The US Air Force sought to attack China with nuclear weapons early on during the Chinese military blockade of Kinmen and Matsu in 1958, but then-US president Dwight D. Eisenhower vetoed the idea, newly declassified Air Force histories released on Wednesday show.
But while Eisenhower rejected the use of the nuclear weapons as a first response to the Chinese actions, he and his top officials did not rule out their use if the crisis went on for an extended period. In that case, “nuclear strikes apparently would follow,” the documents reveal.
Air Force officials advocated hitting targets in the area of Xiamen and other cities, including Shanghai, if the crisis escalated, the documents, released by the National Security Archives, an anti-secrecy research institute located at George Washington University in Washington showed.
As the crisis grew, members of Eisenhower’s Cabinet and military leaders “accepted the idea that the United States would have to resort to nuclear weapons to prevent the Communists from using ships and aircraft to isolate the Nationalist-held islands,” one document said.
The chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, General Nathan Twining, advocated dropping 10 kiloton to 15 kiloton nuclear bombs near what was then known as Amoy, and possibly on “airfields as far distant as Shanghai,” the document says.
While admitting that such acts “might bring down nuclear vengeance” on Taiwan, he “considered this is a risk that would have to be taken if the offshore islands were to be defended,” it says.
Pacific Air Force commander, General Laurence Kuter, was the main proponent of the immediate nuclear option, and was astounded when he found out that Eisenhower rejected it, the history says. Based on his assumption, in mid-August of 1958, five Strategic Air Command B-47s on Guam went on alert “to conduct nuclear raids against mainland airfields,” the document says.
On Aug. 25, at a White House meeting, Eisenhower “rejected the idea of using atomic weapons immediately upon the outbreak of hostilities. Instead, he insisted that the first strikes be made with high explosives, although nuclear weapons would be available if needed for subsequent attacks,” the history shows.
By October, the crisis subsided as China apparently concluded that the massive US response in defense of dictator Chiang Kai-shek (將介石) and his government rendered an all-out attack on the offshore islands not worth the effort, the history suggests.
The 10 formerly secret and top-secret histories of the US Air Force, which contain the history of the 1958 Taiwan crisis, were obtained by the archives under a Freedom of Information Act request initially filed in the 1990s and released only after a recent court action.
An analysis accompanying the Quemoy-Matsu crisis history suggests that the incident had a wider implication for US military strategy, and especially its thoughts on nuclear warfare.
“The assumption that the United States would meet Communist aggression by immediate nuclear retaliation did not survive the Taiwan crisis of 1958,” the document says. “The caution [Eisenhower] displayed at the time ... forced US military planners to review their attitudes concerning nuclear wars.”

Taiwan is to commence mass production of the Tien Kung (天弓, “Sky Bow”) III, IV and V missiles by the second quarter of this year if the legislature approves the government’s NT$1.25 trillion (US$39.78 billion) special defense budget, an official said yesterday. Commenting on condition of anonymity, a defense official with knowledge of the matter said that the advanced systems are expected to provide crucial capabilities against ballistic and cruise missiles for the proposed “T-Dome,” an advanced, multi-layered air defense network. The Tien Kung III is an air defense missile with a maximum interception altitude of 35km. The Tien Kung IV and V
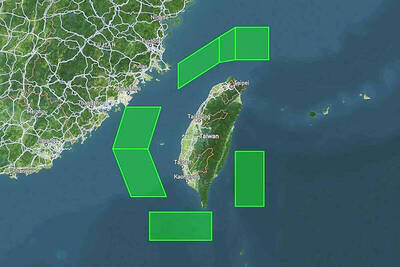
The disruption of 941 flights in and out of Taiwan due to China’s large-scale military exercises was no accident, but rather the result of a “quasi-blockade” used to simulate creating the air and sea routes needed for an amphibious landing, a military expert said. The disruptions occurred on Tuesday and lasted about 10 hours as China conducted live-fire drills in the Taiwan Strait. The Civil Aviation Administration (CAA) said the exercises affected 857 international flights and 84 domestic flights, affecting more than 100,000 travelers. Su Tzu-yun (蘇紫雲), a research fellow at the government-sponsored Institute for National Defense and Security Research, said the air

A strong continental cold air mass is to bring pollutants to Taiwan from tomorrow, the Ministry of Environment said today, as it issued an “orange” air quality alert for most of the country. All of Taiwan except for Hualien and Taitung counties is to be under an “orange” air quality alert tomorrow, indicating air quality that is unhealthy for sensitive groups. In China, areas from Shandong to Shanghai have been enveloped in haze since Saturday, the ministry said in a news release. Yesterday, hourly concentrations of PM2.5 in these areas ranged from 65 to 160 micrograms per cubic meter (mg/m³), and pollutants were

Taiwan lacks effective and cost-efficient armaments to intercept rockets, making the planned “T-Dome” interception system necessary, two experts said on Tuesday. The concerns were raised after China’s military fired two waves of rockets during live-fire drills around Taiwan on Tuesday, part of two-day exercises code-named “Justice Mission 2025.” The first wave involved 17 rockets launched at 9am from Pingtan in China’s Fujian Province, according to Lieutenant General Hsieh Jih-sheng (謝日升) of the Office of the Deputy Chief of the General Staff for Intelligence at the Ministry of National Defense. Those rockets landed 70 nautical miles (129.6km) northeast of Keelung without flying over Taiwan,