A White House official who once led the oil industry's fight against limits on greenhouse gases has repeatedly edited government climate reports in ways that play down links between such emissions and global warming, according to internal documents.
In handwritten notes on drafts of several reports issued in 2002 and 2003, the official, Philip Cooney, removed or adjusted descriptions of climate research that government scientists and their supervisors, including some senior Bush administration officials, had already approved. In most cases, the changes appeared in the final reports.
The dozens of changes, while sometimes as subtle as the insertion of the phrase "significant and fundamental" before the word "uncertainties," tend to produce an air of doubt about findings that most climate experts say are robust.
Cooney is chief of staff for the White House Council on Environmental Quality, the office that helps devise and promote administration policies on environmental issues.
Before going to the White House in 2001, he was the "climate team leader" and a lobbyist at the American Petroleum Institute. A lawyer with a bachelor's degree in economics, he has no scientific training.
The documents were obtained by the New York Times from the Government Accountability Project, a nonprofit legal-assistance group for government whistle-blowers. The group is representing Rick Piltz, who resigned in March as a senior associate in the office that coordinates government climate research.
A White House spokeswoman, Michele St. Martin, said Tuesday that Cooney would not be made available to comment because he was not cleared as a spokesman.
Other White House officials said the changes made by Cooney were part of the normal interagency review that takes place on all documents related to global environmental change. Cooney's alterations are sometimes as simple as the insertion of an adjective, but they cause clear shifts in the meaning of the documents.
Meanwhile, President George W. Bush's decision not to sign the US up to the Kyoto global warming treaty was partly a result of pressure from ExxonMobil, the world's most powerful oil company, and other industries, according to US State Department papers seen by the Guardian.
The documents reinforce widely-held suspicions of how close the company is to the administration and its role in helping to formulate US policy.
In briefing papers given before meetings to the US under-secretary of state, Paula Dobriansky, between 2001 and last year, the administration is found thanking Exxon executives for the company's "active involvement" in helping to determine climate change policy, and also seeking its advice on what climate change policies the company might find acceptable.
Other papers suggest that Dobriansky should sound out Exxon executives and other anti-Kyoto business groups on potential alternatives to Kyoto.
Until now Exxon has publicly maintained that it had no involvement in the US' rejection of Kyoto.

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a

China yesterday held a low-key memorial ceremony for the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, with Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平) not attending, despite a diplomatic crisis between Beijing and Tokyo over Taiwan. Beijing has raged at Tokyo since Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi last month said that a hypothetical Chinese attack on Taiwan could trigger a military response from Japan. China and Japan have long sparred over their painful history. China consistently reminds its people of the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, in which it says Japanese troops killed 300,000 people in what was then its capital. A post-World War II Allied tribunal put the death toll
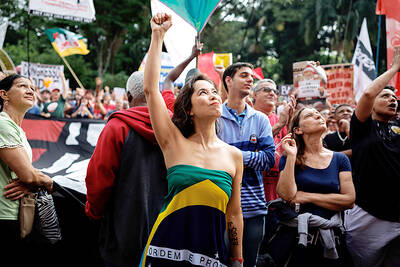
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

FALLEN: The nine soldiers who were killed while carrying out combat and engineering tasks in Russia were given the title of Hero of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea North Korean leader Kim Jong-un attended a welcoming ceremony for an army engineering unit that had returned home after carrying out duties in Russia, North Korean state media KCNA reported on Saturday. In a speech carried by KCNA, Kim praised officers and soldiers of the 528th Regiment of Engineers of the Korean People’s Army (KPA) for “heroic” conduct and “mass heroism” in fulfilling orders issued by the ruling Workers’ Party of Korea during a 120-day overseas deployment. Video footage released by North Korea showed uniformed soldiers disembarking from an aircraft, Kim hugging a soldier seated in a wheelchair, and soldiers and officials