The US supports cross-strait military confidence-building measures (CBM), but there is no policy of actively promoting them, a Washington roundtable discussion was told on Tuesday.
“That is an important distinc-tion,” said Bonnie Glaser, a consultant for the US government on East Asia.
The cross-strait agenda, whether it is CBMs or other issues, is up to the two sides of the Taiwan Strait to determine, she said.
“We don’t push, we don’t pressure Taiwan in any dialogue or any issue that Taiwan judges to be premature,” said Glaser, who works on Chinese foreign and security policy with the Center for Strategic and International Studies.
President Ma Ying-jeou (馬英九) is worried that if Taiwan pursues military CBMs with China it will result in a reduction or an end to arms sales from the US, she said.
“I have heard the president profess this concern several times,” she said.
However, Glaser said at the roundtable organized by the Sigur Center for Asian Studies at George Washington University that this was not likely to be an outcome of certain kinds of CBMs between Taiwan and China.
Glaser, a frequent visitor to Taiwan, said the US had the “utmost confidence” that Taiwan could decide for itself what was in its interests.
She said claims that the US had “strongly told” the Ma administration not to talk about military CBMs with China were “nonsense.”
Some kinds of CBMs — for example an emergency “hotline” — could enable both sides to avoid an incident from escalating.
“The US supports CBMs if and when Taiwan is ready to discuss them,” Glaser said.
Former US president George W. Bush convinced Beijing that the US does not support Taiwanese independence, she said.
“Bush told Beijing leaders privately that the US opposed Taiwan independence,” she said.
However, China is not confident that the US will accept peaceful unification.
“US arms sales to Taiwan pretty clearly are not for a Taiwan offensive against the mainland [China],” she said. “The logic that makes sense is that China reduces the threat opposite Taiwan and Taiwan might then reconsider or factor into the decisions it makes about the arms it needs to buy and about the defense capabilities it needs to have,” Glaser said.
She said that maybe then Taiwan would feel it did not need to buy weapons from the US.
Alan Romberg, director of the East Asia program at the Stimson Center, said that Beijing maintained a large missile force opposite Taiwan to deter independence.
“Even though I believe the possibility of any Taiwan leadership moving towards de jure independence is somewhere between zero and minus-70, Beijing fears the consequences of saying that it would not use force in any circumstances,” Romberg said.
“Until the day of unification the PLA [People’s Liberation Army] is going to be required to maintain the capability to deal with any move toward independence,” he said.
Romberg said that China was not “looking for a fight” and wanted to achieve its goals by diplomacy, but there was concern Beijing would “lose patience.”
Despite China’s suspicions to the contrary, the US relationship with Taiwan was not part of “some strategy to constrain China and limit its power much less to advance Taiwan independence,” he said.
“The US does not favor or support Taiwan independence, but if the two sides miraculously agreed to it we would certainly be happy to go along,” Romberg said.
Even though Taiwan remained a potential cause of friction between Washington and Beijing, Romberg said, the situation had evolved to the point where all three parties were being careful not to create turmoil or crisis.
“In this situation, over time, certain kinds of CBMs might be considered,” he said.
However, Li Da-jung (李大中), an associate professor in the Graduate Institute of International Affairs and Strategic Studies at Tamkang University, said that cross-strait negotiations were moving into a new phase, with Taipei trying to set the pace.
He said Taiwan was carefully choosing the issues on the negotiating table, but that there was a lack of domestic consensus in support of CBMs.

An essay competition jointly organized by a local writing society and a publisher affiliated with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) might have contravened the Act Governing Relations Between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area (臺灣地區與大陸地區人民關係條例), the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) said on Thursday. “In this case, the partner organization is clearly an agency under the CCP’s Fujian Provincial Committee,” MAC Deputy Minister and spokesperson Liang Wen-chieh (梁文傑) said at a news briefing in Taipei. “It also involves bringing Taiwanese students to China with all-expenses-paid arrangements to attend award ceremonies and camps,” Liang said. Those two “characteristics” are typically sufficient
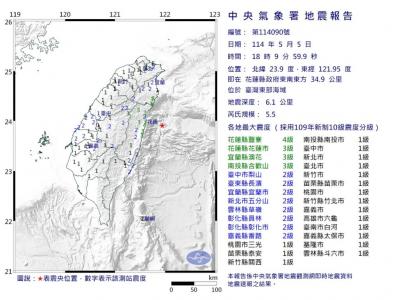
A magnitude 5.9 earthquake that struck about 33km off the coast of Hualien City was the "main shock" in a series of quakes in the area, with aftershocks expected over the next three days, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said yesterday. Prior to the magnitude 5.9 quake shaking most of Taiwan at 6:53pm yesterday, six other earthquakes stronger than a magnitude of 4, starting with a magnitude 5.5 quake at 6:09pm, occurred in the area. CWA Seismological Center Director Wu Chien-fu (吳健富) confirmed that the quakes were all part of the same series and that the magnitude 5.5 temblor was

The brilliant blue waters, thick foliage and bucolic atmosphere on this seemingly idyllic archipelago deep in the Pacific Ocean belie the key role it now plays in a titanic geopolitical struggle. Palau is again on the front line as China, and the US and its allies prepare their forces in an intensifying contest for control over the Asia-Pacific region. The democratic nation of just 17,000 people hosts US-controlled airstrips and soon-to-be-completed radar installations that the US military describes as “critical” to monitoring vast swathes of water and airspace. It is also a key piece of the second island chain, a string of

The Central Weather Administration has issued a heat alert for southeastern Taiwan, warning of temperatures as high as 36°C today, while alerting some coastal areas of strong winds later in the day. Kaohsiung’s Neimen District (內門) and Pingtung County’s Neipu Township (內埔) are under an orange heat alert, which warns of temperatures as high as 36°C for three consecutive days, the CWA said, citing southwest winds. The heat would also extend to Tainan’s Nansi (楠西) and Yujing (玉井) districts, as well as Pingtung’s Gaoshu (高樹), Yanpu (鹽埔) and Majia (瑪家) townships, it said, forecasting highs of up to 36°C in those areas