As US lawmakers demand to know how a would-be attacker smuggled explosives aboard a plane on Christmas Day, the use of body scanners at airport security points is likely to be revisited.
The machines are considered effective and have been tested at numerous international airports, but they are also controversial because they scan beneath clothing to detect items that may be hidden from ordinary view.
Security experts believe that the scanners could have detected the explosives that Umar Farouk Abdulmutallab was hiding as he boarded a Northwest Airlines plane in Amsterdam last week.
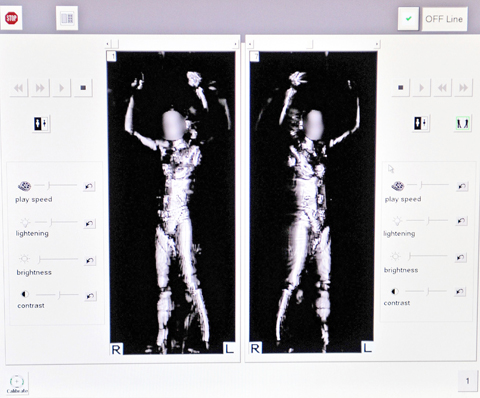
PHOTO: AFP
Abdulmutallab attempted to bring down the Airbus 330 by combining a flammable liquid he was carrying in a syringe with an explosive powder known as pentaerythritol (PETN) that was sewn into his underwear.
The metal detectors that passengers ordinarily step through as their luggage is being X-rayed would not have detected either component, experts said.
In the wake of the failed attack, British Interior Minister Alan Johnson said on Monday he would consider installing full body scanners at British airports “as quickly as possible.”
In the US, the scanners are already used at 19 airports and a handful of courthouses and prisons, the US Transportation Security Administration says.
The machines look like small booths and use radio frequencies to scan underneath clothing and produce a 3D image of the individual’s body.
While the scanner does not produce an image of the naked body, it has caused consternation among privacy advocates because it does faithfully reproduce individual curves hidden beneath clothing, from the shape of a breast to a roll of fat.
The device has been tested in numerous European airports, but its use was halted after the EU expressed concerns and protested a plan to install the scanners at airports throughout the EU.
EU representative Martine Roure praised the mothballing of the project, saying it would have been “disproportionate to submit all passengers to this type of check in the name of the fight against terrorism.”
But Thursday’s failed attack could prompt lawmakers worldwide to change their minds about the body scanners.
Successful and failed terror attacks targeting airplanes have already led to significant changes to the way people fly.
After the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks, pilots began locking the cockpit door behind them to prevent hijackers from accessing the flight controls.
In the wake of Richard Reid’s failed December 2001 attempt to detonate explosives in his shoes, passengers now routinely submit their footwear to inspection before boarding a plane.
And after authorities uncovered a plot in 2006 to blow up airliners with explosives in liquid containers, new regulations were imposed limiting the amount of fluid each traveler could bring aboard a flight.
Bruce Hoffman, a terrorism expert at Georgetown University, told reporters that traditional security measures simply would not be able to detect the sort of explosive Abdulmutallab was carrying.
“There is no other way, except for a body scan, to detect it,” he said.
Even the secondary screening measures sometimes used at airports would have failed, he said.
“If [if the explosive PETN] was sealed extremely tight in plastic, dogs wouldn’t have picked it up,” he said.
Douglas Laird, a former security director for Northwest Airlines, agreed, noting it was virtually impossible to know what was beneath clothing without the scanners.
But some are more skeptical about the efficacy of the machines, including Jimmie Carol Oxley, the co-director of the Center of Excellence in Explosive Detection, Mitigation, Response and Characterization at the University of Rhode Island.
“Anything is hard to detect if you’re not looking for it,” he pointed out, noting that airport security already has machines that can detect PETN. “If you go through the airport and they ever pull you over for your carry-on and they swab your carry-on, they can pick up that, those machines detect it.”
The machines also come with another problem: They cost around US$1 million, 20 times more than a standard X-ray machines, Laird said.

ACTIONABLE ADVICE: The majority of chatbots tested provided guidance on weapons, tactics and target selections, with Perplexity and Meta AI deemed to be the least safe From school shootings to synagogue bombings, leading artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots helped researchers plot violent attacks, according to a study published on Wednesday that highlighted the technology’s potential for real-world harm. Researchers from the nonprofit watchdog Center for Countering Digital Hate and CNN posed as 13-year-old boys in the US and Ireland to test 10 chatbots, including ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Perplexity, Deepseek and Meta AI. Eight of the chatbots assisted the make-believe attackers in more than half the responses, providing advice on “locations to target” and “weapons to use” in an attack, the study said. The chatbots had become a “powerful accelerant for

Australians were downloading virtual private networks (VPNs) in droves, while one of the world’s largest porn distributors said it was blocking users from its platforms as the country yesterday rolled out sweeping online age restriction. Australia in December became the first country to impose a nationwide ban on teenagers using social media. A separate law now requires artificial intelligence (AI)-powered chatbot services to keep certain content — including pornography, extreme violence and self-harm and eating disorder material — from minors or face fines of up to A$49.5 million (US$34.6 million). The country also joined Britain, France and dozens of US states requiring

Hungarian authorities temporarily detained seven Ukrainian citizens and seized two armored cars carrying tens of millions of euros in cash across Hungary on suspicion of money laundering, officials said on Friday. The Ukrainians were released on Friday, following their detention on Thursday, but Hungarian officials held onto the cash, prompting Ukraine to accuse Hungary’s Russia-friendly government of illegally seizing the money. “We will not tolerate this state banditism,” Ukrainian Minister of Foreign Affairs Andrii Sybiha said. The seven detained Ukrainians were employees of the Ukrainian state-owned Oschadbank, who were traveling in the two armored cars that were carrying the money between Austria and

Kosovar President Vjosa Osmani on Friday after dissolving the Kosovar parliament said a snap election should be held as soon as possible to avoid another prolonged political crisis in the Balkan country at a time of global turmoil. Osmani said it is important for Kosovo to wrap up the upcoming election process and form functional institutions for political stability as the war rages in the Middle East. “Precisely because the geopolitical situation is that complex, it is important to finish this electoral process which is coming up,” she said. “It is very hard now to imagine what will happen next.” Kosovo, which declared