Every Taiwanese child knows that the Dutch once came to Taiwan. They also know that they were driven away by Koxinga, a pirate turned patriot of Chinese-Japanese descent who was little more than an opportunist. It's a fact nonetheless that gives rise to warm feelings of nationalism at colonial powers getting their just deserts.
Scratch at this veneer of knowledge and most people know little more. And these days, beyond the ubiquitous presence of Philips household electronics, few people know there remains a significant Dutch presence on the island.
The reason the Dutch are here hasn't changed much. Their arrival in 1624 coincided with a conflict of interest between European powers that were positioning themselves to benefit from new Asian markets and from the sale of exotic commodities such as silk and spices. In 2000, western corporations still drool over the riches that Asian markets are expected to yield. The rules of the game may have become a bit more genteel, but fundamentally they remain the same. "The commercial spirit remains strong," says Paul Zeven, CEO of Philips Electronics, Taiwan, with a wry smile.

HISTORICAL PRINTS: COURTESY OF PAUL OVERMAAT
Zeven points out that Philips is now heavily invested in Taiwan's high-tech industry, in which it hopes to play a leading role. Yet despite its 30 years on the island and more than 10,000 staff, its presence is still relatively low-key. This was not always the case with the Dutch. While in Taiwan, they established two of the island's most imposing fortresses -- Fort Zeelandia in Tainan and Fort San Domingo in Tamsui.
Detailed records
But apart from ruins, what else did the Dutch leave behind? Cao Yung-ho (曹永和), a specialist on the Dutch maritime empire at Academia Sinica, says you only have to stand in the countryside and look around. The fields of rice and sugarcane, two of Taiwan's most important crops, are primarily due to Dutch exploration of the island's agriculture.

HISTORICAL PRINTS: COURTESY OF PAUL OVERMAAT
Another permanent and valuable contribution made by the Dutch was in providing some of the earliest detailed descriptions of life in Taiwan. The Dutch in Fort Zeelandia kept "day books," similar to a ship's log, which became invaluable historical documents in the study of Taiwan's early history.
For a taste of what the Dutch left behind, organizers of a recently opened exhibit titled "From Holland to Formosa" have created the newspaper-like Formosa Gazetteer, which offers extracts from historical records. Speaking of the unhealthy conditions that faced the Dutch, there is a matter-of-fact comment from 1649 that "many people in the service of the Dutch East India company died again this year in the southern villages on the island [from disease]." And for Oct. 25, 1645, records show that the "Chinese who are continuously inciting the natives have been subdued and chased away." These minor but often fatal incidents were the daily trials that comprised life and death for many Dutch living in Taiwan.
Based on other materials left by the Dutch, the Shung Ye Museum of Formosan Aborigines (順益台灣原住民博物館) has already published one of the earliest studies of Taiwan's aborigines. This is available in English with a Chinese version in preparation.

HISTORICAL PRINTS: COURTESY OF PAUL OVERMAAT
One of the most important results the preservation of these early materials is the reaffirmation of Taiwan's fundamentally multicultural roots. Everything about "From Holland to Formosa" seems designed to emphasize the cooperative nature of Taiwan's development. The venue itself is virtually a distillation of Taiwan's relationship with the west. The Dutch built Fort San Domingo, but the name is taken from an earlier Spanish stockade. The building was taken over by the British in 1860 and was not formally transferred to the ROC government until 1980.
Monumental venue
Holding the exhibition at this historic site has also inspired the Taipei Civil Affairs Department to alter its perceptions of what can be achieved with Taiwan's historic monuments. This is the first time that the venue has been loaned out for such a purpose, largely due to the efforts of Robin Ruizendaal, director of the Holland Festival and an organizer of the event.

