For centuries, people have puzzled over lemmings, the northern rodents whose populations surge and crash so quickly and so regularly that they inspired an enduring myth: that lemmings commit mass suicide when their numbers grow too large, eagerly pitching themselves off cliffs to their deaths in a foamy sea.
Scientists debunked that notion decades ago. But they have never been certain what causes the rapid boom-and-bust cycles that gave rise to it. Now, in a study of collared lemmings in Greenland, published on Friday in the journal Science, a team of European researchers reported that the real reason has nothing to do with self-annihilation and everything to do with hungry predators.
After 15 years of research, the scientists report, they discovered that the combined actions of four predator species -- snowy owls, seabirds called long-tailed skuas, arctic foxes and weasel-like creatures known as stoats -- create the four-year cycles during which lemming populations explode and then nearly disappear.
Scientists say such cycles have been one of the most enduring -- and hotly debated -- mysteries in ecology.
"There have been several dozen hypotheses and sometimes everybody was almost killing each other they were sticking so close to their hypothesis," said Olivier Gilg, an ecologist at the University of Helsinki in Finland who is an author of the paper.
Many suspected the cycles might be caused by an array of forces, Gilg said, "but we were able to explain this cycle with only predation, and that was very surprising; it was very exciting."
Peter Hudson, a population ecologist at Penn State University who was not involved with the work but who wrote a commentary for Science on the paper, called it a textbook case, noting that population cycles are also found in birds, insects and larger mammals, like lynx.
"These animals show this lovely clockwork change in numbers," he said of lemmings, "and yet we haven't been able to nail it down. This paper reveals the mechanism. That's why this study is particularly important."
Though their research deals with brown 18cm rodents, ecologists can be forgiven their excitement. Lemming population cycles have captured human imagination for hundreds of years. In Scandinavia, ancient sagas describe lemming outbreaks, and as early as the 1500s there were writings attempting to explain why lemmings would periodically overrun regions, some suggesting that the animals rained down from the sky.
Recently, scientists have tested more plausible explanations, including climate change and the idea that the quality of plants eaten by lemmings might vary cyclically or that high densities might stress lemmings, decreasing their ability to reproduce and causing populations to crash. Even sunspots had been proposed as a possible cause.
In the new study, researchers took advantage of Greenland's never-ending daylight in summer to do extended observations of predators. The open tundra environment also allowed the small, skittering rodents to be seen and counted easily.
The scientists found that the tundra provided an excess of food and of sandy soil to burrow in, a setting for explosive lemming population growth.
But when lemming numbers began to soar, foxes, skuas and owls began eating them in greater and greater quantity. A pair of snowy owls can bring back as many as 50 lemmings a day for their hungry nestlings.
Stoats specialize in hunting lemmings, and after a banner lemming year, stoat populations explode, decimating the lemmings the following year. Then the four-year cycle begins all over again.
When researchers created a model to predict lemming populations, based only on the behavior of their four predators, they found that the model precisely predicted nature's four-year fluctuations in numbers.
Despite the new finding, lemming scientists expect to continue to be plagued by suicide queries. In particular, they blame a 1958 Walt Disney nature film, White Wilderness, in which lemmings were shown hurling themselves off a cliff.
In 1983 a Canadian documentary, Cruel Camera, about abuse of animals in movies, asserted that the scene was faked, using lemmings bought from Eskimo children and herded into the water. That conclusion has come to be widely accepted, and on Thursday Rena Langley, a spokeswoman for the Walt Disney Co, did not dispute it.
"We have done extensive research into what happened more than 40 years ago," she said, "but have been unable to determine exactly what techniques were used in producing White Wilderness. The standards and techniques were certainly different then than they are now."

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a

China yesterday held a low-key memorial ceremony for the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, with Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平) not attending, despite a diplomatic crisis between Beijing and Tokyo over Taiwan. Beijing has raged at Tokyo since Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi last month said that a hypothetical Chinese attack on Taiwan could trigger a military response from Japan. China and Japan have long sparred over their painful history. China consistently reminds its people of the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, in which it says Japanese troops killed 300,000 people in what was then its capital. A post-World War II Allied tribunal put the death toll
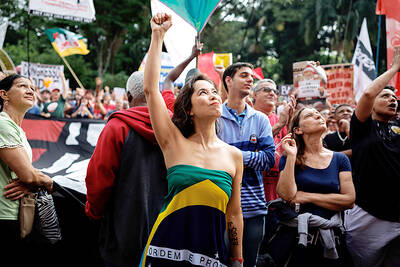
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

FALLEN: The nine soldiers who were killed while carrying out combat and engineering tasks in Russia were given the title of Hero of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea North Korean leader Kim Jong-un attended a welcoming ceremony for an army engineering unit that had returned home after carrying out duties in Russia, North Korean state media KCNA reported on Saturday. In a speech carried by KCNA, Kim praised officers and soldiers of the 528th Regiment of Engineers of the Korean People’s Army (KPA) for “heroic” conduct and “mass heroism” in fulfilling orders issued by the ruling Workers’ Party of Korea during a 120-day overseas deployment. Video footage released by North Korea showed uniformed soldiers disembarking from an aircraft, Kim hugging a soldier seated in a wheelchair, and soldiers and officials