One of the cleaning ladies in the building won’t enter the room where the vials are stored because she can feel the restless souls inside them.
But for 33-year-old biologist Amela Jamakovic, the 11 vials, each containing a few grains of bone powder that look like sand, are her daily assignment.
She’s part of a team of six at the laboratory of the International Commission for Missing Persons in Sarajevo that’s on a daunting mission: analyzing DNA from bones found in mass graves from atrocities or natural disasters around the world and matching it to lost lives.
The researchers try to restore identity to nameless remains by comparing the DNA to genetic material collected from living relatives. The detective work has been carried out on remains of victims from the 1990s Balkan wars, the Pinochet regime in Chile, Typhoon Frank in the Philippines, Hurricane Katrina in Louisiana and Asia’s December 2004 tsunami.
Those efforts have been dwarfed by the commission’s latest mission: helping Iraqis find and identify the victims of former Iraqi president Saddam Hussein.
Officials in Baghdad estimate that 350,000 human remains are hidden in mass graves throughout the country. Human rights groups say it could be close to 1 million.
When Jamakovic adds liquid to the grains of bone to form a solution ready for analysis, she likes to think she is performing a kind of alchemy that will conjure up an identity from dust and lead to peace and closure for a bereaved family.
For the past two years, the team has been bringing Iraqi forensic archeologists, anthropologists, nurses and other experts to Bosnia for training on collecting blood samples, excavating mass graves and setting up labs in Iraq.
Some of the dead were killed in the Iran-Iraq War in the 1980s.
Others were Kurds, killed because of their ethnicity, or Shiites, massacred because of their religion, or Sunnis, eliminated because of their political views.
If the estimates of human rights groups prove accurate, “they represent a crime against humanity surpassed only by the Rwandan genocide of 1994, Pol Pot’s Cambodian killing fields in the 1970s and the Nazi Holocaust of World War II,” a 2004 report from the US Agency for International Development said.
Building on the Iraq numbers are the unknown number of mass graves filled by victims of post-Saddam revenge killings as Sunnis, Shiites and rival political factions used the turmoil to settle scores.
It could take decades to find names for the bones from Iraq, but it will contribute to peace, said Adam Boys, the deputy head of the commission, who sees his work as “not for the dead, but for the living.”
In Iraq, there are likely to be millions enduring that fate.
The current situation “has catastrophic effects on Iraqi society and politics,” Baghdad political analyst Hadi Jallu said. “The missing people are from Iraqi sects, and unless this problem is solved, these sects will still continue to mistrust and still seek revenge from each other.”
Jonathan McCaskill, the International Commission for Missing Persons chief in Iraq, said locals are being taught about forensic archeology, anthropology and databases created to store genetic information and match it with living relatives.
Iraqi archeologists, anthropologists, forensic experts, nurses, doctors and lawyers have been visiting Sarajevo for courses on excavating bones, DNA extraction and taking blood samples. Software the commission has developed is being translated into Arabic and Kurdish.
In Baghdad, thousands of remains have been collected at the morgues of the Medical Legal Institute, brought in during the months after the April 2003 invasion. Iraqi experts have extracted DNA from many of the remains, but so far have nothing with which to match them.
Munqith al-Dezali, the head of the Medico-Legal Institute in Baghdad, said each set of remains needs blood samples from three or four relatives to yield a positive identification.
Boys said much education is needed before the work of collecting those samples can even start. He cited the case of a Kurdish village where some villagers had reservations about the procedure.
When an International Commission for Missing Persons representative told them that DNA extraction was necessary to help find missing loved ones, they asked how long one can live without DNA, thinking it was an organ.

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a
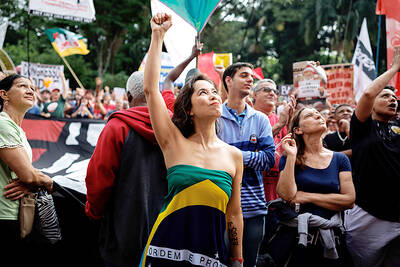
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

‘EAST SHIELD’: State-run Belma said it would produce up to 6 million mines to lay along Poland’s 800km eastern border, and sell excess to nations bordering Russia and Belarus Poland has decided to start producing anti-personnel mines for the first time since the Cold War, and plans to deploy them along its eastern border and might export them to Ukraine, the deputy defense minister said. Joining a broader regional shift that has seen almost all European countries bordering Russia, with the exception of Norway, announce plans to quit the global treaty banning such weapons, Poland wants to use anti-personnel mines to beef up its borders with Belarus and Russia. “We are interested in large quantities as soon as possible,” Deputy Minister of National Defense Pawel Zalewski said. The mines would be part

Cozy knits, sparkly bobbles and Santa hats were all the canine rage on Sunday, as hundreds of sausage dogs and their owners converged on central London for an annual parade and get-together. The dachshunds’ gathering in London’s Hyde Park came after a previous “Sausage Walk” planned for Halloween had to be postponed, because it had become so popular organizers needed to apply for an events licence. “It was going to be too much fun so they canceled it,” laughed Nicky Bailey, the owner of three sausage dogs: Una and her two 19-week-old puppies Ember and Finnegan, wearing matching red coats and silver