Kim Jong-il's regime in North Korea desperately needs security guarantees for economic reforms to take root, but he is unlikely to get them at six-nation talks on the Stalinist state's nuclear program starting today.
In the streets of Pyongyang small businesses have always been state-owned but the prices are now fixed by the market, and buyers use cash instead of ration coupons.
For those who have money, several hundred market salesmen on Unification Street now offer imported goods from China or Southeast Asia, such as clothing, televisions and washing machines.
"When we are in North Korea, it is like going back 20 years" to a time when economic reforms first started in China, said Cheng Peng, vice president of the Society for Friendship and Sino-Korean cultural exchange which organizes trips for Chinese businessmen.
Quoted in the Chinese economic journal Zhongguo Jingying Bao, Cheng talks of "virgin territory" and gives assurances that there are dream opportunities for small and medium-sized Chinese enterprises in the country.
But the chances of the reforms lasting depends on the regime's own chances of survival.
"In North Korea the reforms are imposed from on high. They are there to stabilize the system and to make the situation better for the elite," Ruediger Frank, a specialist on Korea at Vienna University, said.
But he said the North's leaders were yet to be convinced that "foreigners are not going to exploit internal conflict caused by the reforms to provoke a change in regime."
"For the economic situation in North Korea to improve in the long run, it must transform its military-run industries into civilian ones," said Zhao Huji, a specialist on North Korea from the Central Party School in Beijing.
"But for that to happen North Korea needs security guarantees, a requirement the United States refuses to meet since Pyongyang is only offering a compromise, and not a dismantling of its nuclear program," said Zhao.
While North Korea admits to having a plutonium-based nuclear program, which it has offered to freeze, it denies the existence of a uranium-enrichment one, which the US insists it must dismantle.
China, Russia, South Korea and perhaps Japan could for their part accept the more basic compromise, the Chinese expert suggests, but much depends on the US.
Seoul recently signed agreements to develop its economic relations with the North, while pledging a huge aid package if a solution is found to the nuclear standoff that erupted in 2002 with US claims that Pyongyang had resumed its nuclear program.
"South Korea seems determined to press ahead with engagement, regardless of the nuclear situation," said Marcus Noland, a researcher at the International Economics Institute in Washington.
Washington realizes this and, in order to prevent it becoming isolated, "the United States is likely to present more evidence regarding North Korea's second, highly enriched uranium-based, nuclear program, in an effort to keep China and others on board," Noland said.

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a

China yesterday held a low-key memorial ceremony for the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, with Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平) not attending, despite a diplomatic crisis between Beijing and Tokyo over Taiwan. Beijing has raged at Tokyo since Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi last month said that a hypothetical Chinese attack on Taiwan could trigger a military response from Japan. China and Japan have long sparred over their painful history. China consistently reminds its people of the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, in which it says Japanese troops killed 300,000 people in what was then its capital. A post-World War II Allied tribunal put the death toll
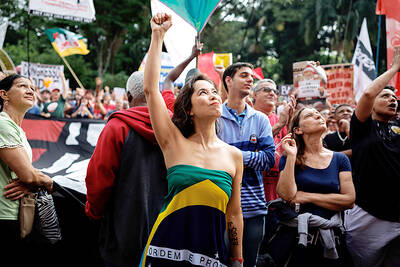
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

FALLEN: The nine soldiers who were killed while carrying out combat and engineering tasks in Russia were given the title of Hero of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea North Korean leader Kim Jong-un attended a welcoming ceremony for an army engineering unit that had returned home after carrying out duties in Russia, North Korean state media KCNA reported on Saturday. In a speech carried by KCNA, Kim praised officers and soldiers of the 528th Regiment of Engineers of the Korean People’s Army (KPA) for “heroic” conduct and “mass heroism” in fulfilling orders issued by the ruling Workers’ Party of Korea during a 120-day overseas deployment. Video footage released by North Korea showed uniformed soldiers disembarking from an aircraft, Kim hugging a soldier seated in a wheelchair, and soldiers and officials