Taiwan in Time: Oct. 10 to Oct. 16
On the morning of Oct.10, 1935, after the firing of three gun salutes, 1,500 doves were released into the Taihoku (today’s Taipei) sky as a band played Taiwan Leaping Forward, a Japanese song written especially for the occasion.
For the next 50 days, the entire country would be abuzz with activity as the extravagant and ambitious Taiwan Exhibition held to celebrate 40 years of Japanese rule took place not only in its main Taihoku venues, but with secondary exhibits in numerous cities such as Kirun (Keelung), Takao (Kaohsiung) and Karen (Hualien).

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
The main exhibition space of more than 130,000m2 was spread across 40 exhibition halls in Taihoku, showcasing more than 300,000 items including the products, industries and latest technologies of Japan, as well as Taiwan and its other colonies, and military, transportation and cultural displays.
The goal was not only for the Japanese to showcase to the world the accomplishments of 40 years of colonization, but it was also a display of might, as they intended to use Taiwan as a springboard for their military “southward expansion” plan (it’s not a coincidence that the exhibition included a whole section devoted to South China and Southeast Asia). Less than a year later, the colonial government began its Japanization program of the Taiwanese people to make them an even more integral part of the empire.
CHEN YI VISITS TAIWAN
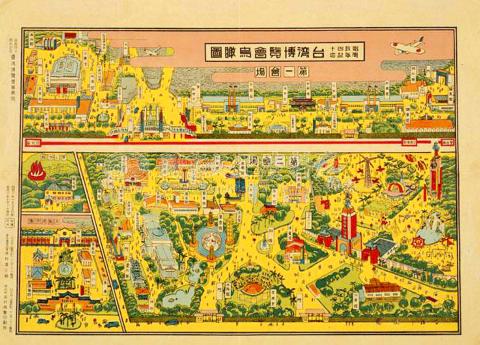
Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
The Japanese government invited officials from around the world to attend. One of them was Fujian Province governor Chen Yi (陳儀) — whose name would later be forever etched into Taiwanese history as the governor under whose rule (or misrule) the 228 Incident took place.
Chen enjoyed close ties with Japan as he had lived there for several years as a student and married a Japanese woman, and he had reportedly been tasked by Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) leader Chiang Kai-shek (蔣介石) to maintain a friendly relationship with Japan. Chen had already sent an observation team to Taiwan in 1934 to use it as a case study of how to bring Fujian out of poverty, noting in a report that despite being much smaller in land area, Taiwan’s production was about six times that of Fujian’s.
On Oct. 21, 1935, Chen became the highest-ranking Chinese official to visit Taiwan during Japanese rule, staying for seven days as he visited the exposition and took a tour showcasing important colonial construction projects. He also met with Taiwan’s governor-general Nakagawa Kenzo and reached an agreement to cooperate economically. In 1936, Chen sent yet another observation team to Taiwan, filing a detailed report to Chiang.

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Fo Guang University professor Chen Hsin-yuan (陳信元) writes in his study Chen Yi, Hsu Shou-shang and the Taiwan Provincial Editorial and Translation Bureau (陳儀, 許壽裳 與台灣省編譯館) that to save the Chinese officials face, exhibition staff removed signs mentioning “40 years of colonial rule” when they visited the exhibition. This mutual goodwill did not last long, as Japan would launch a full-scale invasion of China less than two years later.
The real consequence here is that this experience undoubtedly made Chen the prime candidate for governor-general of Taiwan after Japanese defeat, as he was “one of the very few important KMT figures after World War II who had any Taiwan experience,” writes Cheng Chia-hui (程佳慧) in her book The First Major Exposition in Taiwan’s History (台灣史上第一大博覽會).
GARGANTUAN EFFORT
The Japanese put a great amount of effort into this event. In addition to the aggressive promotion and number of people on the planning team, Cheng writes that they set up 46,999 temporary lights in Taihoku — making it the brightest city in Taiwan.
To involve the public, a contest was held for a theme song for the exposition — the top two winning songs were even pressed into records and widely played. Children were encouraged to submit essays about the event which they would read on public radio, and planes dropped about 600,000 fliers over various cities with free tickets and other promotions.
Other more sustainable changes were made, such as a concerted effort to prevent and eradicate typhoid fever and meningitis, which had ravaged the colony earlier that year. The government also improved air, sea and land transportation, and took the opportunity to promote tourism, renovating many historical sites and improving facilities.
Undoubtedly, some Taiwanese denounced the event — in Chu Tien-jen’s (朱點人) short story Autumn Letter (秋信), protagonist Dou Wen (斗文) laments: “The ‘Great Leap Forward of Taiwan’s Productivity’ indeed. Only you Japanese devils can leap forward. I’m afraid Taiwan’s youth don’t even have a chance to inch forward.”
But on the other hand, many local elites and businessmen worked with the Japanese to realize the event. Cheng writes that there were 6,506 Taiwanese members on the roster of the civilian Taiwan Exhibition Support and Sponsor Association (台灣博覽會協贊會). She also estimates that partially due to heavy propaganda and urging by the government, almost half of the Taiwanese population visited the exhibition in Taihoku.
Although Cheng writes that the exposition was “a product of Japanese imperial ambition,” it was also a microcosm of Taiwanese society in the 1930s. There have only been two comparable events in Taiwan’s history — the 1948 Taiwan Province Expo and the 2010 Taipei International Flora Expo.
Taiwan in Time, a column about Taiwan’s history that is published every Sunday, spotlights important or interesting events around the nation that have anniversaries this week.

March 31 to April 6 On May 13, 1950, National Taiwan University Hospital otolaryngologist Su You-peng (蘇友鵬) was summoned to the director’s office. He thought someone had complained about him practicing the violin at night, but when he entered the room, he knew something was terribly wrong. He saw several burly men who appeared to be government secret agents, and three other resident doctors: internist Hsu Chiang (許強), dermatologist Hu Pao-chen (胡寶珍) and ophthalmologist Hu Hsin-lin (胡鑫麟). They were handcuffed, herded onto two jeeps and taken to the Secrecy Bureau (保密局) for questioning. Su was still in his doctor’s robes at
A vaccine to fight dementia? It turns out there may already be one — shots that prevent painful shingles also appear to protect aging brains. A new study found shingles vaccination cut older adults’ risk of developing dementia over the next seven years by 20 percent. The research, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, is part of growing understanding about how many factors influence brain health as we age — and what we can do about it. “It’s a very robust finding,” said lead researcher Pascal Geldsetzer of Stanford University. And “women seem to benefit more,” important as they’re at higher risk of

Last week the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) said that the budget cuts voted for by the China-aligned parties in the legislature, are intended to force the DPP to hike electricity rates. The public would then blame it for the rate hike. It’s fairly clear that the first part of that is correct. Slashing the budget of state-run Taiwan Power Co (Taipower, 台電) is a move intended to cause discontent with the DPP when electricity rates go up. Taipower’s debt, NT$422.9 billion (US$12.78 billion), is one of the numerous permanent crises created by the nation’s construction-industrial state and the developmentalist mentality it

Experts say that the devastating earthquake in Myanmar on Friday was likely the strongest to hit the country in decades, with disaster modeling suggesting thousands could be dead. Automatic assessments from the US Geological Survey (USGS) said the shallow 7.7-magnitude quake northwest of the central Myanmar city of Sagaing triggered a red alert for shaking-related fatalities and economic losses. “High casualties and extensive damage are probable and the disaster is likely widespread,” it said, locating the epicentre near the central Myanmar city of Mandalay, home to more than a million people. Myanmar’s ruling junta said on Saturday morning that the number killed had