If you saw Brian Steidle on the street in Los Angeles, you wouldn't give him a second glance. Dressed the day we meet in the city's Venice district in regulation T-shirt, shades and cargos, he looks much like all the other gym-fit, cropped-haired young men loafing about somewhere between college and middle age. Which is precisely his strength.
Three years ago, fresh out of serving with the US marines in Kosovo and elsewhere, Steidle saw a job opening for a US monitor attached to the African Union peacekeeping mission in the Sudan. "I had no idea," he says. "I was looking for some adventure. My goal was to make money, to have a good time making it and to retire early."
Without knowing it, he was heading into a genocide in the making and towards becoming an unlikely, but highly effective, campaigner. The result is that alongside the big players such as Washington and Beijing, whose political calculations lie behind the new Security Council agreement to send an international force to Sudan's conflict zone, it is a small player in the person of Steidle - with his everyman demeanor and eyewitness evidence - who crucially set the stage by helping to make Sudan's government-sponsored slaughter a cause du jour in the US.
At first, Steidle's Sudan job was a breeze, running a team of three that monitored and reported on the relatively tranquil life of the people of the Nuba mountains. But after seven months, he went to Darfur, a then-obscure region in the west of the African nation, a region about to become infamous for some of the most brutal repression seen on the continent. The conflict, pitting Arab Muslims backed by the Sudanese government against black African Muslims, has claimed an estimated 400,000 lives since it broke out in early 2003.
"I was blown away by what I saw [in Darfur], because nobody knew about it. Not even us, in the same country, 300km away." What he saw is detailed in The Devil Came on Horseback, the book he went on to co-write with his sister Gretchen.
It opens with the heartbreaking account of Steidle's moment of awakening, when he comes upon a baby girl who has been shot in the back but is still alive, being dispassionately offered up to him by her aunt. Steidle does his job: he asks questions about the incident, takes photographs, goes on his way. As soon as his African Union helicopter takes off he begins to berate himself. Why did he not break the rules of his mission and take the girl with him? What would become of her? It is, he writes, the greatest regret of his life, and his recent book is an attempt to make amends.
Which raises the question of whether there is any point in using unarmed observers to monitor cease-fires. Undermanned and underfunded, the African Union's Darfur mission is a case in point, as the Security Council's belated establishment of a fully fledged mission seems to recognize.
Steidle writes that even when the African Union monitors knew the location and timing of impending attacks, no action was taken. Instead, bureaucratic processes prevailed: incidents were logged, reports filed, suppers eaten. He tells the story of how his warnings of an imminent attack by the government-sponsored Janjaweed militia on the village of Hamada were dismissed by one of his commanding officers with the words: "How is it you think you can predict what the Janjaweed will do?" A few days later 107 of the 450 villagers, he writes, were "tortured and murdered. Bodies were strewn along blood-soaked village paths. Infants had been crushed. "
Three years later, Steidle still sounds angry. "We could publish no reports, or lots of reports, and it would still go on," he says. The self-serving dynamic of the monitoring mission even extended to what, in Steidle's eyes, were significant discoveries. He once found himself at an al-Qaeda training camp, a legacy of the days when Osama bin Laden was based in Sudan, surrounded by jumpy men bearing Kalashnikovs. "I got the guys' names, took pictures of them, had the GPS coordinates," he says, clicking his fingers with each point. "I thought, wow, this is going to be big news. Nothing." With hindsight, Steidle understands why nobody moved against the camp: "They would just pop up somewhere else ... . So it's better for us to watch, until we get the head guys. "
Whatever the justifications, the impotence of watching the situation worsen - the helicopters taking off loaded with weapons for the government-sponsored killing squads and returning empty a few hours later, the discovery of rockets adapted to carry tear gas, the catalogue of bodies and villages burned - eventually led Steidle to leave Sudan. Marginalized by a new commander, he decided to take the more than 1,000 photographs he had gathered, along with witness statements, and go home.
"I wanted to forget about it, go hide out in the woods. I thought I'd be watching this on CNN or the BBC, but it wasn't there. So that's when I thought, OK, let's share it." He took his material -- including stark aerial pictures of burning villages, the likes of which the US had never seen from Darfur -- to the New York Times and then to just about any media outlet that would look and listen, as well as members of congress and US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice.
