An increasing percentage of greenhouse gas emissions is a result of deforestation and forest degradation, said Fitrian Ardiansyah, climate and energy program director for the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
"The current split of greenhouse gas contribution is 80/20, between energy sources and deforestation. However, that percentage may alter if we don't stop chopping down trees," Ardiansyah told the Taipei Times in an interview earlier this month.
Deforestation may also be behind the severe La Nina effect this year, as deforestation fuels climate change, he said. In Taiwan, La Nina has been blamed for strong cold fronts and dust storms this year and has been pinned for causing unusual weather elsewhere around the globe.
"While energy sources include power plants, electricity usage and transportation, deforestation means the complete demolition of forests. And forest degradation means that the larger trees are chopped for timber, leaving the forest with only lesser trees," he said.
The three countries producing the most emissions through deforestation and forest degradation are Indonesia with 35 percent of such emissions, Brazil with 19 percent and Malaysia with 10 percent, said the WWF official, who comes from Indonesia.
"As the possessor of the world's largest tracts of forests, it is our responsibility to protect them," he said.
A number of factors are driving deforestation, all of which have to do with population growth and development, Ardiansyah said.
"Firstly, population growth brings demands for more housing and commodities such as timber, paper and agricultural goods. So we flatten forests for residential space or farm plantations and harvest the wood for timber or wood by-products," he said.
For example, oil palm plantations in Indonesia and Malaysia are a source of concern, he said. Both countries earn much of their GDP from exports of palm oil, which is used in food, biofuels and cosmetic products.
Statistics from the Indonesian Ministry of Forestry data indicate, however, that "70 percent of Indonesia's oil palm plantations were originally forests," Ardiansyah said.
The demand for palm oil places a heavy burden on the environment for two reasons, he said: When forests are converted to plantations, not only is biodiversity affected, driving some species into extinction, the tree count per hectare is also reduced to one-third of the original density, reducing a crucial resource in the fight against global warming.
The solution, he said, lies in international policy and collaboration between countries.
"For example, in Japan, government buildings can only use timber harvested from legal sources, which can help cut down on illegal logging," he said.
International projects such as the Bali Roadmap are also leading to new forest-conservation incentives. The Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation scheme, for example, lets nations contribute to their Kyoto protocol emission goals by sustaining forests in developing countries, he said.
"For example, Australia has invested A$200 million [US$188 million] in Indonesia to conserve forests that would otherwise be logged," he said.
A major obstacle in forest conservation is the issue of ownership. Property rights for forests are often unclear, making it difficult for conservationists to prevent logging, he said.
"There is no clear definition as to who owns the forests: Is it the nation, the people who live there or the investors who pay to conserve them? Without clear definitions, the carbon credits do not have clear ownership and the number of parties willing to pay to protect the forests may remain scarce," he said.
Countries with tropical forests have created alliances such as the Coalition of Rainforest Nations and regional and bilateral initiatives like the Heart of Borneo, which brings together Indonesia,Malaysia and Brunei, or the Global Initiative on Forests and Climate.
These are good examples of efforts to fight deforestation, but "all these efforts combined may still not be enough to combat the force of an economy yearning to prosper," Ardiansyah said.
"Australia may be investing millions in our forests, but at the same time, China is investing US$8 billion in our palm oil industry -- a victory of economic might over environmental protection," he said.
Citing WWF data, Ardiansyah said that rising economies such as China, with its population of 1.3 billion, had sent demand for commodities skyrocketing in recent years, with no signs of a slowdown in sight.
The key to reducing deforestation may be to increase land-use consistency, he said.
"By adopting a cross-sectoral approach to forest management -- fostering greater policy coherence amongst agriculture, forestry and energy sectors -- we can establish, for example, a maximum capacity of commodities that a given amount of land can produce depending on its location," he said.
Agricultural developments should also be employed to ensure the productivity of existing farm land is maximized to avoid further loss of forests, he said.
No matter what methods are employed, effective policy will require "urgent and international action, pricing for damage from greenhouse gases, support for technology development and combatting deforestation."
Ardiansyah quoted the Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change, a 700-page report published in 2006 for the British government by economist Nicholas Stern, former chief economist and senior vice president of the World Bank.
"Improving land management and reducing deforestation is highly cost-effective and significant in reducing [greenhouse gas] emissions," Ardiansyah said, citing Stern.
"And think about it, on top of carbon emission reductions, forests are also good for the ecosystem, sustaining a solid biodiversity and keeping the soil and water nutritious and clean. That's killing a lot of birds with one stone," he said.

An essay competition jointly organized by a local writing society and a publisher affiliated with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) might have contravened the Act Governing Relations Between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area (臺灣地區與大陸地區人民關係條例), the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) said on Thursday. “In this case, the partner organization is clearly an agency under the CCP’s Fujian Provincial Committee,” MAC Deputy Minister and spokesperson Liang Wen-chieh (梁文傑) said at a news briefing in Taipei. “It also involves bringing Taiwanese students to China with all-expenses-paid arrangements to attend award ceremonies and camps,” Liang said. Those two “characteristics” are typically sufficient
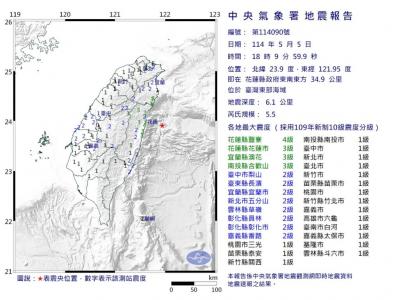
A magnitude 5.9 earthquake that struck about 33km off the coast of Hualien City was the "main shock" in a series of quakes in the area, with aftershocks expected over the next three days, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said yesterday. Prior to the magnitude 5.9 quake shaking most of Taiwan at 6:53pm yesterday, six other earthquakes stronger than a magnitude of 4, starting with a magnitude 5.5 quake at 6:09pm, occurred in the area. CWA Seismological Center Director Wu Chien-fu (吳健富) confirmed that the quakes were all part of the same series and that the magnitude 5.5 temblor was

The brilliant blue waters, thick foliage and bucolic atmosphere on this seemingly idyllic archipelago deep in the Pacific Ocean belie the key role it now plays in a titanic geopolitical struggle. Palau is again on the front line as China, and the US and its allies prepare their forces in an intensifying contest for control over the Asia-Pacific region. The democratic nation of just 17,000 people hosts US-controlled airstrips and soon-to-be-completed radar installations that the US military describes as “critical” to monitoring vast swathes of water and airspace. It is also a key piece of the second island chain, a string of

The Central Weather Administration has issued a heat alert for southeastern Taiwan, warning of temperatures as high as 36°C today, while alerting some coastal areas of strong winds later in the day. Kaohsiung’s Neimen District (內門) and Pingtung County’s Neipu Township (內埔) are under an orange heat alert, which warns of temperatures as high as 36°C for three consecutive days, the CWA said, citing southwest winds. The heat would also extend to Tainan’s Nansi (楠西) and Yujing (玉井) districts, as well as Pingtung’s Gaoshu (高樹), Yanpu (鹽埔) and Majia (瑪家) townships, it said, forecasting highs of up to 36°C in those areas