Authorities in St. Croix rushed to contain oil spills on Friday after more than 40 boats sank or washed ashore during Hurricane Omar.
About half the vessels lost their anchors, including houseboats, catamarans and pricey yachts and sailboats owned by tourists. The other half were tied at marinas but broke loose, said Carlos Fachette, enforcement director for the US Department of Planning and Natural Resources.
The hurricane caught many local boaters off-guard because they did not take the storm seriously, Kim Jones of the St. Croix Yacht Club said.
“It’s devastating,” she said of the damage. “That puts a brake into people getting into boating, which is such a way of life in the Caribbean. It’s going to take a lot to rebound.”
Roughly 400 boats are registered in St. Croix, she said.
Police on Friday also had to rescue three people from a 11m catamaran when it hit a reef and ran aground near Salt River Bay, Fachette said.
All St. Croix beaches have been deemed unsafe because of high pollution levels, and the Schooner Channel area of the Christiansted Harbor remained closed.
Omar passed overnight on Wednesday between St. Martin and the US Virgin Islands, where the government has spent more than US$1 million in cleanup costs.
The storm caused more than US$700,000 in damages to roads in St. Croix and destroyed more than 100 utility poles in the east. About half of the island’s 55,000 people remained with power on Friday, Water and Power Authority spokeswoman Cassandra Dunn said.
St. Croix also reported heavy crop damage, as did Antigua and Barbados.

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a

China yesterday held a low-key memorial ceremony for the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, with Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平) not attending, despite a diplomatic crisis between Beijing and Tokyo over Taiwan. Beijing has raged at Tokyo since Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi last month said that a hypothetical Chinese attack on Taiwan could trigger a military response from Japan. China and Japan have long sparred over their painful history. China consistently reminds its people of the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, in which it says Japanese troops killed 300,000 people in what was then its capital. A post-World War II Allied tribunal put the death toll
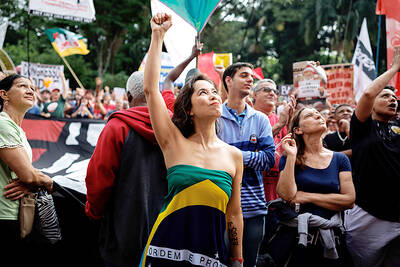
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

FALLEN: The nine soldiers who were killed while carrying out combat and engineering tasks in Russia were given the title of Hero of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea North Korean leader Kim Jong-un attended a welcoming ceremony for an army engineering unit that had returned home after carrying out duties in Russia, North Korean state media KCNA reported on Saturday. In a speech carried by KCNA, Kim praised officers and soldiers of the 528th Regiment of Engineers of the Korean People’s Army (KPA) for “heroic” conduct and “mass heroism” in fulfilling orders issued by the ruling Workers’ Party of Korea during a 120-day overseas deployment. Video footage released by North Korea showed uniformed soldiers disembarking from an aircraft, Kim hugging a soldier seated in a wheelchair, and soldiers and officials