Among the hundreds of thousands of US soldiers and support staff who have served overseas in the past decade and a half -- in the Kuwait war, in Bosnia, in Afghanistan, and now in Iraq -- Steidle is one of a handful who have taken action back home over the catastrophic plight of the people they left behind. His military training -- he grew up in a military family, and says he knew from an early age that he wanted to serve in the Marines -- prevents him from speaking ill of his elected superiors, but the frustration is obvious: "We should have stopped this a long time ago."
When we speak again, after last month's decision by the UN to send a peacekeeping force with a mandate to protect civilians, he sounds a bit more cheerful. "It's a big step in the right direction," he says by phone from San Francisco. "We've got to make sure that the UN has the authority to protect civilians and villages, that they have the proper mandate. But at the same time there are a lot of other things that could be implemented" -- such as keeping pressure on China, initiating prosecutions at the International Criminal Court, making sure Khartoum suffers consequences if it obstructs the UN.
Despite his mistrust of Khartoum, he doesn't seem to think it has been let off lightly. "Concessions have been made," he says, "but all the key countries have said that if Sudan does not honor them, they will undertake the next step."
While Steidle's campaigning ignited US public awareness of the Darfur genocide, it also alienated aid agencies and some elements in the US State Department, which feel his outspokenness has harmed their mission.
"I was told by a state department official that the agencies can't get their [Sudan] visas in a timely manner because of me," he says. "I was like, too bad. You have to wait two weeks instead of 48 hours. Too bad. The world should have known about a genocide." He cites the recent resignation of the director of the Save Darfur Coalition, the broad-based advocacy group that has spearheaded the high-profile campaign in the US, as evidence of the Sudanese government's success in intimidating the aid agencies into silence. "We can provide food and tents forever, it's not going to stop the situation. It has to go hand in hand with advocacy."
Steidle plans to keep on going. A documentary based on his experiences and using some of his pictures, is showing in the US.
As with so much to do with action over Darfur, the model for the next stage of Steidle's protest is Rwanda: he is in California lobbying studios to make a feature film. "Feature films reach millions of people. Even if you haven't seen Blood Diamond you know what it's about. The same with Hotel Rwanda. Hollywood is a great tool." Steidle has talked to Don Cheadle, star of Hotel Rwanda and a big voice in the Darfur campaign, as well as Steven Spielberg, who used his clout as an artistic adviser to the 2008 Beijing Olympics to urge China to reappraise its oil-fuelled relationship with the government of Sudan.
I ask Steidle what stays with him from Sudan. Instead of an atrocity story, he talks about the time he and a documentary crew were talking to Darfur refugees in Chad. "When we interviewed the people," he says, "we'd put the camera on them and say, all right, now speak to America, tell them directly what you want. And they'd look at the camera and they'd say, thank you for everything you've done for us."
"I wanted to forget about it, go hide out in the woods. I thought I'd be watching this on CNN or the BBC, but it wasn't there. So that's when I thought, OK, let's share it." He took his material - including stark aerial pictures of burning villages, the likes of which the US had never seen from Darfur - to the New York Times and then to just about any media outlet that would look and listen, as well as members of congress and US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice.
Among the hundreds of thousands of US soldiers and support staff who have served overseas in the past decade and a half - in the Kuwait war, in Bosnia, in Afghanistan, and now in Iraq - Steidle is one of a handful who have taken action back home over the catastrophic plight of the people they left behind. His military training - he grew up in a military family, and says he knew from an early age that he wanted to serve in the Marines - prevents him from speaking ill of his elected superiors, but the frustration is obvious: "We should have stopped this a long time ago."
When we speak again, after last month's decision by the UN to send a peacekeeping force with a mandate to protect civilians, he sounds a bit more cheerful. "It's a big step in the right direction," he says by phone from San Francisco. "We've got to make sure that the UN has the authority to protect civilians and villages, that they have the proper mandate. But at the same time there are a lot of other things that could be implemented" - such as keeping pressure on China, initiating prosecutions at the International Criminal Court, making sure Khartoum suffers consequences if it obstructs the UN.
