Taiwanese researchers at a biotechnology fair in Taipei have showcased the initial results of their efforts to map fruit flies’ brains, which they said will pave the way for mapping the human brain to find treatments for diseases that cannot be cured today.
“Just like humans, fruit flies can also suffer from Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, depression, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or autism,” said Chiang Ann-shyn (江安世), director of National Tsing Hua University’s Brain Research Center, on the sidelines of the Bio Taiwan fair that runs from Thursday to today.
More understanding
“When we understand the neural circuits of a fruit fly’s brain, we will be able to know which neuronal cells or genes go wrong and then fix them,” he said.
Chiang, in charge of the project, said the research team’s technology allows 3D visualization of internal structures at cellular and sub-cellular levels, with high resolution and without tissue embedding and sectioning.
The same concept can be applied to eventually mapping and understanding the human brain, Chiang said.
BRAIN MAP
“The key thing we lack today is such a brain map,” he said. “We hope to create a Google Earth of the human brain in the future and provide it to scientists around the world to use.”
“In the future, scientists can just use this system and search for certain brain networks or gene expressions,” he said.
The field of brain mapping is at the cutting edge of biotechnology. Only a small number of top institutes in the world are undertaking such research.
The government has already identified the research team’s technologies as one of the country’s six potential star industries in the future.
So far, the Chiang-led research team has achieved initial results in mapping a small part of a fruit fly’s brain, which has 130,000 neurons, but a human brain is 100,000 times more complex than that of a fruit fly.
3D TECHNOLOGY
Chiang also envisions that in 10 years, medical doctors will be able to rely on a 3D visualization of every human organ to facilitate their treatment of diseases.
At the fair, the research team set up a small theater to allow visitors to see a 3D presentation of the mapped parts of a fruit fly’s brain on a big screen.
The research team colored different neurons in the 3D picture of the brain, which can be turned horizontally and vertically, and can be zoomed in and out, to help viewers better understand the structure of the neurological systems.
Yao Chih-min (姚志明), deputy director-general of the National Center for High-Performance Computing, who is part of the research team, explained why the team chose fruit flies as the subject of their experiments.
“It’s because they are low-cost and easy to obtain, “ he said. “You can get only one single neuron when you kill a fruit fly, so you can imagine how many of them have been sacrificed in order to build the database we see now.”
Chiang urged the government to help step up development of this field as rival foreign research teams have allocated far more investment and resources than Taiwan.
“Other countries also see this field as the future and they can outperform us, even though they started later than we did,” he said.
It will take a long time for any team in the world to map the human brain because of its complexity, Yao said.

An essay competition jointly organized by a local writing society and a publisher affiliated with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) might have contravened the Act Governing Relations Between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area (臺灣地區與大陸地區人民關係條例), the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) said on Thursday. “In this case, the partner organization is clearly an agency under the CCP’s Fujian Provincial Committee,” MAC Deputy Minister and spokesperson Liang Wen-chieh (梁文傑) said at a news briefing in Taipei. “It also involves bringing Taiwanese students to China with all-expenses-paid arrangements to attend award ceremonies and camps,” Liang said. Those two “characteristics” are typically sufficient
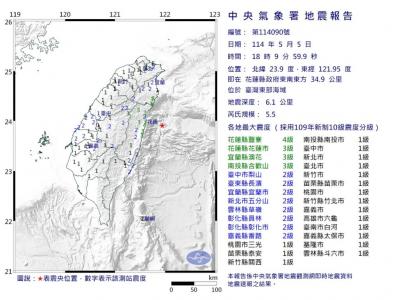
A magnitude 5.9 earthquake that struck about 33km off the coast of Hualien City was the "main shock" in a series of quakes in the area, with aftershocks expected over the next three days, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said yesterday. Prior to the magnitude 5.9 quake shaking most of Taiwan at 6:53pm yesterday, six other earthquakes stronger than a magnitude of 4, starting with a magnitude 5.5 quake at 6:09pm, occurred in the area. CWA Seismological Center Director Wu Chien-fu (吳健富) confirmed that the quakes were all part of the same series and that the magnitude 5.5 temblor was

The brilliant blue waters, thick foliage and bucolic atmosphere on this seemingly idyllic archipelago deep in the Pacific Ocean belie the key role it now plays in a titanic geopolitical struggle. Palau is again on the front line as China, and the US and its allies prepare their forces in an intensifying contest for control over the Asia-Pacific region. The democratic nation of just 17,000 people hosts US-controlled airstrips and soon-to-be-completed radar installations that the US military describes as “critical” to monitoring vast swathes of water and airspace. It is also a key piece of the second island chain, a string of

The Central Weather Administration has issued a heat alert for southeastern Taiwan, warning of temperatures as high as 36°C today, while alerting some coastal areas of strong winds later in the day. Kaohsiung’s Neimen District (內門) and Pingtung County’s Neipu Township (內埔) are under an orange heat alert, which warns of temperatures as high as 36°C for three consecutive days, the CWA said, citing southwest winds. The heat would also extend to Tainan’s Nansi (楠西) and Yujing (玉井) districts, as well as Pingtung’s Gaoshu (高樹), Yanpu (鹽埔) and Majia (瑪家) townships, it said, forecasting highs of up to 36°C in those areas