On the surface, the forthcoming console game Invincible Tiger looks very familiar: a smoothly executed sideways-scrolling beat ’em up with roots that can be traced back to 1980s classics such as Double Dragon and Final Fight. But given the right equipment — that means a special TV set and a pair of glasses — it literally takes on a new dimension; vanquished baddies fly out of the screen toward you and the lavish background artwork appears to stretch into the distance. Plenty of games industry executives think this is the future.
Cinema is already experiencing its own three-dimensional (3D) revival, with audiences turning out in droves to watch animations including Monsters vs Aliens, Coraline and Pixar’s forthcoming Up. Now games companies think they could be on the verge of bringing real 3D into the living room.
At the Game Developers Conference in San Francisco this year, Sony was giving demonstrations of a system it hopes will encourage the take-up of true 3D gaming. And Blitz Games, the British makers of Invincible Tiger, was previewing the title as a way to introduce its new product — a suite of developer tools for making true 3D games.
“When people have actually seen it, they say it’s cool — very, very cool,” says Andrew Oliver, Blitz’s chief technical officer. “Suddenly HD [high definition] doesn’t seem as good.”
“A lot of people have said it’s a gimmick; it’s not,” he says. “It does add something quite significant to the games — if you have the TV and glasses, it adds something, it feels like a fuller world. It’s about the immersion.”
Moving into this area is certainly a gamble for Blitz, founded by Oliver and his twin brother, Philip Oliver, who first made their names as teenage programmers in the 1980s with the Dizzy series. They are hoping 3D gaming will open up a new business for them, even if they have found it requires considerable technical skill to create a 3D system.
“We thought, ‘We’ve got a fast graphics engine and it’s only a TV display — how difficult could it be?’” he says. “We then found it was really difficult. It has to be Full HD and not only does it have to be 60 frames a second, but you have to feed it a left and a right every time, so you’re actually rendering everything twice.”
Difficulties aside, though, the technology certainly has the backing of some big names, among them Hollywood director Steven Spielberg, who has worked in collaboration with Electronic Arts recently. He told the Guardian that seeing 3D gaming take off was one of his unfulfilled ambitions.
“I have a lot of dreams, but in the short-term I would love to start seeing 3D games being developed, where — with a good pair of glasses — we get a real three-dimensional experience in front of an appropriate monitor that is designed just for 3D,” he said. “I would love to see 3D start to kick in to the thinking of the powers that be.”
Spielberg may not be known for his insight into the future of the games industry; his biggest involvement has been the GameWorks chain of arcades, which went bankrupt after he pulled out his investment several years ago. But in the case of 3D gaming, at least, he is not alone.
Sir Howard Stringer, the chief executive of Sony, has hinted that the company will move even further into 3D, and earlier this year demonstrated a new version of Gran Turismo, which amazed audiences at the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas.
“You’ve never seen the game like that,” he told them.
But while there are big names backing the new technology, plenty of people remain unconvinced regarding long-term prospects for 3D in the home. Marie Bloomfield, an analyst with Screen Digest, said the development of 3D gaming and TV is trapped in a no man’s land.
“The home 3D market is in a catch-22 situation,” she commented in a recent report on the subject. “Consumers will not be persuaded to invest in new equipment to experience 3D until there is enough content, and content production will not ramp up until there is a significant audience.”
It will be tough to convince cash-strapped consumers who have already been inundated with a number of “must-have” TV technologies in recent years to buy into a 3D system. Broadly popular systems such as digital broadcasting, HD and digital video recorders have required new hardware and significant investment from buyers — not to mention the host of extras offered by manufacturers such as Samsung, Sony, LG and Phillips.
Aren’t people going to get turned off the idea of having to splash out yet again?
Andrew Oliver says that millions of people have, in fact, already bought 3D TV sets but they don’t realize it because the manufacturers don’t market the capability, as nobody uses it right now.
“You can’t sell it because there’s no 3D content out there,” he says. “The manufacturers realize that 3D movies are being made. It’ll be a little while before they sort themselves out, but we’ll get on with making the games.”
In the meantime, he says, encouraging the games industry to take up the technology could be the best way to get it into people’s homes — providing an outlet for a new technology, just as the Xbox and PlayStation 3 proved to be a way to get people watching HD.
“Gamers are the first adopters of this technology. They don’t mind wearing glasses at first, and to get a cool experience like this they think it’s well worth it. It’s an easy sell to a gamer,” he said.

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
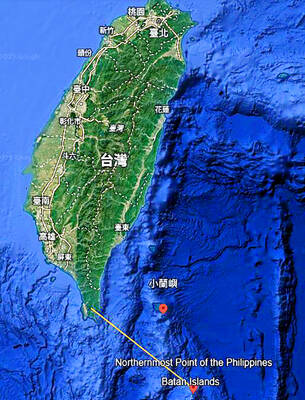
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College