The Taiwanese navy can no longer hope to compete with China for control of the waters adjoining Taiwan and should instead embark on a program that focuses on “sea denial,” two academics argue in a landmark study of Taiwan’s naval strategy.
Calling for a break with Taiwan’s naval power paradigm, Chinese navy experts James Holmes and Toshi Yoshihara of the US Naval War College write that denying the People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) use of the waters around Taiwan would be nearly as effective for homeland defense as fighting for outright sea control, as designated in the current strategy.
To achieve sea denial — the naval strategy of the weaker side in a conflict — Taipei would have to “forgo its desire for sea control” and “resist the allure of the high-end ships strong navies use to take command of vital expanses,” they write in the 67-page Defending the Strait: Taiwan’s Naval Strategy in the 21st Century published this week by the Jamestown Foundation, adding that “reconfiguring the fleet and devising inventive tactics would let the ROCN [Republic of China Navy] take advantage of the -island’s geography.”
The days when the Taiwanese navy could rely on technological superiority to overcome numerical inferiority are gone, the authors say. Given this, rather than aim for high-value platforms such as the Kidd-class destroyers acquired in 2005 and 2006, Taiwan should develop and deploy “swarms of small surface and subsurface combatants” to wage a “people’s war at sea” that would make its naval forces “an exceptionally hard target that packs a wallop.”
Such a fleet, they write, would likely be sufficient to deter the Chinese or buy sufficient time for the US and perhaps Japan to intervene.
This paradigm shift would require a culture change in the navy, the authors argue, as the required doctrine, strategy and acquisition “inverts the natural order of things for naval officers accustomed to commanding the sea.”
It would also require Taipei to forgo “desirable,” albeit no longer feasible, priorities such as sea-lane security and the defense of the Spratlys — a tough sell with government officials, influential academics and, perhaps to a lesser extent, the electorate.
“Protecting the homeland comes first. It avails Taiwan little to sacrifice its independence for the sake of secondary objectives,” they write.
It will also mean abandoning the concept of surface action groups (SAG) inherited from the US Navy. This concept, which revolves around a high-value flagship accompanied by a flotilla, reflects the long-term strategic competition that pitted the US and the Soviet Union against each other during the Cold War and remains relevant today for navies whose power projection is global in scope. While a SAG-based strategy applies to a certain extent to the PLAN, it is of little relevance to Taiwan today, which has more limited capabilities and requirements.
Taiwan no longer has the luxury of a “balanced fleet that is capable in every dimension of naval warfare,” such as securing sea lanes and breaking maritime blockades, and should instead create “an unbalanced fleet, seeking out comparative advantages, targeting finite resources to bolster these advantages, and cutting back ruthlessly on functions that lie beyond the ROCN’s means.”
This would require changes in fleet and culture, and the divorcing of sea-denial and coastal defense asymmetrical means like fast--attack craft and shore-based missiles from high-value platforms intended for sea control.
A decentralization of command-and-control would also be necessary to meet that objective and ensure more autonomy in decision-making, they write.
This approach appears to have received the blessing of President Ma Ying-jeou (馬英九) and Deputy Minister of National Defense Andrew Yang (楊念祖), they write, though there is scant reason to believe that the Taiwanese military establishment has accepted it, as demonstrated by successive editions of the National Defense Report that leave the statement of aims practically unchanged.
Clinging to a SAG naval strategy will only create opportunities for China to defeat Taiwan’s military on day one, the authors write. As such, a new strategy that exploits the advantages of the weaker party is the best, and possibly only, option for Taiwan.
“If the only options are fruitless war and peace on Chinese terms, then Taiwanese officials may opt for the less destructive choice, regardless of whether it conforms to their wishes or those of the citizenry,” they write. “So long as Taipei can deter war or hold off a Chinese attack long enough for US forces to intervene, then an agreeable outcome — indefinite de facto independence — will remain in view.”

Taiwan is stepping up plans to create self-sufficient supply chains for combat drones and increase foreign orders from the US to counter China’s numerical superiority, a defense official said on Saturday. Commenting on condition of anonymity, the official said the nation’s armed forces are in agreement with US Admiral Samuel Paparo’s assessment that Taiwan’s military must be prepared to turn the nation’s waters into a “hellscape” for the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA). Paparo, the commander of the US Indo-Pacific Command, reiterated the concept during a Congressional hearing in Washington on Wednesday. He first coined the term in a security conference last

DEFENSE: The National Security Bureau promised to expand communication and intelligence cooperation with global partners and enhance its strategic analytical skills China has not only increased military exercises and “gray zone” tactics against Taiwan this year, but also continues to recruit military personnel for espionage, the National Security Bureau (NSB) said yesterday in a report to the Legislative Yuan. The bureau submitted the report ahead of NSB Director-General Tsai Ming-yen’s (蔡明彥) appearance before the Foreign and National Defense Committee today. Last year, the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) conducted “Joint Sword-2024A and B” military exercises targeting Taiwan and carried out 40 combat readiness patrols, the bureau said. In addition, Chinese military aircraft entered Taiwan’s airspace 3,070 times last year, up about
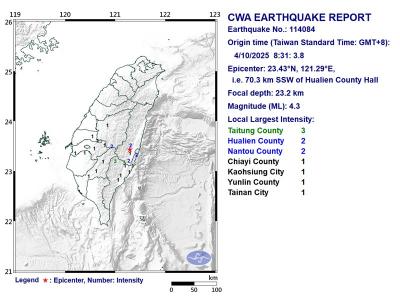
A magnitude 4.3 earthquake struck eastern Taiwan's Hualien County at 8:31am today, according to the Central Weather Administration (CWA). The epicenter of the temblor was located in Hualien County, about 70.3 kilometers south southwest of Hualien County Hall, at a depth of 23.2km, according to the administration. There were no immediate reports of damage resulting from the quake. The earthquake's intensity, which gauges the actual effect of a temblor, was highest in Taitung County, where it measured 3 on Taiwan's 7-tier intensity scale. The quake also measured an intensity of 2 in Hualien and Nantou counties, the CWA said.

The Overseas Community Affairs Council (OCAC) yesterday announced a fundraising campaign to support survivors of the magnitude 7.7 earthquake that struck Myanmar on March 28, with two prayer events scheduled in Taipei and Taichung later this week. “While initial rescue operations have concluded [in Myanmar], many survivors are now facing increasingly difficult living conditions,” OCAC Minister Hsu Chia-ching (徐佳青) told a news conference in Taipei. The fundraising campaign, which runs through May 31, is focused on supporting the reconstruction of damaged overseas compatriot schools, assisting students from Myanmar in Taiwan, and providing essential items, such as drinking water, food and medical supplies,