HISTORICAL PRINTS: COURTESY OF PAUL OVERMAAT
Moreover, during the exhibition, the grounds of Fort San Domingo will be opened at night for the first time (each Saturday). This has partially been made possible by Philips, who has provided lighting for inside and outside the fort. Lin Tsyr-ling (林慈玲), the newly appointed head of the Civil Affairs Department, is currently negotiating to have the external lighting loaned by Philips made into permanent fixtures to allow for regular night openings to make this heritage site a more dynamic tourism location.
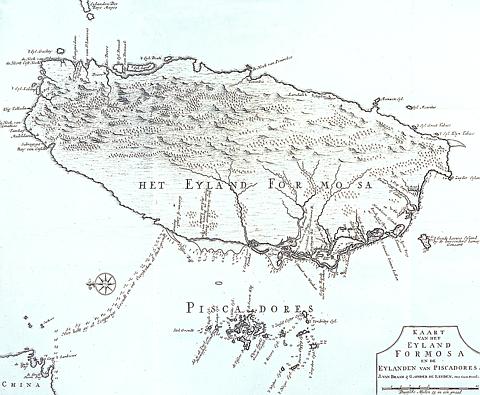
The exhibition organizers have gone out of their way to make the event truly accessible, with a particular emphasis on young visitors. The exhibition is introduced by four cartoon children, who lead the way through an exploration of the Dutch and their lives and concerns in Taiwan. These children form part of a dynamic interface between the exhibits and the audience. After all, as Ruizendaal points out, "one map of Taiwan looks pretty much like another," unless you do something with the arrangement of objects to highlight points of interest.
As for the bigger picture, Seibe Schuur of the Netherlands Trade and Investment Office saw the project as an affirmation of the cooperation between Taiwan and the Netherlands. "Taiwan has always been at a crossroads of many cultures," he says. "There are lessons we can learn from the past that can be applied to the future."

ILLUSTRATION: COURTESY OF NISAN WU
For your information:
What: From Formosa to Holland
An exhibition of 17th century Dutch culture
HISTORICAL PRINTS: COURTESY OF PAUL OVERMAAT
When: Until June 30
Where: Fort San Domingo (Hung Mao Cheng, 紅毛城), Tamsui

On April 26, The Lancet published a letter from two doctors at Taichung-based China Medical University Hospital (CMUH) warning that “Taiwan’s Health Care System is on the Brink of Collapse.” The authors said that “Years of policy inaction and mismanagement of resources have led to the National Health Insurance system operating under unsustainable conditions.” The pushback was immediate. Errors in the paper were quickly identified and publicized, to discredit the authors (the hospital apologized). CNA reported that CMUH said the letter described Taiwan in 2021 as having 62 nurses per 10,000 people, when the correct number was 78 nurses per 10,000

As we live longer, our risk of cognitive impairment is increasing. How can we delay the onset of symptoms? Do we have to give up every indulgence or can small changes make a difference? We asked neurologists for tips on how to keep our brains healthy for life. TAKE CARE OF YOUR HEALTH “All of the sensible things that apply to bodily health apply to brain health,” says Suzanne O’Sullivan, a consultant in neurology at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery in London, and the author of The Age of Diagnosis. “When you’re 20, you can get away with absolute

May 5 to May 11 What started out as friction between Taiwanese students at Taichung First High School and a Japanese head cook escalated dramatically over the first two weeks of May 1927. It began on April 30 when the cook’s wife knew that lotus starch used in that night’s dinner had rat feces in it, but failed to inform staff until the meal was already prepared. The students believed that her silence was intentional, and filed a complaint. The school’s Japanese administrators sided with the cook’s family, dismissing the students as troublemakers and clamping down on their freedoms — with

As Donald Trump’s executive order in March led to the shuttering of Voice of America (VOA) — the global broadcaster whose roots date back to the fight against Nazi propaganda — he quickly attracted support from figures not used to aligning themselves with any US administration. Trump had ordered the US Agency for Global Media, the federal agency that funds VOA and other groups promoting independent journalism overseas, to be “eliminated to the maximum extent consistent with applicable law.” The decision suddenly halted programming in 49 languages to more than 425 million people. In Moscow, Margarita Simonyan, the hardline editor-in-chief of the