There hasn't been much change in the world of beverage cans since the stay-on tab replaced the ring-pull tab in the late 1980s. But now Japan has put a new twist on the old can, and it's coming your way.
The "bottle can," an aluminum can with a screw cap, has taken Japan by storm, as consumers show a growing thirst for its novelty value and the ability to re-close it like a bottle.
Now the can is set to take on international markets.

PHOTO: REUTERS
"Many customers in the US are interested in this new form of packaging, and in Europe too several companies are keen," Yoshiaki Adachi, head of research at privately owned Daiwa Can Company, Japan's largest can maker, said.
Since Daiwa Can launched the new can in late 1999, Japanese bottle can sales have jumped to 1.7 billion from last year, from 240 million in 2000 and are set to grow to two billion this year.
Drink makers in the US and Europe are vying to get their hands on the new technology, and Daiwa Can is now selling the cans to Kraft Foods Inc, which is using them for its "Capri Sun" children's fruit drink in the US.
"The new Capri Sun Island Refreshers line is the first in the US to launch a juice drink in a revolutionary aluminum `bottle can,'" Kraft, the largest US food maker, said on its Web site.
If Daiwa Can can, more will follow.
Adachi said his firm is in talks with other potential US customers, adding that negotiations were under way with Ball Corporation, one of the largest US metal can manufacturers, about producing the bottle-cans in the US.
"There is no doubt that screw-top cans will take off outside Japan, both in the US and Europe, though so far can makers there have not had the confidence to invest in them," said John Nutting, editor-in-chief of London-based The Canmaker magazine.
He said the new cans could boost a global market of 235 billion cans a year, partly because re-sealable cans could reclaim shelf space in motorway service areas. "Regular cans are not re-closable, so drivers do not buy them," Nutting said.
The cans, which come in a range of sizes up to 500ml, are a hit in Japan, and not only with drivers.
"They're so much better than regular cans. You can take a sip, close them, and put them in your bag," said Mamta Reid, a language teacher in Tokyo.
Others just buy them for the look.
"If I have a choice of buying a Coke in a plastic bottle or a screw-cap can, I buy the can. It looks good, it's space-age packaging," said Gavin Skinstad, a Tokyo-based banker.
Industry watchers question whether consumers outside Japan will be willing to pay more for a bottle-can that costs about twice as much as an ordinary aluminum can.
"Elsewhere in the world, people less easily accept having to pay more for attractive packaging," Nutting said.
Smaller bottle cans, up to 300ml, look like a regular can with a conical top and a screw-cap, but the bigger sizes look more like an aluminum bottle.
Can makers tout their technical advantages.
"These cans are better than plastic bottles at shutting out sunlight and oxygen," said Toru Komano, a spokesman for Mitsubishi Materials, Japan's third-largest can-maker, which started making bottle cans in 2002.
The aluminum bottle cans are also lighter than plastic bottles and easier to recycle, producers said.
Last year, about 8 percent of the estimated 18 billion cans sold in Japan had a screw cap, and that number is set to grow to 14 percent this year, Komano said.
The new cans were first used by Japanese beverage makers such as Kirin Brewery Co Ltd, but a big breakthrough came in June ;last year, when Coca-Cola (Japan) Company started selling Coke, Fanta and Sprite in 275ml bottle cans through its ubiquitous vending machines.
For now, Coca-Cola Co does not use the cans in other countries, a Coca-Cola Japan spokeswoman said.
Japanese can makers expect the bottle can will help their industry win back market share from plastic bottles.
The use of plastic bottles (called "PET" bottles, after the kind of plastic they are made from) in Japan has soared since 1996, when bottle producers dropped an environment-friendly gentleman's agreement not to produce small bottles.
From just 2.2 billion in 1997, consumption of PET bottles rose to 8.8 billion last year, mainly at the expense of steel cans, whose numbers crumpled to 16.1 billion per year from 21.5 billion, according to Mitsubishi Materials.
Over the same period, aluminum cans held their ground with sales stable at about 18 billion cans per year, but the fizz was out of the market.
"The plastic bottle makers started invading our market. We developed the bottle can to restore market share for metal packaging," Daiwa Can's Adachi said.
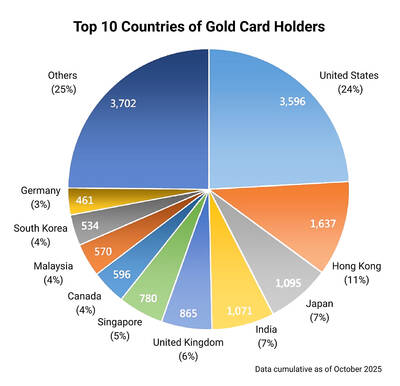
Seven hundred job applications. One interview. Marco Mascaro arrived in Taiwan last year with a PhD in engineering physics and years of experience at a European research center. He thought his Gold Card would guarantee him a foothold in Taiwan’s job market. “It’s marketed as if Taiwan really needs you,” the 33-year-old Italian says. “The reality is that companies here don’t really need us.” The Employment Gold Card was designed to fix Taiwan’s labor shortage by offering foreign professionals a combined resident visa and open work permit valid for three years. But for many, like Mascaro, the welcome mat ends at the door. A

The Western media once again enthusiastically forwarded Beijing’s talking points on Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi’s comment two weeks ago that an attack by the People’s Republic of China (PRC) on Taiwan was an existential threat to Japan and would trigger Japanese military intervention in defense of Taiwan. The predictable reach for clickbait meant that a string of teachable moments was lost, “like tears in the rain.” Again. The Economist led the way, assigning the blame to the victim. “Takaichi Sanae was bound to rile China sooner rather than later,” the magazine asserted. It then explained: “Japan’s new prime minister is
NOV. 24 to NOV. 30 It wasn’t famine, disaster or war that drove the people of Soansai to flee their homeland, but a blanket-stealing demon. At least that’s how Poan Yu-pie (潘有秘), a resident of the Indigenous settlement of Kipatauw in what is today Taipei’s Beitou District (北投), told it to Japanese anthropologist Kanori Ino in 1897. Unable to sleep out of fear, the villagers built a raft large enough to fit everyone and set sail. They drifted for days before arriving at what is now Shenao Port (深奧) on Taiwan’s north coast,

Divadlo feels like your warm neighborhood slice of home — even if you’ve only ever spent a few days in Prague, like myself. A projector is screening retro animations by Czech director Karel Zeman, the shelves are lined with books and vinyl, and the owner will sit with you to share stories over a glass of pear brandy. The food is also fantastic, not just a new cultural experience but filled with nostalgia, recipes from home and laden with soul-warming carbs, perfect as the weather turns chilly. A Prague native, Kaio Picha has been in Taipei for 13 years and