Taiwan in Time: Feb.15 to Feb. 21
On the morning of May 28, 1963, Chen Chih-hsiung (陳智雄) was woken up by several executioners, who lifted him up and dragged him out of his cell in the military prison on Qingdao E Road (青島東路).
According to several cell mates, including fellow Taiwanese independence activist Shih Ming-hsiung (施明雄), Chen shouted at the top of his lungs, “Long live Taiwan Independence!” several times before he was taken to the execution grounds.
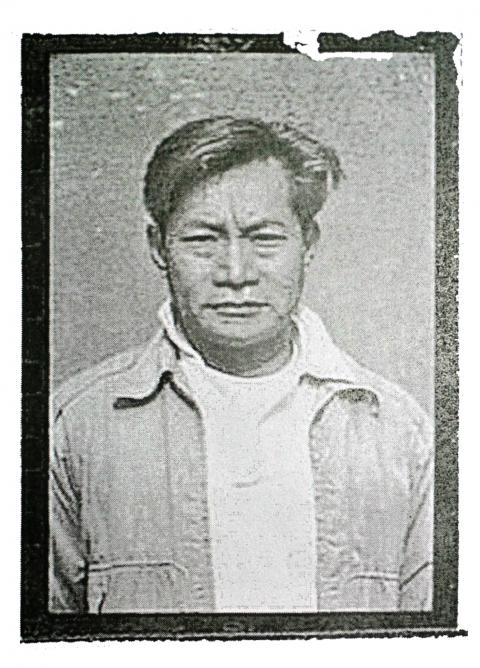

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Shih writes in his book The White Terror in the Dark Ages: A History of Taiwanese Sufferings (白色恐怖黑暗時代:台灣人受難史) that instead of removing Chen’s shackles, the guards cut off his feet so he could not walk to his execution with his head held high.
Another cellmate, Liu Chin-shih (劉金獅), says the guards did so because of Chen’s unwavering belief in his ideals and his refusal to be intimidated by prison officials or the fear of death. Shih writes that during Chen’s many trials, he refused to speak Mandarin, responding exclusively in Hoklo (commonly known as Taiwanese), further angering prison officials.
He was the first independence activist to be executed in Taiwan.

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Born on Feb. 18, 1916 in today’s Pingtung County, much of Chen’s life was spent overseas. He first studied abroad as a Dutch language major at Tokyo University of Foreign Languages and was reportedly able to speak English, Japanese, Dutch, Malay, Hoklo and Mandarin.
When Japan conquered the Dutch East Indies (today’s Indonesia) in 1942, the government sent Chen there as either an ambassador or translator. After Japan lost the war, Chen remained in Indonesia as a jewelry dealer.
When the war for Indonesian independence broke out, Chen assisted in Sukarno’s efforts against the Dutch, who were attempting to re-colonize the area, by providing weapons left behind by the Japanese. He was imprisoned by the Dutch for one year because of his actions. After Sukarno won the war, he reportedly honored Chen in person for his help.

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Several sources indicate that the success of Indonesia’s independence efforts inspired Chen to do the same for his homeland, which had then been taken over by the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT).
Chen worked closely with Thomas Liao (廖文毅), who founded the Japan-based Formosa Democratic Independence Party (台灣民主獨立黨) in 1950. It was reportedly through Chen’s connections that Liao was able to attend the 1955 Asian-African Conference in Indonesia.
In 1956, Liao formed the Republic of Taiwan Provisional Government (台灣共和國臨時政府), still based in Japan, and appointed Chen as its ambassador to Southeast Asia.
Sources differ on whether it was under pressure from the KMT or the Chinese Communist Party, but Chen was arrested by Indonesian authorities. Historian Chen Ching-lee (陳慶立) writes in a book on Liao that Chen was eventually released, but lost his Indonesian passport and was deported.
Officially stateless, no country would accept Chen and he flew back and forth between Indonesia and Japan, eventually ending up in Switzerland. From there, he returned to Japan one final time and joined Liao to continue to work for Taiwanese independence.
But the KMT was watching, and its ambassador to Japan worked with local authorities to arrest Chen and force him to return to Taiwan. Chen Ching-lee writes that the KMT promised Japan that Chen would not be punished.
Chen was released shortly after he landed in Taiwan under the condition that he cease all Taiwanese independence activities.
But Chen didn’t stop. He formed another pro-independence group in 1961 with three stated goals: End the brutal reign of the KMT, restore the political, social and economic rights of Taiwanese and establish a free, happy and prosperous Republic of Taiwan.
In the summer of 1962, Chen was arrested by the Taiwan Garrison Command, charged with rebellion and sentenced to death.
In 2013, Chen’s daughter received a final letter written before his execution. On it were the names of his three children and one sentence, written in Japanese: “I died for the people of Taiwan.”
Taiwan in Time, a column about Taiwan’s history that is published every Sunday, spotlights important or interesting events around the nation that have anniversaries this week.
A vaccine to fight dementia? It turns out there may already be one — shots that prevent painful shingles also appear to protect aging brains. A new study found shingles vaccination cut older adults’ risk of developing dementia over the next seven years by 20 percent. The research, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, is part of growing understanding about how many factors influence brain health as we age — and what we can do about it. “It’s a very robust finding,” said lead researcher Pascal Geldsetzer of Stanford University. And “women seem to benefit more,” important as they’re at higher risk of

Eric Finkelstein is a world record junkie. The American’s Guinness World Records include the largest flag mosaic made from table tennis balls, the longest table tennis serve and eating at the most Michelin-starred restaurants in 24 hours in New York. Many would probably share the opinion of Finkelstein’s sister when talking about his records: “You’re a lunatic.” But that’s not stopping him from his next big feat, and this time he is teaming up with his wife, Taiwanese native Jackie Cheng (鄭佳祺): visit and purchase a

April 7 to April 13 After spending over two years with the Republic of China (ROC) Army, A-Mei (阿美) boarded a ship in April 1947 bound for Taiwan. But instead of walking on board with his comrades, his roughly 5-tonne body was lifted using a cargo net. He wasn’t the only elephant; A-Lan (阿蘭) and A-Pei (阿沛) were also on board. The trio had been through hell since they’d been captured by the Japanese Army in Myanmar to transport supplies during World War II. The pachyderms were seized by the ROC New 1st Army’s 30th Division in January 1945, serving
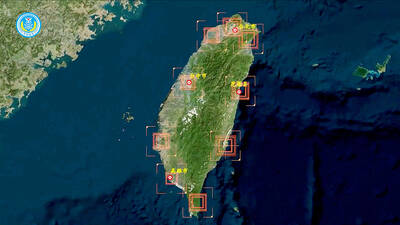
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) last week offered us a glimpse of the violence it plans against Taiwan, with two days of blockade drills conducted around the nation and live-fire exercises not far away in the East China Sea. The PRC said it had practiced hitting “simulated targets of key ports and energy facilities.” Taiwan confirmed on Thursday that PRC Coast Guard ships were directed by the its Eastern Theater Command, meaning that they are assumed to be military assets in a confrontation. Because of this, the number of assets available to the PRC navy is far, far bigger