Pressure mounted on Europe to reveal the viability of its crisis-hit banks after a meeting of G8 finance ministers in southern Italy over the weekend ended in disarray over the thorny issue.
Britain and the US have already carried out “stress tests” to gauge the capital requirements of their banks — a painful exercise seen as boosting confidence in a sector at the epicenter of the global economic crisis.
But Berlin has resisted calls for tests on its banks saying they could undermine fragile economic confidence. London, meanwhile, warned its European partners that their failure to clean up banks could hold back Britain’s recovery.
The contentious issue was not even mentioned in a statement at the end of the G8 meeting despite it dominating on the sidelines of the talks.
“The uncomfortable truth for Europe is that, however flawed it might have been, the US stress test exercise has so far proved effective in bolstering confidence and helping banks to raise capital,” said Marco Annunziata, chief economist at Italian banking giant Unicredit.
“Eurozone policymakers appeared somewhat divided against criticism that Europe has not yet undertaken a coordinated and transparent stress testing of its major financial institutions,” he added.
Annunziata said the tests, which last month showed that 10 big US banks need US$74.6 billion in extra capital, were “the most important recent effort to restore confidence in the financial system.”
Asked about the tests, G8 meeting host and Italian Finance Minister Giulio Tremonti said they should be coordinated at the European level and added: “In Europe we haven’t begun speaking about stress tests.”
“Each one of us is following its own schedule,” French Finance Minister Christine Lagarde said. “We’re not looking at the example of this or that country.”
“We’re not hiding anything under the carpet,” she added.
Canadian Minister of Finance James Flaherty took a more conciliatory tone after the meeting, saying he was “much less frustrated now” after he said Europe had agreed to report on the results of bank stress tests on a systematic basis.
“The difference of opinion now is whether one reports with respect to the results of specific institutions and name the institutions or whether one reports about one’s system,” Flaherty told reporters.
Speaking earlier this month, however, German Finance Minister Peer Steinbrueck voiced skepticism on the tests.
“We are for a stress test of the whole system not with a view of the specific capital situation of banks,” Steinbrueck said, adding that publication of the results as Washington has done could prove “counterproductive” by jolting investors.
“There is a clear difference between the banks in Europe and in the United States,” he said.
EU finance ministers have agreed to subject their biggest banks to tests in the coming months to check for nasty surprises lurking on their balance sheets. The aim is not to identify which banks need more capital and how much, but rather to spot the risks that may threaten the broader financial sector.
The IMF has urged Europe to carry out these tests as part of a “resolute and coordinated clean up of the banking system” which it said was “essential” for restoring confidence in the financial sector.
“Europe can hardly afford a piecemeal approach which perpetuates uncertainty, leaves private investors sidelined, and allows government involvement in the sector to weigh on overall efficiency,” the IMF said.

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
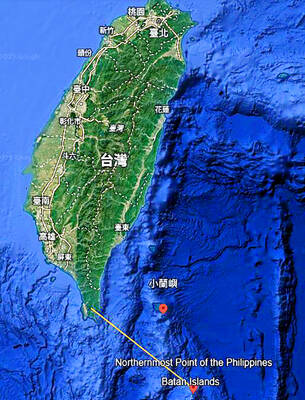
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College