Celebrating its 20th anniversary, the Godot Theater Company (果陀劇場) has taken on the huge task of staging a Chinese-language version of Othello. The production premiered at the end of last month in Kaohsiung, and yesterday opened at the Metropolitan Hall in Taipei. Godot has had plenty of experience adapting Western works for the Chinese stage, but a work by Shakespeare was an especial challenge, for which they brought in the talents of two of Taiwan’s greatest stage actors, Li Li-qun (李立群) and Chin Shih-jie (金士傑).
The show has been enormously anticipated, and a final dress rehearsal on Thursday played before an almost full house of friends of the company, theatrical insiders and media. The celebratory atmosphere was very much in evidence, but, sad to say, the show itself was less than riveting.
I had gone into the performance with some degree of trepidation, having seen Li in the early rehearsals of the production done up in boot polish makeup and Chin sporting a prosthetic nose that gave him a sly look. This would have been bad enough, but this literalism seems to have been carried through into many other aspects of the production as well, to the considerable detriment of any real dramatic interest.
One of the great challenges of the production had been to produce a script that would be accessible to the masses. Contemporary Chinese vernacular is used throughout, but the writers seemed uncertain of how close they should keep to the letter of the original. It was in the occasional departures, all too few, that the language gained some natural vigor, but otherwise actors where left floundering with lines that were at best plodding, and sometimes so unnatural as to approach parody.
The desire to bring stars to the stage clearly outweighed other considerations. Li and Chin showed flashes of their prodigious talents, but neither could sustain roles for which they were unsuited. Neither was convincing as veteran soldiers of bloody campaigns, for both are bookish and articulate rather than physical actors. Li’s Othello never had a sufficiently commanding physical presence, and Chin worked so hard at being sly, seemingly unconvinced that his words could achieve this effect, that he created a parody that might have been funny had it been intentional.
One of the greatest difficulties that the play failed to overcome is the inherent absurdity of the story. Take away the intricately layered language of Shakespeare, and what is left is the story of a rather stupid and jealous man who kills his wife. As Othello works through his own tortuous logic to convince himself of his wife’s infidelity, there is more laughter than tears among the audience. Without the heroic and the tragic, what’s left? To make the dialogue accessible, the producers have pretty much gutted the play, and the best efforts of the actors could not save it.
All this is not helped by the bombastic score that simply couldn’t leave any emotional point alone, constantly building tension with deep bass notes and underlining tender emotion with caressing violins. Once again, it’s as if the producers can’t trust the script to get the point across. So intrusive was the music, and so crass (one section sounded as if it was lifted from Phantom of the Opera) that it would hardly have been surprising if the characters had suddenly burst into song. It would at least have been diverting, and Godot has a reputation for producing musicals.
Perhaps I shouldn’t have gone into the theater looking for Shakespeare, for he had clearly left the building. What I found was a brave effort to what may have been an inherently impossible task — a serious and accessible production of a Shakespearean tragedy. The most tragic thing about Godot’s Othello was watching two talented actors floundering and eventually being overcome by forces they could no longer control. They were victims of a play that didn’t know where it wanted to go.
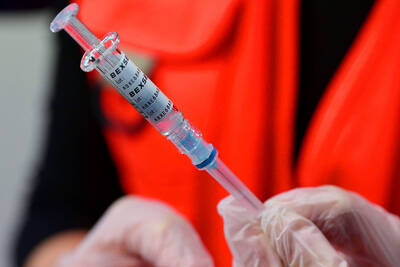
A vaccine to fight dementia? It turns out there may already be one — shots that prevent painful shingles also appear to protect aging brains. A new study found shingles vaccination cut older adults’ risk of developing dementia over the next seven years by 20 percent. The research, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, is part of growing understanding about how many factors influence brain health as we age — and what we can do about it. “It’s a very robust finding,” said lead researcher Pascal Geldsetzer of Stanford University. And “women seem to benefit more,” important as they’re at higher risk of

Last week the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) said that the budget cuts voted for by the China-aligned parties in the legislature, are intended to force the DPP to hike electricity rates. The public would then blame it for the rate hike. It’s fairly clear that the first part of that is correct. Slashing the budget of state-run Taiwan Power Co (Taipower, 台電) is a move intended to cause discontent with the DPP when electricity rates go up. Taipower’s debt, NT$422.9 billion (US$12.78 billion), is one of the numerous permanent crises created by the nation’s construction-industrial state and the developmentalist mentality it

Experts say that the devastating earthquake in Myanmar on Friday was likely the strongest to hit the country in decades, with disaster modeling suggesting thousands could be dead. Automatic assessments from the US Geological Survey (USGS) said the shallow 7.7-magnitude quake northwest of the central Myanmar city of Sagaing triggered a red alert for shaking-related fatalities and economic losses. “High casualties and extensive damage are probable and the disaster is likely widespread,” it said, locating the epicentre near the central Myanmar city of Mandalay, home to more than a million people. Myanmar’s ruling junta said on Saturday morning that the number killed had

Mother Nature gives and Mother Nature takes away. When it comes to scenic beauty, Hualien was dealt a winning hand. But one year ago today, a 7.2-magnitude earthquake wrecked the county’s number-one tourist attraction, Taroko Gorge in Taroko National Park. Then, in the second half of last year, two typhoons inflicted further damage and disruption. Not surprisingly, for Hualien’s tourist-focused businesses, the twelve months since the earthquake have been more than dismal. Among those who experienced a precipitous drop in customer count are Sofia Chiu (邱心怡) and Monica Lin (林宸伶), co-founders of Karenko Kitchen, which they describe as a space where they