ith newly discovered signs of liquid water, a moon of Saturn joins the small, highly select group of places in the solar system that could plausibly support life.
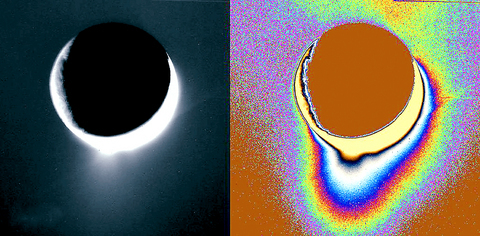
The moon, Enceladus, is only 400km wide, and planetary scientists expected that it would be nothing more than a frozen chunk of ice and rock. Instead, NASA's Cassini spacecraft has spotted eruptions of icy crystals, which hint at pockets of liquid water near the surface.
"It's startling," said Dr. Carolyn Porco of the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado, leader of the imaging team for Cassini. Nine scientific papers about Enceladus appeared in Friday's issue of the journal Science. "I wouldn't be surprised see to the planetary community clamoring for a future exploratory expedition to land on the south polar terrain of Enceladus," said Porco, lead author of one of the Science papers. "We have found an environment that is potentially suitable for living organisms."
PHOTOS: NY TIMES NEWS SERVICE
Life requires at least three essential ingredients -- water, heat and carbon-based molecules -- and Enceladus may possess all three. As Cassini flew through the plumes of tiny ice crystals rising into space from the eruptions, it also detected simple carbon-based molecules like methane and carbon dioxide, which suggest more complicated carbon molecules might lie on the moon's surface.
The lack of a crater suggests that the heat is not the result of a meteor impact. Based on the initial observations, some scientists think that this warm region near the south pole may have somehow persisted for millions or billions of years, sufficient time for life to arise.
"It's an exciting place," said James Head, a professor of geological sciences at Brown University, who was not involved with any of the research reported in Science. "That's what exploration is all about. You go out there. It isn't A. It isn't B. It isn't C. It's D, none of the above."
Planetary scientists immediately started pointing to the discovery as an argument for preserving and continuing NASA's space science efforts. The agency's proposed budget would cut US$3 billion from space science over the next five years to help pay for the completion of the space station and plans to send astronauts back to the moon. NASA's astrobiology institute, which finances research on the possibility of life elsewhere in the solar system and universe, is to see its budget cut in half.
"They must now provide sufficient funds for NASA to conduct both human flight and robotic exploration missions," Porco said. "Right now, the funding is inadequate."
Cassini flew by Enceladus three times last year. For the first two fly-bys, Cassini's observations of the Enceladus' equatorial region turned up nothing odd -- except that it seemed to be deflecting Saturn's magnetic fields. That implied that Enceladus was somehow generating its own magnetic field.
NASA tweaked the trajectory of Cassini's July fly-by to pass within about 150km of Enceladus' surface. For the first time, the spacecraft got a look at the south pole, which turned out to be surprisingly smooth compared to the pockmarked northern hemisphere. And it was warm.
The expectation was that the temperature would be about -330? Fahrenheit. It turned out to be more than 100? warmer. "Which is fairly dramatic and blew us away when we first saw it," said John Spencer, a planetary scientist at the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder and a team member working with a Cassini instrument that measures infrared emissions. "It's a lot of heat to come out of such a tiny object."
Images of the moon also showed towering plumes of ice crystals coming off at high speed from the surface. The jets seem to originate from fissures near the south pole, Porco said.
Porco said their calculations eliminated the possibility that the particles were produced by warm vapor rising off warm ice at the surface. The best explanation, she said, is that pockets of liquid water exist under high pressure below a few tens of meters of ice. When the ice ruptures, the water shoots out and immediately freezes into ice crystals.
"We think we've got geysers," Porco said.
A small body like Enceladus would be unlikely to hold enough radioactive elements to produce continuing warmth. A more likely explanation is that the gravitational tugging on Enceladus by Saturn and another moon, Dione, squishes Enceladus, and that friction creates the heat. Another mystery is why the heat is concentrated around the south pole.

That US assistance was a model for Taiwan’s spectacular development success was early recognized by policymakers and analysts. In a report to the US Congress for the fiscal year 1962, former President John F. Kennedy noted Taiwan’s “rapid economic growth,” was “producing a substantial net gain in living.” Kennedy had a stake in Taiwan’s achievements and the US’ official development assistance (ODA) in general: In September 1961, his entreaty to make the 1960s a “decade of development,” and an accompanying proposal for dedicated legislation to this end, had been formalized by congressional passage of the Foreign Assistance Act. Two

Despite the intense sunshine, we were hardly breaking a sweat as we cruised along the flat, dedicated bike lane, well protected from the heat by a canopy of trees. The electric assist on the bikes likely made a difference, too. Far removed from the bustle and noise of the Taichung traffic, we admired the serene rural scenery, making our way over rivers, alongside rice paddies and through pear orchards. Our route for the day covered two bike paths that connect in Fengyuan District (豐原) and are best done together. The Hou-Feng Bike Path (后豐鐵馬道) runs southward from Houli District (后里) while the

March 31 to April 6 On May 13, 1950, National Taiwan University Hospital otolaryngologist Su You-peng (蘇友鵬) was summoned to the director’s office. He thought someone had complained about him practicing the violin at night, but when he entered the room, he knew something was terribly wrong. He saw several burly men who appeared to be government secret agents, and three other resident doctors: internist Hsu Chiang (許強), dermatologist Hu Pao-chen (胡寶珍) and ophthalmologist Hu Hsin-lin (胡鑫麟). They were handcuffed, herded onto two jeeps and taken to the Secrecy Bureau (保密局) for questioning. Su was still in his doctor’s robes at
Mirror mirror on the wall, what’s the fairest Disney live-action remake of them all? Wait, mirror. Hold on a second. Maybe choosing from the likes of Alice in Wonderland (2010), Mulan (2020) and The Lion King (2019) isn’t such a good idea. Mirror, on second thought, what’s on Netflix? Even the most devoted fans would have to acknowledge that these have not been the most illustrious illustrations of Disney magic. At their best (Pete’s Dragon? Cinderella?) they breathe life into old classics that could use a little updating. At their worst, well, blue Will Smith. Given the rapacious rate of remakes in modern