSE Taiwan Index Futures — a benchmark for Taiwanese equities traded in Singapore — tumbling 9.2 percent over the past two sessions. Meanwhile, the American depositary receipts (ADRs) of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電), the most heavily weighted stock on the TAIEX, plunged 13.8 percent in

A wave of stop-loss selling and panic selling hit Taiwan's stock market at its opening today, with the weighted index plunging 2,086 points — a drop of more than 9.7 percent — marking the largest intraday point and percentage loss on record. The index bottomed out at 19,212.02, while futures were locked limit-down, with more than 1,000 stocks hitting their daily drop limit. Three heavyweight stocks — Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電), Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (Foxconn, 鴻海精密) and MediaTek (聯發科) — hit their limit-down prices as soon as the market opened, falling to NT$848 (US$25.54), NT$138.5 and NT$1,295 respectively. TSMC's

TARIFFS: The global ‘panic atmosphere remains strong,’ and foreign investors have continued to sell their holdings since the start of the year, the Ministry of Finance said The government yesterday authorized the activation of its NT$500 billion (US$15.15 billion) National Stabilization Fund (NSF) to prop up the local stock market after two days of sharp falls in reaction to US President Donald Trump’s new import tariffs. The Ministry of Finance said in a statement after the market close that the steering committee of the fund had been given the go-ahead to intervene in the market to bolster Taiwanese shares in a time of crisis. The fund has been authorized to use its assets “to carry out market stabilization tasks as appropriate to maintain the stability of Taiwan’s

In a small town in Paraguay, a showdown is brewing between traditional producers of yerba mate, a bitter herbal tea popular across South America, and miners of a shinier treasure: gold. A rush for the precious metal is pitting mate growers and indigenous groups against the expanding operations of small-scale miners who, until recently, were their neighbors, not nemeses. “They [the miners] have destroyed everything... The canals, springs, swamps,” said Vidal Britez, president of the Yerba Mate Producers’ Association of the town of Paso Yobai, about 210km east of capital Asuncion. “You can see the pollution from the dead fish.