Business sentiment of Asian companies sank to an 11-year low in the second quarter, a Thomson Reuters/INSEAD survey found, with about two-thirds of the firms surveyed flagging a worsening COVID-19 pandemic as the biggest risk over the next six months.
While the pandemic’s initial impact was reflected in the March survey, confidence during this quarter fell by a third to 35, only the second time that the Thomson Reuters/INSEAD Asian Business Sentiment Index has slumped below 50 since the survey began in the second quarter of 2009.
A reading above 50 indicates a positive outlook.

Photo: AFP
The last time the index showed a reading below that was in its debut quarter, when it hit 45.
About 16 percent of the 93 companies surveyed also said that a deepening recession was a key risk for the next six months, with more than half expecting staffing levels and business volumes to decline.
“We ran this survey right at the edge when things were getting really bad,” Antonio Fatas, a Singapore-based economics professor at the global business school INSEAD, said of the survey conducted between May 29 and Friday last week.
“We can see this complete pessimism which is spread across sectors and countries in a way that we haven’t seen before,” he said.
Many nations are easing COVID-19-related lockdowns, but worries have mounted that another wave of infections could hurt economies that have been battered from weeks of curbs on travel and movement.
Coronavirus cases globally have crossed 8 million.
After weeks with almost no new COVID-19 infections, China recorded dozens of new cases this week, roiling fragile equity markets. South Korea also faces an uptick after early successful containment.
Companies from 11 Asia-Pacific nations responded to the Thomson Reuters/INSEAD survey.
Participants included Taiwanese contract manufacturer Wistron Corp (緯創), Thai hospitality group Minor International PCL (MINT), Japanese automaker Suzuki Motor Corp and Australia-listed Oil Search Ltd.
China, where COVID-19 was first detected, reported that industrial output quickened for a second straight month last month, but a weaker-than-expected gain suggested that the recovery remains fragile.
“It tells us that the recovery will take time and it won’t be a V-shaped recovery,” said Jeff Ng, senior treasury strategist at HL Bank Singapore (豐隆銀行).
Governments have rolled out stimulus measures to support ailing economies. Singapore and Hong Kong, among the most open economies in Asia, have backed sectors such as airlines that are bearing the brunt of travel restrictions.
The US Federal Reserve last week said that it would likely hold its benchmark interest rate near zero through 2022, signaling it expects a long road to recovery.
However, recessions in most major economies are still expected to be more severe this year than forecast, Reuters polls of more than 250 economists published late last month showed.
Chaiyapat Paitoon, chief strategy officer at Bangkok-based MINT — which operates brands such as Marriott and Four Seasons, and gets the bulk of its revenue from Europe — said that the company had taken several cost-saving measures to minimize the impact on its profits.
“MINT’s main priorities are to survive, stabilize and grow,” Paitoon said.

Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (鴻海精密) yesterday said that its research institute has launched its first advanced artificial intelligence (AI) large language model (LLM) using traditional Chinese, with technology assistance from Nvidia Corp. Hon Hai, also known as Foxconn Technology Group (富士康科技集團), said the LLM, FoxBrain, is expected to improve its data analysis capabilities for smart manufacturing, and electric vehicle and smart city development. An LLM is a type of AI trained on vast amounts of text data and uses deep learning techniques, particularly neural networks, to process and generate language. They are essential for building and improving AI-powered servers. Nvidia provided assistance
DOMESTIC SUPPLY: The probe comes as Donald Trump has called for the repeal of the US$52.7 billion CHIPS and Science Act, which the US Congress passed in 2022 The Office of the US Trade Representative is to hold a hearing tomorrow into older Chinese-made “legacy” semiconductors that could heap more US tariffs on chips from China that power everyday goods from cars to washing machines to telecoms equipment. The probe, which began during former US president Joe Biden’s tenure in December last year, aims to protect US and other semiconductor producers from China’s massive state-driven buildup of domestic chip supply. A 50 percent US tariff on Chinese semiconductors began on Jan. 1. Legacy chips use older manufacturing processes introduced more than a decade ago and are often far simpler than

STILL HOPEFUL: Delayed payment of NT$5.35 billion from an Indian server client sent its earnings plunging last year, but the firm expects a gradual pickup ahead Asustek Computer Inc (華碩), the world’s No. 5 PC vendor, yesterday reported an 87 percent slump in net profit for last year, dragged by a massive overdue payment from an Indian cloud service provider. The Indian customer has delayed payment totaling NT$5.35 billion (US$162.7 million), Asustek chief financial officer Nick Wu (吳長榮) told an online earnings conference. Asustek shipped servers to India between April and June last year. The customer told Asustek that it is launching multiple fundraising projects and expected to repay the debt in the short term, Wu said. The Indian customer accounted for less than 10 percent to Asustek’s
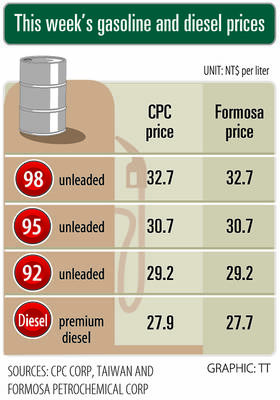
Gasoline and diesel prices this week are to decrease NT$0.5 and NT$1 per liter respectively as international crude prices continued to fall last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (CPC, 台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. Effective today, gasoline prices at CPC and Formosa stations are to decrease to NT$29.2, NT$30.7 and NT$32.7 per liter for 92, 95 and 98-octane unleaded gasoline respectively, while premium diesel is to cost NT$27.9 per liter at CPC stations and NT$27.7 at Formosa pumps, the companies said in separate statements. Global crude oil prices dropped last week after the eight OPEC+ members said they would