More than 1,000 shipments of solar energy components worth hundreds of millions of US dollars have piled up at US ports since June under a new law banning imports from China’s Xinjiang region over concerns about slave labor, US federal customs officials and industry sources said.
The level of seizures, which has not previously been reported, reflects how a policy intended to heap pressure on Beijing over its Uighur detention camps in Xinjiang risks slowing the efforts of US President Joe Biden’s administration to decarbonize the US power sector to fight climate change.
US Customs and Border Protection has seized 1,053 shipments of solar energy equipment between June 21 — when the Uyghur Forced Labor Protection Act (UFLPA) went into effect — and Oct. 25, it said in response to a public records request, adding that none of the shipments have yet been released.
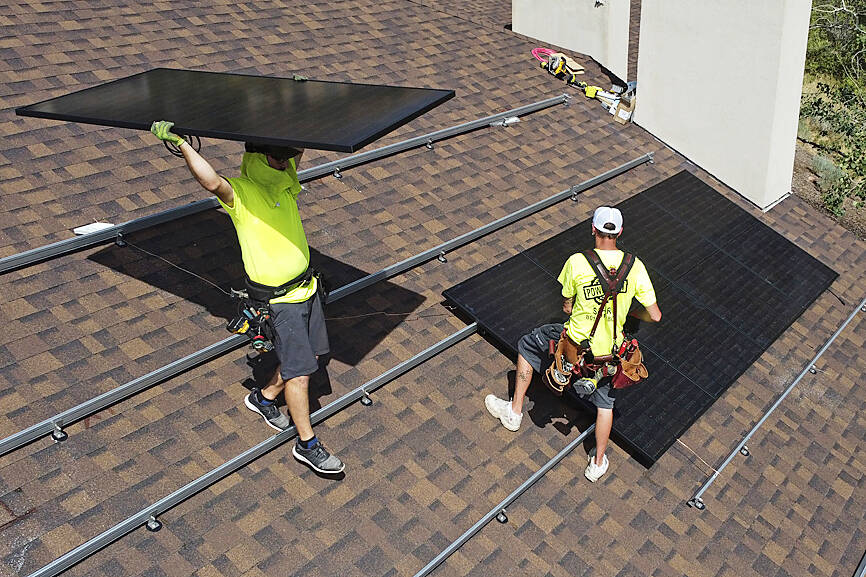

Photo: AP
The agency would not reveal the manufacturers or confirm details about the quantity of solar equipment in the shipments, citing federal law that protects confidential trade secrets.
However, three industry sources with knowledge of the matter said the detained products include panels and polysilicon cells, likely amounting to up to 1 gigawatt of capacity and primarily made by three Chinese manufacturers — Longi Green Energy Technology Co (隆基綠能科技), Trina Solar Co (天合光能) and JinkoSolar Holding Co (晶科能源).
Combined, Longi, Trina and Jinko typically account for up to one-third of US panel supplies. However, the companies have halted new shipments to the US over concerns additional cargoes would also be detained, the industry sources said. The sources asked not to be named because they were not authorized to speak publicly on the matter.
China denies abuses in Xinjiang. It initially denied the existence of any detention camps, but then later said it had set up “vocational training centers” to curb what it said was terrorism, separatism and religious radicalism in Xinjiang.
In an e-mail, Jinko said it is working with US Customs and Border Protection on documentation proving its supplies are not linked to forced labor and is “confident the shipments will be admitted.”
The bottleneck is a challenge to US solar development at a time the Biden administration is seeking to decarbonize the US economy and implement the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), a new law that encourages clean energy technologies to combat climate change.
Solar installations in the US slowed by 23 percent in the third quarter, and nearly 23 gigawatts of solar projects are delayed, largely due to an inability to obtain panels, the American Clean Power Association trade group said.
The association urged the Biden administration to streamline the vetting process for imports.
“After more than four months of solar panels being reviewed under UFLPA, none have been rejected and instead they remain stuck in limbo with no end in sight,” it said in a statement.
The UFLPA essentially presumes that all goods from Xinjiang are made with forced labor and requires producers to show sourcing documentation of imported equipment back to the raw material to prove otherwise before imports can be cleared.

Shares in Taiwan closed at a new high yesterday, the first trading day of the new year, as contract chipmaker Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電) continued to break records amid an artificial intelligence (AI) boom, dealers said. The TAIEX closed up 386.21 points, or 1.33 percent, at 29,349.81, with turnover totaling NT$648.844 billion (US$20.65 billion). “Judging from a stronger Taiwan dollar against the US dollar, I think foreign institutional investors returned from the holidays and brought funds into the local market,” Concord Securities Co (康和證券) analyst Kerry Huang (黃志祺) said. “Foreign investors just rebuilt their positions with TSMC as their top target,

REVENUE PERFORMANCE: Cloud and network products, and electronic components saw strong increases, while smart consumer electronics and computing products fell Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (鴻海精密) yesterday posted 26.51 percent quarterly growth in revenue for last quarter to NT$2.6 trillion (US$82.44 billion), the strongest on record for the period and above expectations, but the company forecast a slight revenue dip this quarter due to seasonal factors. On an annual basis, revenue last quarter grew 22.07 percent, the company said. Analysts on average estimated about NT$2.4 trillion increase. Hon Hai, which assembles servers for Nvidia Corp and iPhones for Apple Inc, is expanding its capacity in the US, adding artificial intelligence (AI) server production in Wisconsin and Texas, where it operates established campuses. This
US President Donald Trump on Friday blocked US photonics firm HieFo Corp’s US$3 million acquisition of assets in New Jersey-based aerospace and defense specialist Emcore Corp, citing national security and China-related concerns. In an order released by the White House, Trump said HieFo was “controlled by a citizen of the People’s Republic of China” and that its 2024 acquisition of Emcore’s businesses led the US president to believe that it might “take action that threatens to impair the national security of the United States.” The order did not name the person or detail Trump’s concerns. “The Transaction is hereby prohibited,”

Garment maker Makalot Industrial Co (聚陽) yesterday reported lower-than-expected fourth-quarter revenue of NT$7.93 billion (US$251.44 million), down 9.48 percent from NT$8.76 billion a year earlier. On a quarterly basis, revenue fell 10.83 percent from NT$8.89 billion, company data showed. The figure was also lower than market expectations of NT$8.05 billion, according to data compiled by Yuanta Securities Investment and Consulting Co (元大投顧), which had projected NT$8.22 billion. Makalot’s revenue this quarter would likely increase by a mid-teens percentage as the industry is entering its high season, Yuanta said. Overall, Makalot’s revenue last year totaled NT$34.43 billion, down 3.08 percent from its record NT$35.52