New Zealand's central bank took markets by surprise yesterday, raising its key interest rate to a record high 8 percent from 7.75 percent in a move to curb inflation.
The Reserve Bank cited strong domestic demand, a buoyant house market, strong employment and investment intentions, robust consumer confidence and increasing government spending as pressures toward inflation.
Yesterday's 25-basis-point hike in the Official Cash Rate was the central bank's third so far this year, with the 8 percent rate the highest since the benchmark rate was introduced in March 1999.
The bank said it was aiming to ensure that inflation remains within a 1 percent to 3 percent range over the medium term.
"Had we not increased the OCR this year, it is likely that the inflation outlook would now be looking uncomfortably high," Reserve Bank Governor Alan Bollard said in the June Monetary Policy Statement.
New Zealand's on-year inflation eased to 2.5 percent in the three months ended March 31, from 2.6 percent in the fourth quarter. But domestic inflation, which excludes import prices, remains at an uncomfortably high 4.1 percent.
Bollard reiterated earlier comments that the New Zealand dollar is trading at exceptionally high and unjustified levels. The New Zealand dollar hit a 25-year high of US$0.7554 this week.
On Wednesday, the European Central Bank (ECB) raised borrowing costs to their highest level in nearly six years, pointing to a humming economy that, while welcome, raised the risk of higher inflation. It also hinted at additional increases, prompting a slide in European stock markets.
The ECB lifted its benchmark interest rate for the 13 countries that use the euro by a quarter percentage point, to 4 percent. That was the eighth increase since December 2005, when the bank began increasing the cost of credit in advance of an economic recovery. Europe is now growing faster than the US.
Bank President Jean-Claude Trichet while declining to commit to a timetable, left little doubt that the bank saw the need for higher interest rates to ward off the threat of higher inflation.
The ECB's strategy has focused on getting ahead of what it sees as inflationary threats from energy prices, increasing bottlenecks in European production -- which allow companies to raise prices more quickly -- and rising wages, which can feed into higher consumer prices. It has also sought to curb explosive bank lending brought on by low interest rates around the world.
For now, the bank has kept inflation under firm control. On a monthly rate, it is now running at less than 2 percent, almost precisely within the bank's target.
"What we have been doing since December 2005 has served us very well," Trichet said. "We have been fully vindicated."
The ECB has wagered that a strong global economy would continue to stoke economic growth in Europe by buying its exports and that business conditions in the US would pick up as the year progressed, as the US Federal Reserve has predicted.
In the statement issued after its regular monthly meeting, the ECB slightly modified the language that it employed to describe interest rates to hint at future increases. It said that rates were "still" accommodating European economic growth, a formulation that Trichet said was an oblique way of indicating that the bank would not stop at 4 percent.

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
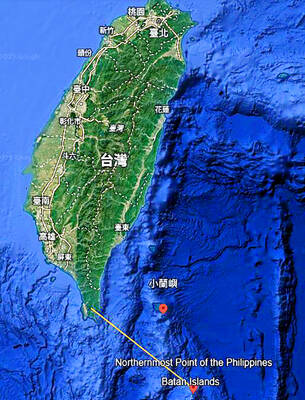
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College