Despite his mistrust of Khartoum, he doesn't seem to think it has been let off lightly. "Concessions have been made," he says, "but all the key countries have said that if Sudan does not honor them, they will undertake the next step."
While Steidle's campaigning ignited US public awareness of the Darfur genocide, it also alienated aid agencies and some elements in the US State Department, which feel his outspokenness has harmed their mission.
"I was told by a state department official that the agencies can't get their [Sudan] visas in a timely manner because of me," he says. "I was like, too bad. You have to wait two weeks instead of 48 hours. Too bad. The world should have known about a genocide." He cites the recent resignation of the director of the Save Darfur Coalition, the broad-based advocacy group that has spearheaded the high-profile campaign in the US, as evidence of the Sudanese government's success in intimidating the aid agencies into silence. "We can provide food and tents forever, it's not going to stop the situation. It has to go hand in hand with advocacy."
Steidle plans to keep on going. A documentary based on his experiences and using some of his pictures, is showing in the US.
As with so much to do with action over Darfur, the model for the next stage of Steidle's protest is Rwanda: he is in California lobbying studios to make a feature film. "Feature films reach millions of people. Even if you haven't seen Blood Diamond you know what it's about. The same with Hotel Rwanda. Hollywood is a great tool." Steidle has talked to Don Cheadle, star of Hotel Rwanda and a big voice in the Darfur campaign, as well as Steven Spielberg, who used his clout as an artistic adviser to the 2008 Beijing Olympics to urge China to reappraise its oil-fuelled relationship with the government of Sudan.
I ask Steidle what stays with him from Sudan. Instead of an atrocity story, he talks about the time he and a documentary crew were talking to Darfur refugees in Chad. "When we interviewed the people," he says, "we'd put the camera on them and say, all right, now speak to America, tell them directly what you want. And they'd look at the camera and they'd say, thank you for everything you've done for us."
A vaccine to fight dementia? It turns out there may already be one — shots that prevent painful shingles also appear to protect aging brains. A new study found shingles vaccination cut older adults’ risk of developing dementia over the next seven years by 20 percent. The research, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, is part of growing understanding about how many factors influence brain health as we age — and what we can do about it. “It’s a very robust finding,” said lead researcher Pascal Geldsetzer of Stanford University. And “women seem to benefit more,” important as they’re at higher risk of

Eric Finkelstein is a world record junkie. The American’s Guinness World Records include the largest flag mosaic made from table tennis balls, the longest table tennis serve and eating at the most Michelin-starred restaurants in 24 hours in New York. Many would probably share the opinion of Finkelstein’s sister when talking about his records: “You’re a lunatic.” But that’s not stopping him from his next big feat, and this time he is teaming up with his wife, Taiwanese native Jackie Cheng (鄭佳祺): visit and purchase a

April 7 to April 13 After spending over two years with the Republic of China (ROC) Army, A-Mei (阿美) boarded a ship in April 1947 bound for Taiwan. But instead of walking on board with his comrades, his roughly 5-tonne body was lifted using a cargo net. He wasn’t the only elephant; A-Lan (阿蘭) and A-Pei (阿沛) were also on board. The trio had been through hell since they’d been captured by the Japanese Army in Myanmar to transport supplies during World War II. The pachyderms were seized by the ROC New 1st Army’s 30th Division in January 1945, serving
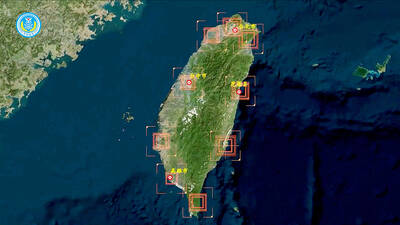
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) last week offered us a glimpse of the violence it plans against Taiwan, with two days of blockade drills conducted around the nation and live-fire exercises not far away in the East China Sea. The PRC said it had practiced hitting “simulated targets of key ports and energy facilities.” Taiwan confirmed on Thursday that PRC Coast Guard ships were directed by the its Eastern Theater Command, meaning that they are assumed to be military assets in a confrontation. Because of this, the number of assets available to the PRC navy is far, far bigger