From the outside, the rustic red-brick mill on a bend in Maine’s Penobscot River resembles any other struggling US pulp and paper mill.
But along with its usual business of pulp-making, the century-old mill is doing something unprecedented: Developing technology to produce bio-butanol, a jet fuel, from parts of trees that would otherwise go to waste, one of the world’s first to do so.
Production is still two years away, but the reinvention of Maine’s Old Town Fuel & Fiber mill is already drawing interest as a potential model for a new wave of biofuel companies that could slash dependence on oil, create jobs and reduce the emissions that lead to global warming.

PHOTO: REUTERS
Loggers, a fading way of life in rugged northern US and Canada, see the mill as a lifeline for their crippled industry. Environmentalists see it as a test of the Obama administration’s push for a big expansion in biofuels.
And chemical and oil companies are waiting to see if the mill can do what none has done before by extracting sugars from wood chips into a biofuel that many regard as more efficient than corn-based ethanol as a possible substitute for gasoline.
“There has been a lot of interested parties in what we are doing here,” Old Town president Dick Arnold said. “There have been several oil companies that have been interested in our extract and production of biofuels. There has been a number of chemical companies that have expressed the same desire.”

PHOTO: REUTERS
Like its once-mighty peers, Old Maine’s mill has suffered in recent years from declining pulp prices and loss of market share to Chinese and Latin American rivals. Georgia-Pacific Llc, the maker of Quilted Northern bathroom tissue, shut it in May 2006, laying off all 400 workers. A group of investors known as Red Shield bought it a few months later.
Red Shield won a US$30 million grant from the US Department of Energy to work with the nearby University of Maine on a pilot ethanol production plant, but they ran out of cash and filed for bankruptcy last year, shutting the plant again.
Enter Lynn Tilton, a New York venture capitalist who owns one of the nation’s largest helicopter makers. Tilton’s Patriarch Partners bought the mill in November, invested about US$40 million and shifted its focus to cellulosic bio-butanol.
Tilton can use bio-butanol in her own helicopter and aircraft businesses but is eyeing a potentially huge market after Congress decreed that the United States must use 79.5 billion liters of “advanced” biofuels such as cellulosic ethanols, bio-butanol and “green gasoline” a year by 2022.
Whether the technology takes off comes down to cost — and to corn. For much of the last decade, federal officials have touted the potential of corn ethanol as the best substitute for gasoline, but critics question that assumption, noting it corrodes pipelines and raises food prices.
Bio-butanol, a relative of ethanol, is less corrosive and easier to mix with gasoline. Unlike ethanol, it can be transported by pipeline. And its energy content is about 30 percent higher than ethanol’s. If regulations allow, it could be pumped into a fuel tank with no changes to a car engine.
Butanol is also used as a petrochemical in brake fluids, paint thinners and plastics. Its supporters include chemicals maker DuPont Co and oil giant BP Plc, which have formed a joint venture to make bio-butanol.
“It’s really comparable to gasoline,” said Mark Bunger, a biofuels analyst at Lux Research, a Boston consulting firm specializing in emerging technologies. “The issue has been that ethanol is easier to make, it’s just not easier to use. Butanol doesn’t have those same restrictions.”
“For a lot of chemical reasons, it’s a good alternative. If you’re a venture capital company and you said you are going to be making ethanol, I would say: ‘Do you have another idea?’ But if they are really focusing on butanol, that is a smart move,” he said.
He cautioned, however, that it remains unclear if bio-butanol can compete on cost with oil or substitutes like ethanol without government subsidies.
“A lot more research and technical development is needed to make it cost competitive,” he said.
Other companies are trying, such as startups Tetravitae Bioscience in Chicago and Cobalt Biofuels in Mountain View, California. But Old Town is the first to do so with a fully functioning timber mill that already generates cash flow by selling traditional pulp to paper companies. Bio-butanol will be derived from wood that would have gone to waste in pulp production, or have been left on the forest floor as unusable by loggers.
“I wouldn’t go deep into a hole without the ability to generate cash flow on what we do now,” Tilton said. “That is the beauty of this. We are not building a startup facility to create ethanol where you are out US$300 million before you start creating any kind of cash flow.”
Already the plant has put in place a system for extracting sugars from the wood and expect by the end of the year to start construction of a biorefinery to turn it into butanol. Tilton says the mill will need US$75 million to meet its target of producing butanol in two years.
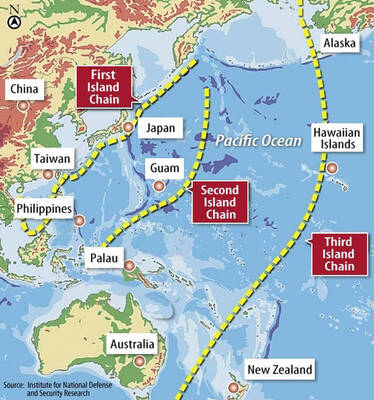
The US government has signed defense cooperation agreements with Japan and the Philippines to boost the deterrence capabilities of countries in the first island chain, a report by the National Security Bureau (NSB) showed. The main countries on the first island chain include the two nations and Taiwan. The bureau is to present the report at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee tomorrow. The US military has deployed Typhon missile systems to Japan’s Yamaguchi Prefecture and Zambales province in the Philippines during their joint military exercises. It has also installed NMESIS anti-ship systems in Japan’s Okinawa

‘WIN-WIN’: The Philippines, and central and eastern European countries are important potential drone cooperation partners, Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung said Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung (林佳龍) in an interview published yesterday confirmed that there are joint ventures between Taiwan and Poland in the drone industry. Lin made the remark in an exclusive interview with the Chinese-language Liberty Times (the Taipei Times’ sister paper). The government-backed Taiwan Excellence Drone International Business Opportunities Alliance and the Polish Chamber of Unmanned Systems on Wednesday last week signed a memorandum of understanding in Poland to develop a “non-China” supply chain for drones and work together on key technologies. Asked if Taiwan prioritized Poland among central and eastern European countries in drone collaboration, Lin

BACK TO WORK? Prosecutors said they are considering filing an appeal, while the Hsinchu City Government said it has applied for Ann Kao’s reinstatement as mayor The High Court yesterday found suspended Hsinchu mayor Ann Kao (高虹安) not guilty of embezzling assistant fees, reducing her sentence to six months in prison commutable to a fine from seven years and four months. The verdict acquitted Kao of the corruption charge, but found her guilty of causing a public official to commit document forgery. The High Prosecutors’ Office said it is reviewing the ruling and considering whether to file an appeal. The Taipei District Court in July last year sentenced Kao to seven years and four months in prison, along with a four-year deprivation of civil rights, for contravening the Anti-Corruption

NO CONFIDENCE MOTION? The premier said that being toppled by the legislature for defending the Constitution would be a democratic badge of honor for him Premier Cho Jung-tai (卓榮泰) yesterday announced that the Cabinet would not countersign the amendments to the local revenue-sharing law passed by the Legislative Yuan last month. Cho said the decision not to countersign the amendments to the Act Governing the Allocation of Government Revenues and Expenditures (財政收支劃分法) was made in accordance with the Constitution. “The decision aims to safeguard our Constitution,” he said. The Constitution stipulates the president shall, in accordance with law, promulgate laws and issue mandates with the countersignature of the head of the Executive Yuan, or with the countersignatures of both the head of the Executive Yuan and ministers or