The world's first cloning of a dog has raised concerns that scientists are one step closer to replicating human embryos, despite the breakthrough pointing to treatments for currently incurable human diseases.
A group of scientists from Seoul National University last week unveiled their creation, a black and white Afghan hound named Snuppy that is genetically identical to its three-year-old "father."
But while geneticists hailed the breakthrough as a step towards beating human diseases, others called for a worldwide ban on human cloning, saying that the pup had brought the human eventuality nearer.
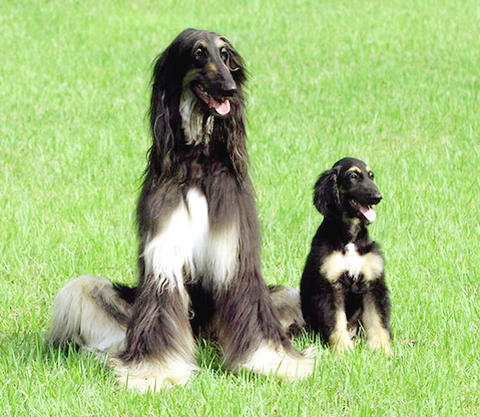

PHOTO: AFP
The achievement of the team led by Professor Hwang Woo-suk is considered so significant because many canine diseases such as diabetes, cancer, dementia and problems in heart muscles, hips and joints are similar to those in humans.
Professor Kong Il-keun, a cloning expert at Suncheon National University, said cloning dogs had immense clinical value because canines have 203 genes that can be used for studying human diseases while the pig has only 65.
King Chow, assistant professor of biotechnology at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology welcomed the latest advance, but warned that the scientific community needed to be on guard against possible human cloning.
"The development of the technology is a good thing in itself but how we monitor it and who we allow to use it will be of great importance," he said.
"If it has been done to help research and understanding of how humans developed from a single cell -- an area in which there are huge holes in our understanding -- then this is a very important development.
"But if it is to be taken further and applied simply to make multiple clones -- then I have strong objections."
In order to create Snuppy -- short for Seoul National University Puppy -- the team had to create 1,095 canine embryos that were transferred into 123 surrogate bitches resulting in three successful pregnancies.
One foetus miscarried but two others were delivered, including Snuppy on April 24. The other cloned dog died after 22 days from pneumonia.
Gerald Schatten of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Hwang's research planning and technology advisor, said the poor success rate justified a ban on human cloning.
"Because this again shows that reproductive cloning is unsafe and inefficient, we call for a worldwide ban on human reproductive cloning, which is also unethical," said Schatten,
Since scientists first cloned a sheep named Dolly in 1997, researchers have gone on to clone mice, cats, goats, pigs, mules, horses and deer.
But of all mammals, the cloning of dogs is technically the most challenging because of the difficulty of acquiring mature eggs.
Some experts say the cloning of a dog demonstrates that most of key techniques needed to clone humans are now available.
"Bring me human eggs, the necessary social consensus and legal permission and I can get you your replica within a year," said Park Se-pill, a senior researcher of Maria Biotech and a top cloning expert.
"In contrast to widespread public belief, cloning a human is much easier than cloning a cow or a pig," Park said.

Eric Finkelstein is a world record junkie. The American’s Guinness World Records include the largest flag mosaic made from table tennis balls, the longest table tennis serve and eating at the most Michelin-starred restaurants in 24 hours in New York. Many would probably share the opinion of Finkelstein’s sister when talking about his records: “You’re a lunatic.” But that’s not stopping him from his next big feat, and this time he is teaming up with his wife, Taiwanese native Jackie Cheng (鄭佳祺): visit and purchase a

April 7 to April 13 After spending over two years with the Republic of China (ROC) Army, A-Mei (阿美) boarded a ship in April 1947 bound for Taiwan. But instead of walking on board with his comrades, his roughly 5-tonne body was lifted using a cargo net. He wasn’t the only elephant; A-Lan (阿蘭) and A-Pei (阿沛) were also on board. The trio had been through hell since they’d been captured by the Japanese Army in Myanmar to transport supplies during World War II. The pachyderms were seized by the ROC New 1st Army’s 30th Division in January 1945, serving
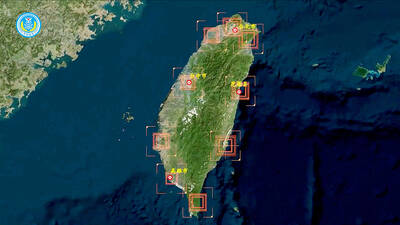
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) last week offered us a glimpse of the violence it plans against Taiwan, with two days of blockade drills conducted around the nation and live-fire exercises not far away in the East China Sea. The PRC said it had practiced hitting “simulated targets of key ports and energy facilities.” Taiwan confirmed on Thursday that PRC Coast Guard ships were directed by the its Eastern Theater Command, meaning that they are assumed to be military assets in a confrontation. Because of this, the number of assets available to the PRC navy is far, far bigger

The 1990s were a turbulent time for the Chinese Nationalist Party’s (KMT) patronage factions. For a look at how they formed, check out the March 2 “Deep Dives.” In the boom years of the 1980s and 1990s the factions amassed fortunes from corruption, access to the levers of local government and prime access to property. They also moved into industries like construction and the gravel business, devastating river ecosystems while the governments they controlled looked the other way. By this period, the factions had largely carved out geographical feifdoms in the local jurisdictions the national KMT restrained them to. For example,