It is time for the banks to fully disclose their US home loan losses to prevent fear from making a tough credit crunch worse since the central banks have done about all they can to restore confidence, analysts say.
Central banks "can't do any more" to boost confidence in the financial markets, Commerzbank economist Michael Schubert said, while Bank of America's Gilles Moec urged the private sector to state clearly "who lost what and how much."
They pointed to the vital link between information and confidence, with today a key test of whether the markets take a more positive view of the central bank rescue operation of last week or instead turn more sceptical still.
At stake is the possibility of ever tighter funding for businesses and even a recession in the US economy.
Clear statements by finance houses about how much damage the US home loan crisis has done to their accounts "is really the key to the crisis," Moec said.
A solution depends on confidence because banks have stopped lending to each other since they do not know the extent of potential losses incurred by the banks they trade with.
"If you are a medium-sized bank trying to borrow for three months in the interbank market you can more or less forget it," said Investec Securities chief economist Philip Shaw, who is based in London. "I've heard of institutions that won't lend beyond one week, to anybody, it doesn't matter who the name is."
That means banks and other major lenders are hoarding cash, diminishing the flow of credit on which business depends.
"Banks cannot borrow beyond a certain maturity and that poses a real threat to the world economy next year," Shaw said, adding that this is what had forced central banks to announce their exceptional joint action last week.
The US Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank (ECB), the Bank of England and their counterparts in Canada and Switzerland mounted a surprise joint action, last seen after the Sept. 11, 2001 attacks, to pump billions of dollars into the credit-starved markets but "this is not a cure," Schubert said.
One of the vital functions of central banks is to prevent the break of a link, or links in the banking chain from freezing the national, and potentially the international, banking system.
"If Northern Rock went under, you'd be faced with a house of cards," Shaw said, referring to the troubled British mortgage lender that had to be bailed out by the Bank of England to the tune of billions of pounds.
The European, US and Swiss central banks said they would provide more than US$60 billion to money markets over longer periods and under easier-than-usual conditions.
"That could help unclog the money market in Europe," where banks have found it particularly hard to find dollars, Moec said.
IMF spokesman Masood Ahmed said "central bank liquidity operations are only one part of addressing the ongoing problems" and that losses had to be evaluated and announced to remove the uncertainty that was the market's biggest enemy.
"Early and focused action to solve valuation problems is critical in moving forward to solve this crisis," Ahmed said.
The world's biggest bank Citigroup said late last week that it would take on board US$49 billion in now much devalued subprime home loans in an effort to draw a line under its problems.
The bank had earlier told investors it faced investment losses of between US$8 billion and US$11 billion, in large part owing to the subprime market meltdown.
A leading name in European finance, UBS bank, also revealed last week an extra US$10 billion hole in its balance sheet owing to losses in the subprime market. Analysts said UBS was sending a message of reassurance that it had dealt with the problem and there would be no more nasty surprises.
An ECB study estimates that 18 of the biggest eurozone banks are exposed to risks which, if handled in the same way, would require additional funding "of approximately 244 billion euros (US$356 billion)."
Central banks involved in the liquidity operation, in particular the ECB, have won respect from many analysts for their handling of the market crisis.
"The ECB has really stayed ahead of the curve on its liquidity management policy," Shaw said.
Schubert agreed central banks "are doing the right thing" by making cash more readily available for longer periods, up to three months in the case of the Bank of England.
The underlying factor however was fear, "uncertainty" in market language, that a borrower might turn out to be saddled with debts and unable to repay a loan.
"When in doubt, people tend to abstain," Moec said, noting that it was clear some had profited from the crisis while others faced serious problems. "The problem for everyone is they don't know if their counterpart belongs to the winners or the losers."
Only transparent disclosures could convince market players a potential partner was solvent, the economist said.
"It's beyond the reach of the central bank," he said.
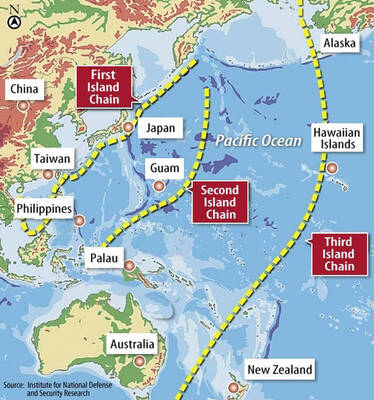
The US government has signed defense cooperation agreements with Japan and the Philippines to boost the deterrence capabilities of countries in the first island chain, a report by the National Security Bureau (NSB) showed. The main countries on the first island chain include the two nations and Taiwan. The bureau is to present the report at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee tomorrow. The US military has deployed Typhon missile systems to Japan’s Yamaguchi Prefecture and Zambales province in the Philippines during their joint military exercises. It has also installed NMESIS anti-ship systems in Japan’s Okinawa

‘WIN-WIN’: The Philippines, and central and eastern European countries are important potential drone cooperation partners, Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung said Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung (林佳龍) in an interview published yesterday confirmed that there are joint ventures between Taiwan and Poland in the drone industry. Lin made the remark in an exclusive interview with the Chinese-language Liberty Times (the Taipei Times’ sister paper). The government-backed Taiwan Excellence Drone International Business Opportunities Alliance and the Polish Chamber of Unmanned Systems on Wednesday last week signed a memorandum of understanding in Poland to develop a “non-China” supply chain for drones and work together on key technologies. Asked if Taiwan prioritized Poland among central and eastern European countries in drone collaboration, Lin

ON ALERT: Taiwan’s partners would issue warnings if China attempted to use Interpol to target Taiwanese, and the global body has mechanisms to prevent it, an official said China has stationed two to four people specializing in Taiwan affairs at its embassies in several democratic countries to monitor and harass Taiwanese, actions that the host nations would not tolerate, National Security Bureau (NSB) Director-General Tsai Ming-yen (蔡明彥) said yesterday. Tsai made the comments at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee, which asked him and Minister of National Defense Wellington Koo (顧立雄) to report on potential conflicts in the Taiwan Strait and military preparedness. Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) Legislator Michelle Lin (林楚茵) expressed concern that Beijing has posted personnel from China’s Taiwan Affairs Office to its

BACK TO WORK? Prosecutors said they are considering filing an appeal, while the Hsinchu City Government said it has applied for Ann Kao’s reinstatement as mayor The High Court yesterday found suspended Hsinchu mayor Ann Kao (高虹安) not guilty of embezzling assistant fees, reducing her sentence to six months in prison commutable to a fine from seven years and four months. The verdict acquitted Kao of the corruption charge, but found her guilty of causing a public official to commit document forgery. The High Prosecutors’ Office said it is reviewing the ruling and considering whether to file an appeal. The Taipei District Court in July last year sentenced Kao to seven years and four months in prison, along with a four-year deprivation of civil rights, for contravening the Anti-Corruption